Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14895-14903
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895
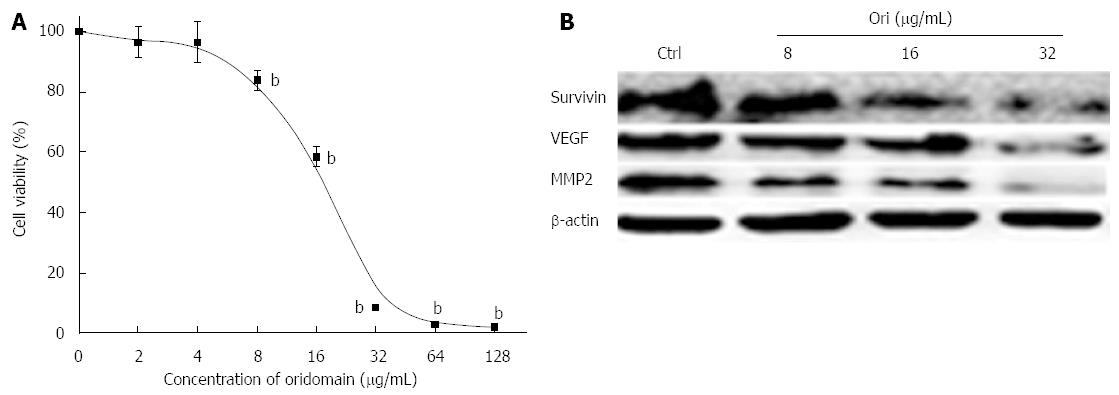
Figure 1 Oridonin-mediated hallmark changes in BxPC-3 cells.
A: BxPC-3 cells were treated with 0.1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) or with 0.1% DMSO containing various concentrations of oridonin. The percentage of inhibition in each sample was determined using an MTT assay. Cytotoxicity is expressed as the percentage of cell inhibition compared with the control (DMSO only). Data are expressed as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs the control treatment; B: Western blot analysis of the effect of oridonin treatment on the target genes of survivin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), and matrix metallopeptidase 2 (MMP-2) in BxPC-3 cells. The BxPC-3 cells were treated with 0, 8, 16, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. Three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown.
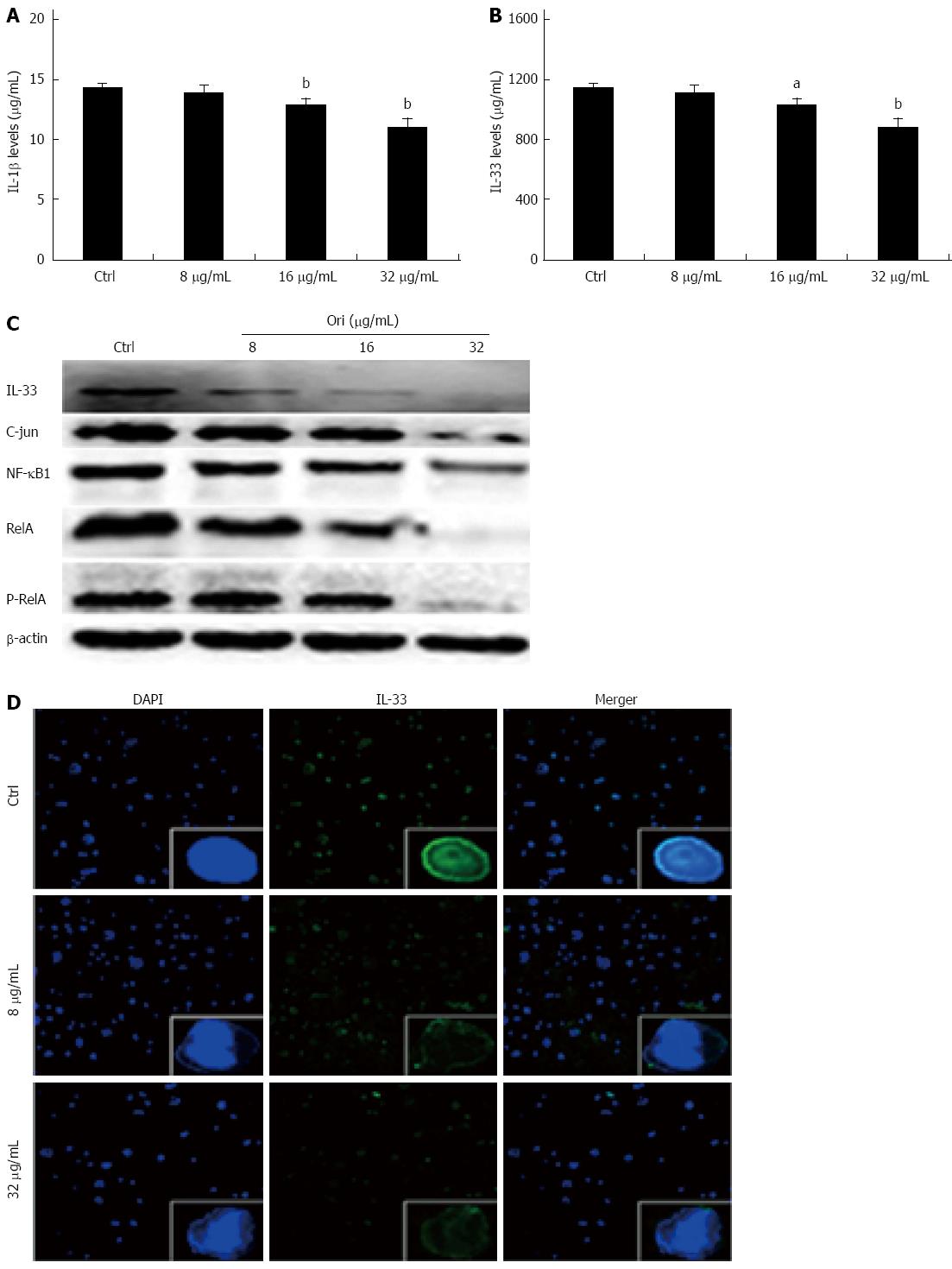
Figure 2 Oridonin decreases both the expression of the nuclear factors nuclear factor κB/activating protein-1/interleukin-33 in BxPC-3 cells and the release of interleukin-1β and interleukin-33 into the supernatant.
