Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17532-17540
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17532
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17532
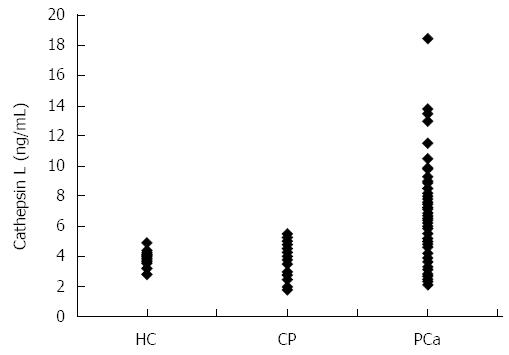
Figure 1 Dot plot showing plasma cathepsin L levels in healthy individuals (HC; n = 26), chronic pancreatitis patients (CP; n = 25) or pancreatic cancer patients (PCa; n = 127).
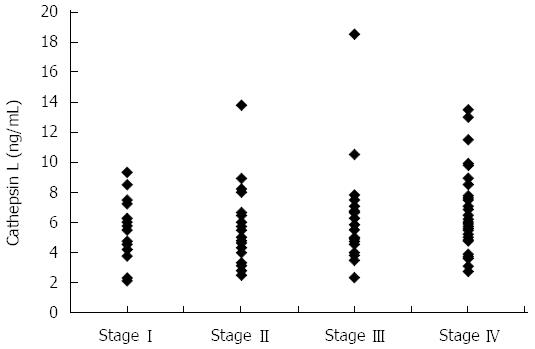
Figure 2 Dot plot showing plasma cathepsin L levels in pancreatic cancer patients with disease at stage I (n = 19), stage II (n = 29), stage III (n = 31) or stage IV (n = 48).
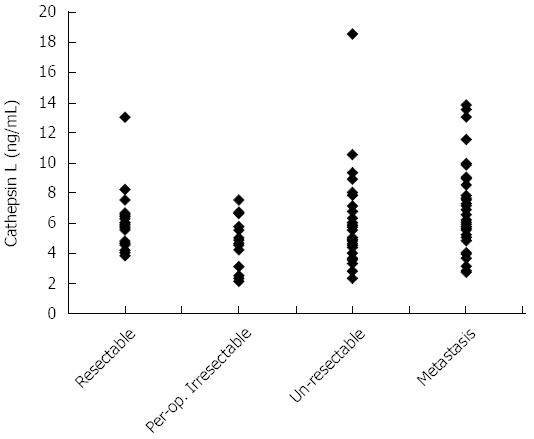
Figure 3 Dot plot showing plasma cathepsin L levels in pancreatic cancer patients who underwent resection (Resectable; n = 25); who were found to be resectable based on imaging but were irresectable on further investigation (Per-op.
Irresectable; n = 15); who were un-resectable due to locally advanced disease (Un-resectable; n = 37); or who had metastasis at presentation (Metastasis; n = 53).
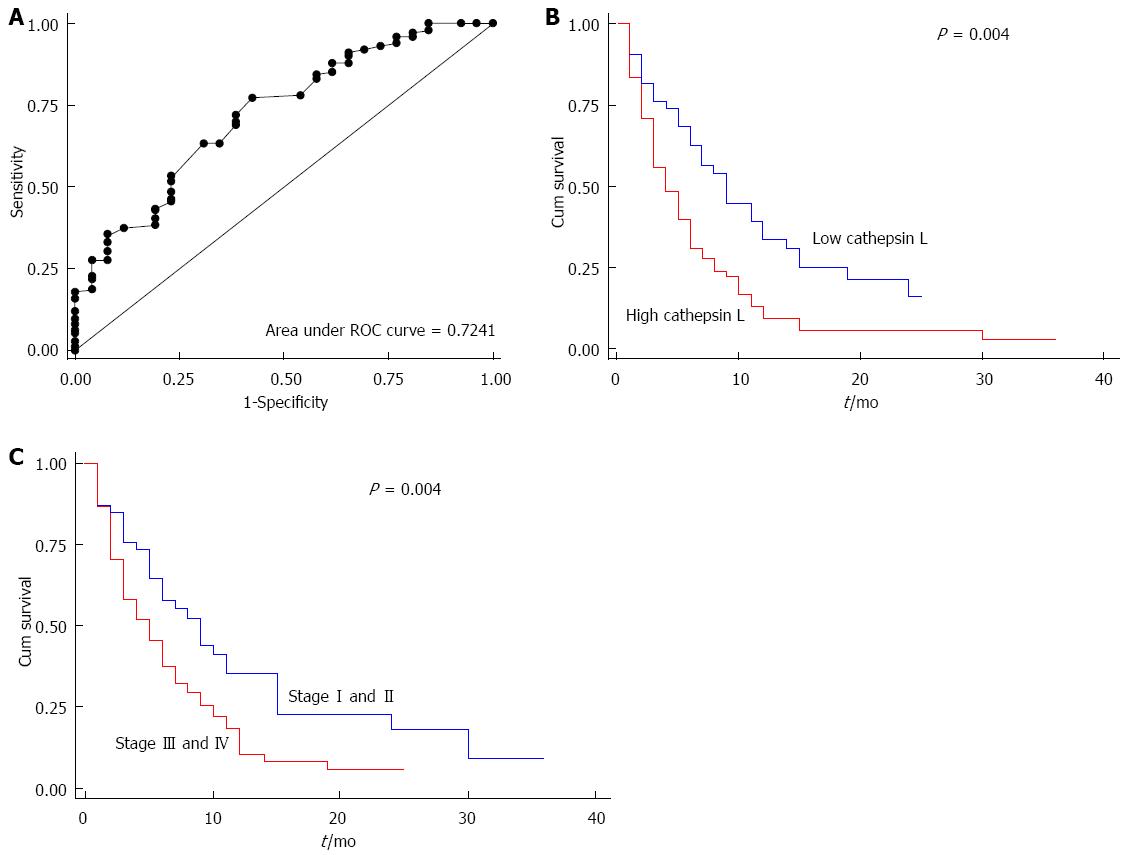
