Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 15955-15964
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.15955
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.15955
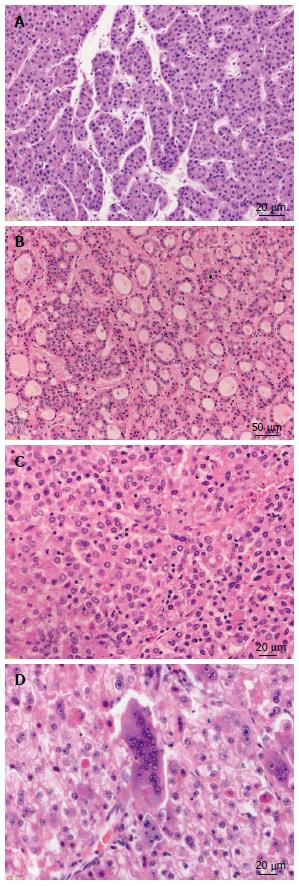
Figure 1 Growth patterns of progressed hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with trabecular growth pattern [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), × 300]; B: HCC with pseudoglandular growth pattern (HE, × 100); C: HCC with solid growth pattern (HE, × 200); D: HCC with giant cell formation (HE, × 200).
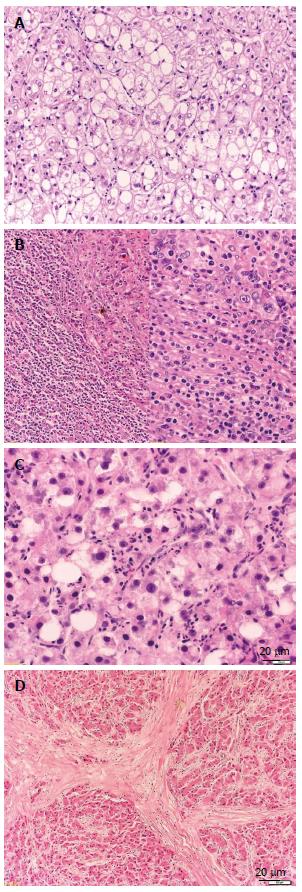
Figure 2 Histologic variants of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), clear cell variant [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), × 100]; B: HCC with lymphoid stroma (HE, × 100/× 200). C: HCC, steatohepatic variant (HE, × 200); D: HCC, fibrolamellar variant (HE, × 50).
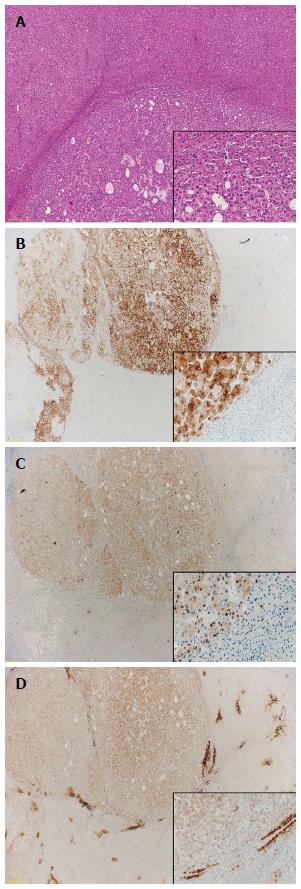
Figure 3 Immunohistochemistry.
A: Well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), × 20]; B: Glypican-3 (HE, × 10/× 200); C: Heat-shock-protein 70 (HE, × 10/× 200); D: Gluthamine-synthetase (HE, × 10/× 200).
- Citation: Schlageter M, Terracciano LM, D’Angelo S, Sorrentino P. Histopathology of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 15955-15964
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/15955.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.15955