Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2014; 20(44): 16559-16569
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16559
Published online Nov 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16559
Figure 1 Algorithm of international consensus diagnostic criteria to diagnose type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis in subjects presenting with obstructive jaundice and/or pancreatic enlargement.
This schematic drawing shows a flow to diagnose type 1 AIP with typical diffuse enlargement of the pancreas on CT/MRI (level 1 parenchymal findings)[25]. AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance image.
Figure 2 Algorithm of international consensus diagnostic criteria to diagnose type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis in subjects presenting with obstructive jaundice and/or pancreatic mass.
This schematic drawing shows a flow to diagnose type 1 AIP with indeterminate or atypical findings of the pancreas on CT/MRI (level 2 parenchymal findings)[25]. AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance image; OOI: Other organ involvement.
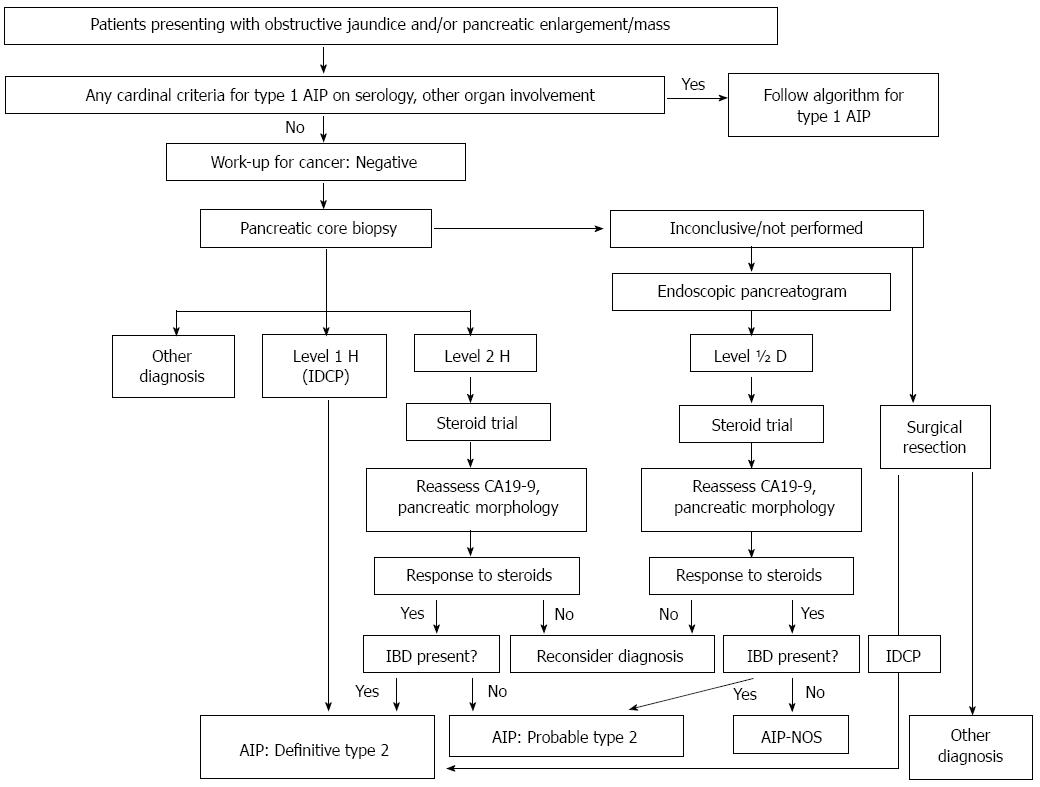
Figure 3 Algorithm of international consensus diagnostic criteria to diagnose type 2 autoimmune pancreatitis in subjects presenting with obstructive jaundice and/or pancreatic mass.
This schematic drawing shows a flow to diagnose type 2 AIP with typical/indeterminate (atypical) findings of the pancreas on CT/MRI (level 1 and 2 parenchymal findings)[25]. AIP: Autoimmune pancreatitis; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; IDCP: Idiopathic duct-centric chronic pancreatitis.
- Citation: Matsubayashi H, Kakushima N, Takizawa K, Tanaka M, Imai K, Hotta K, Ono H. Diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(44): 16559-16569
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i44/16559.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16559