Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2014; 20(42): 15756-15762
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15756
Published online Nov 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15756
Figure 1 Cumulative hepatic encephalopathy-free survival.
Cumulative hepatic encephalopathy (HE)-free survival over the follow-up period in relation to the combination of electroencephalographic (EEG) and clinical abnormalities (panel A, χ2 = 8.2, P = 0.041) and the combination of psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES) and clinical abnormalities (panel B, χ2 = 7.8, P = 0.050) at baseline.
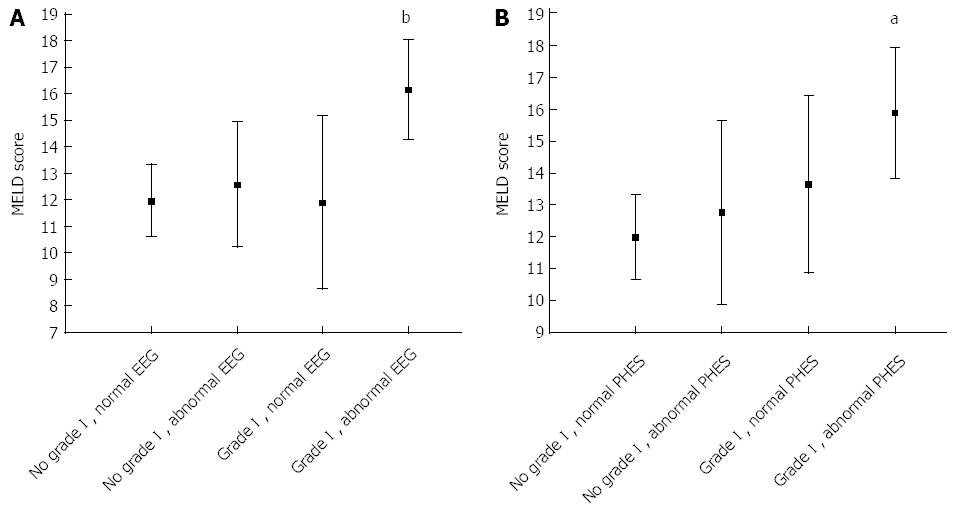
Figure 2 Model for end-stage liver disease scores in patients.
Model for end-stage liver disease scores (MELD) in patients grouped based on the combination of electroencephalographic (EEG) and clinical abnormalities (panel A) and the combination of psychometric hepatic encephalopathy score (PHES) and clinical abnormalities (panel B). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs post-hoc comparisons.
- Citation: Montagnese S, Balistreri E, Schiff S, De Rui M, Angeli P, Zanus G, Cillo U, Bombonato G, Bolognesi M, Sacerdoti D, Gatta A, Merkel C, Amodio P. Covert hepatic encephalopathy: Agreement and predictive validity of different indices. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(42): 15756-15762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i42/15756.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i42.15756