Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14934-14941
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14934
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14934
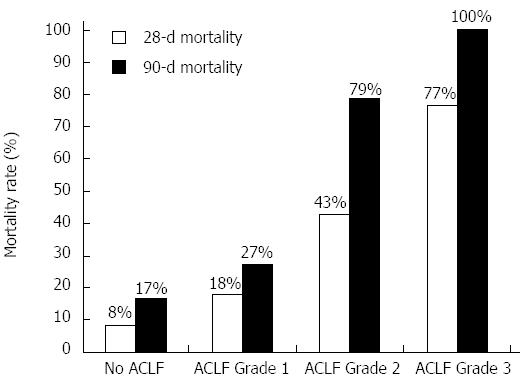
Figure 1 28-d and 90-d mortality according to the grade of acute-on-chronic liver failure.
ACLF: Acute-on-chronic liver failure.
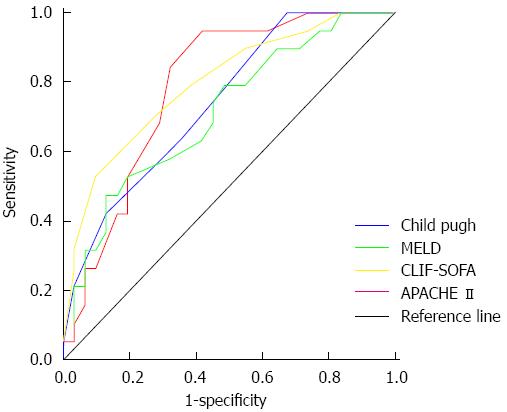
Figure 2 Receiver operating curves of child pugh, model for end-stage liver disease, chronic liver failure-sequential organ failure assessment and acute physiology and chronic health evaluation scores for prediction of 28-d mortality.
APACHE II: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation; CLIF-SOFA: Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease.
- Citation: Dhiman RK, Agrawal S, Gupta T, Duseja A, Chawla Y. Chronic Liver Failure-Sequential Organ Failure Assessment is better than the Asia-Pacific Association for the Study of Liver criteria for defining acute-on-chronic liver failure and predicting outcome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14934-14941
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14934.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14934