Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17265-17278
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17265
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17265
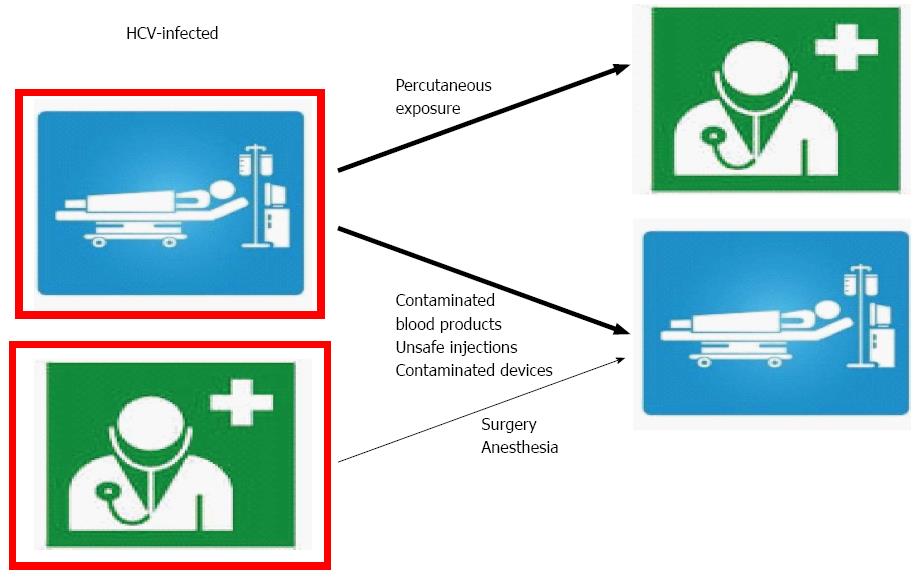
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the different modes of hepatitis C virus transmission in health care settings.
The size of the arrows is proportional to the importance of the risk. A red border symbolizes hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.
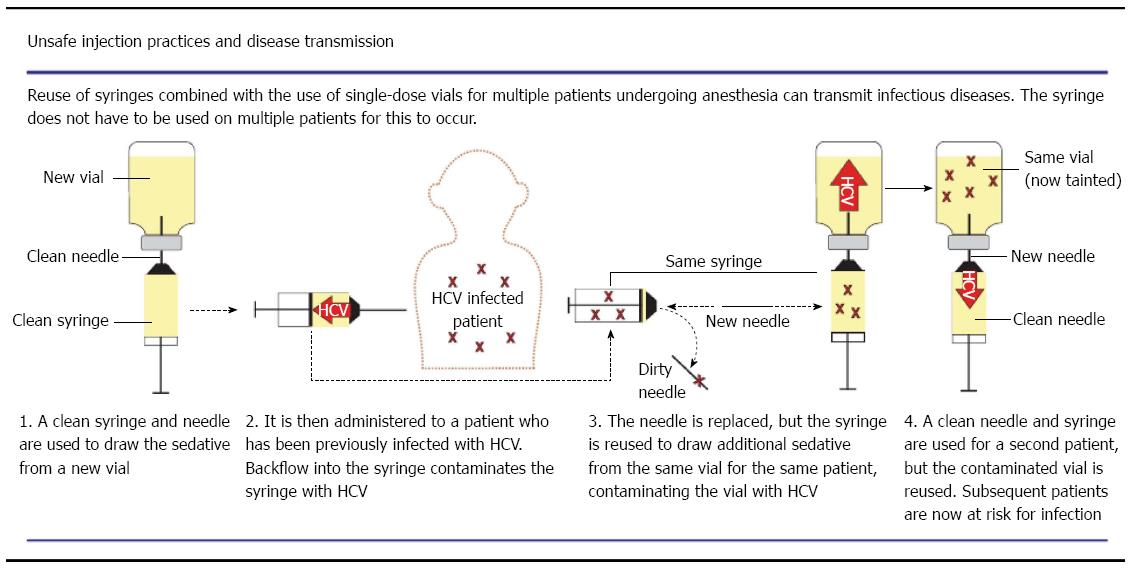
Figure 2 Example of mechanism of hepatitis C virus transmission via unsafe injection practices (borrowed from[44]).
HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Pozzetto B, Memmi M, Garraud O, Roblin X, Berthelot P. Health care-associated hepatitis C virus infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17265-17278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17265