Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15815-15819
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15815
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15815
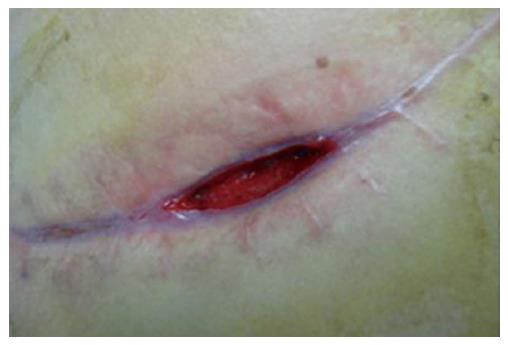
Figure 1 Wound site before closure.
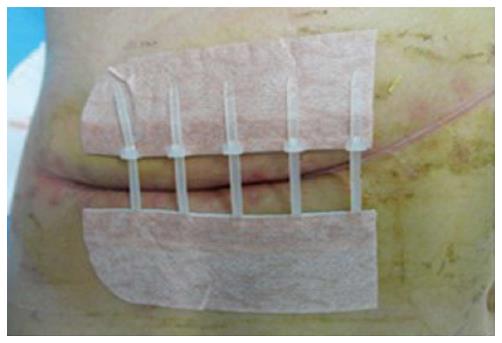
Figure 2 Closure of the infection wound using needle-free incision suture closure.
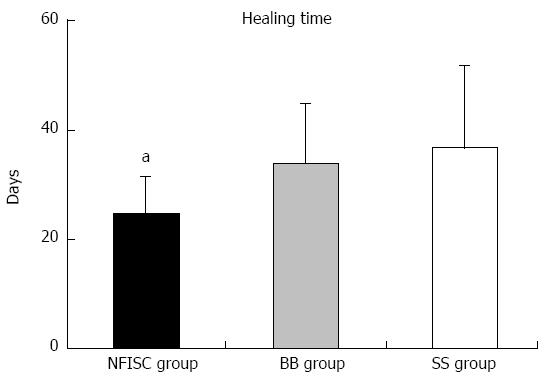
Figure 3 Healing time in patients with incision infection.
The wound healing time in the needle-free incision suture closure (NFISC) group was significantly shorter than that in the traditional butterfly bandage group (BB group) and secondary suture group (SS group). Healing time in the butterfly bandage group appeared to be slightly shorter than that in the secondary suture group, but the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). aP < 0.05 vs BB group and SS group.
- Citation: Ma WJ, Zhou Y, Mao H, Xu RH, Shrestha A, Li FY, Lorance A, Yang Q, Zhang YQ, Jiang T, Feng H, Zhang W, Cheng NS. Healing time of incision infection after hepatobiliary surgery treated by needle-free incision suture closure. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15815-15819
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15815.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15815