Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17656-17660
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17656
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17656
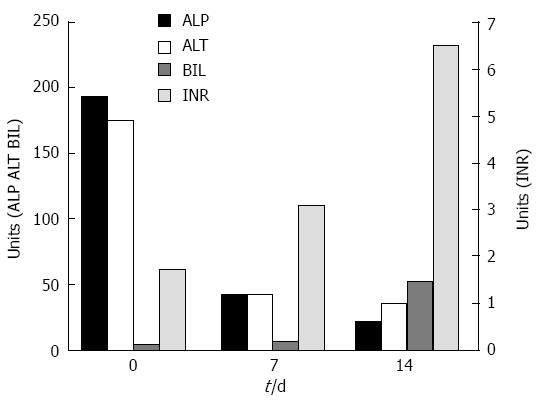
Figure 1 Biochemical parameters and international normalized ratio.
Serum ALP and ALT decreased while bilirubin level increased. The INR level increased dramatically, indicating the fulminant course of the disease. ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; ALT: Alanine transaminase; Bil: Bilirubin; INR: International normalized ratio.
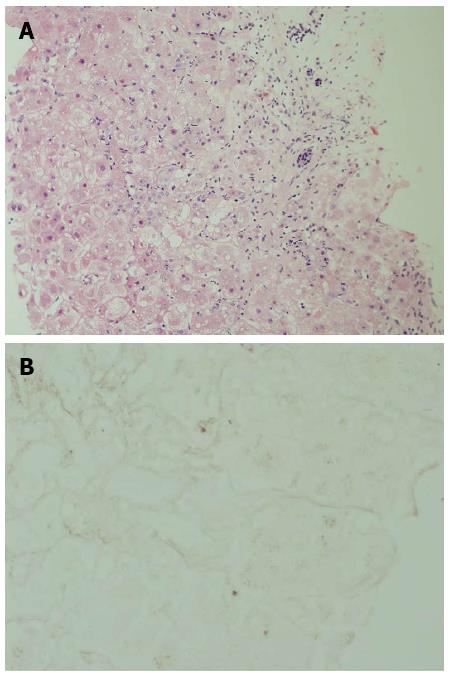
Figure 2 Histological evaluation of liver tissue (hematoxylin-eosin staining, × 20).
A: Histological examination of liver tissue displayed acute hepatitis with bridging necrosis and advanced fibrosis, macro- and micro-vesicular steatosis; B: Using orcein (copper binding protein stain), accumulation of copper binding protein was revealed.
- Citation: Weitzman E, Pappo O, Weiss P, Frydman M, Haviv-Yadid Y, Ben Ari Z. Late onset fulminant Wilson’s disease: A case report and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17656-17660
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17656.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17656