A and B: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis of the effect of oridonin on interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-33 in BxPC-3 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the control treatment; C: Western blot analysis of the effect of oridonin on the levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and phospho-STAT3 in BxPC-3 cells treated with 0, 8, 16, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. Three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown; D: Immunofluorescent staining analysis of the effect of oridonin on IL-33 in BxPC-3 cells (× 100). The BxPC-3 cells were treated with 0, 8, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB.
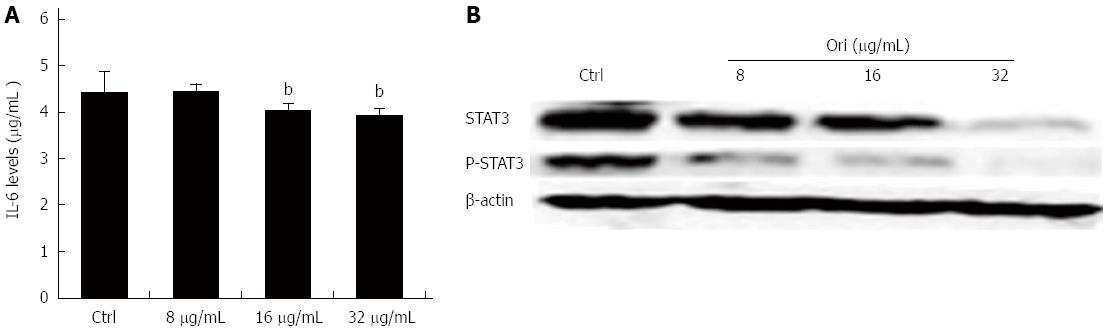
Figure 3 Oridonin reduces both the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 in BxPC-3 cells and the release of interleukin-6 into the supernatant.
A: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis of the effect of oridonin treatment on interleukin (IL)-6 in BxPC-3 cells. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs the control treatment; B: Western blot analysis of the effect of oridonin treatment on the levels of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and phospho-STAT3 in BxPC-3 cells treated with 0, 8, 16, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. Three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown.
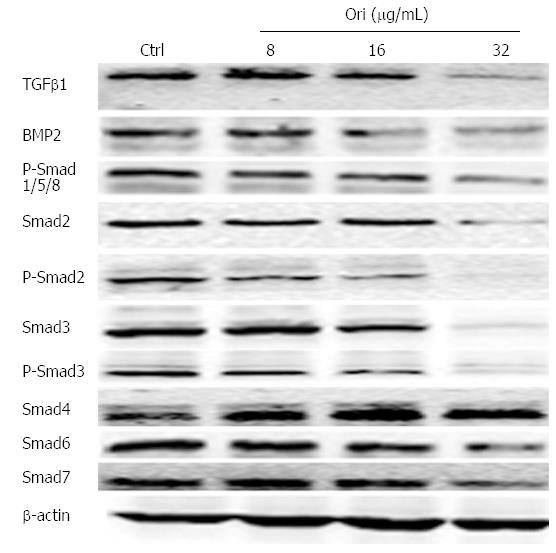
Figure 4 Oridonin regulates the expression of proteins in the transforming growth factor β/Smad pathway.
Western blot analysis of the effect of oridonin on proteins in the Smad signaling pathway in BxPC-3 cells. The BxPC-3 cells were treated with 0, 8, 16, or 32 μg/mL oridonin for 24 h. Three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown. TGFβ1: Transforming growth factor β1; BMP-2: Bone morphogenetic proteins 2; Smads: Sma and mad homologues.
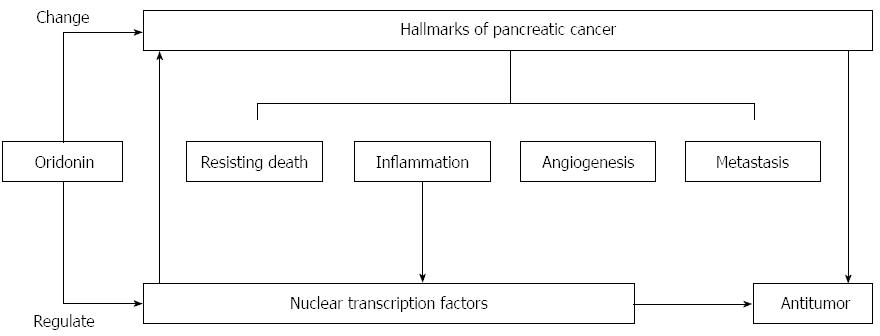
Figure 5 Proposed mechanism of oridonin-induced hallmark changes in BxPC-3 cells.
Oridonin induces anticancer actions, which reflected by hallmarks changes, through regulation of transcription factors.
- Citation: Chen RY, Xu B, Chen SF, Chen SS, Zhang T, Ren J, Xu J. Effect of oridonin-mediated hallmark changes on inflammatory pathways in human pancreatic cancer (BxPC-3) cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14895-14903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14895.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14895