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic curve for cathepsin L (ng/mL) (A); Kaplan Meier survival curve for low (≤ 5 ng/mL; blue line) and high (> 5 ng/mL; red line) cathepsin L levels in plasma of pancreatic cancer patients (B); Kaplan Meier survival curve for pancreatic cancer patients with stage I and II (blue line) or stage III and IV (red line) disease (C).
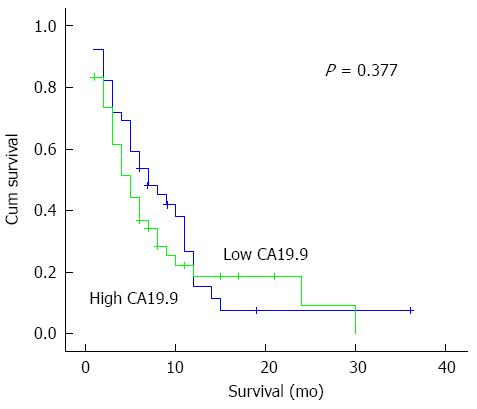
Figure 5 Kaplan meier survival curve for low (≤ 654 U/mL) and high (> 654 U/mL) CA19.
9 levels in plasma of pancreatic cancer patients.
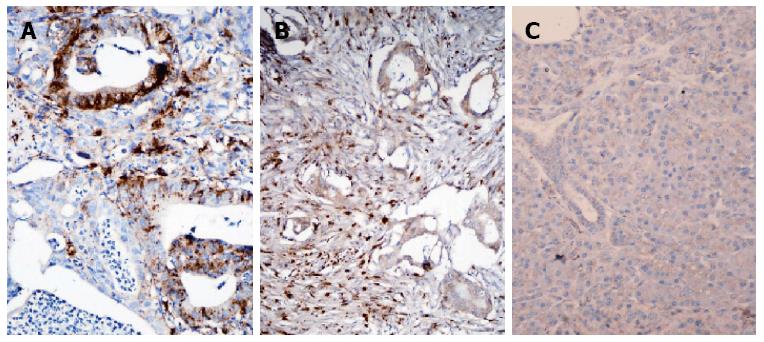
Figure 6 Photomicrographs showing (A) cathepsin L positivity identified at basal cell cytoplasm of malignant ducts in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (IHC × 200) (B) cathepsin L stromal expression in pancreatic adenocarcinoma (IHC × 200) (C) Non- neoplastic region of the pancreas with minimal cathepsin L expression (negative control) (IHC × 200).
- Citation: Singh N, Das P, Gupta S, Sachdev V, Srivasatava S, Datta Gupta S, Pandey RM, Sahni P, Chauhan SS, Saraya A. Plasma cathepsin L: A prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17532-17540
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17532.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17532