Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2014; 20(40): 14726-14732
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14726
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14726
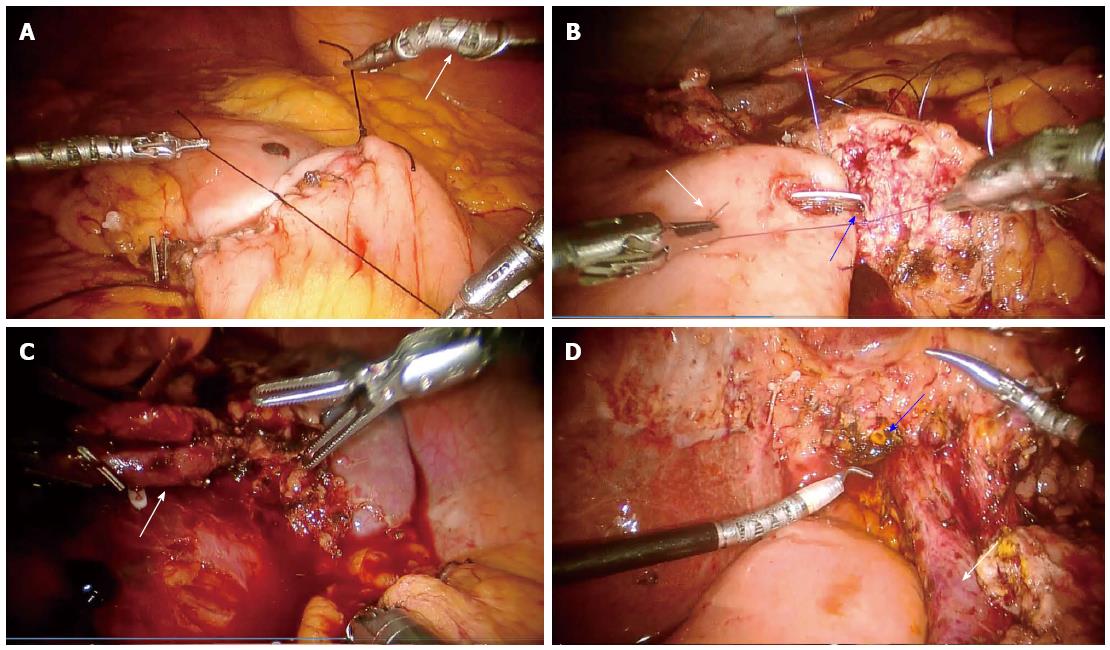
Figure 1 Robotic surgery of the pancreas.
A: Completion of the second layer of the anterior duodenojejunal anastomosis following pancreatoduodenectomy. The white arrow highlights the endowrist® capabilities of the robotic arms; B: Completion of the posterior row of the pancreaticojejunal anastomosis with intracorporeal knot tying. The white arrow indicates the jejunal limb with the blue arrow pointing to a pediatric feeding tube entering the main pancreatic duct; C: Splenic hilum following robotic spleen preserving distal pancreatectomy. The excellent visualization and advanced endowrist® technology allow for a precise dissection of the splenic artery and vein (white arrow); D: Hepatic hilum (common hepatic duct indicated by blue arrow, portal vein indicated by white arrow) following resection of pancreatic head and duodenum.
- Citation: Joyce D, Morris-Stiff G, Falk GA, El-Hayek K, Chalikonda S, Walsh RM. Robotic surgery of the pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(40): 14726-14732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i40/14726.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i40.14726