Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2014; 20(39): 14500-14504
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14500
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14500
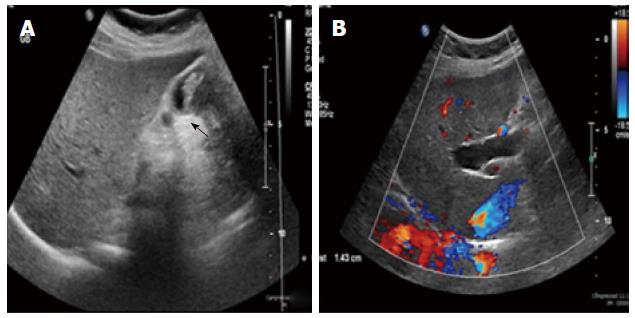
Figure 1 Ultrasound.
A: Ultrasound showing thick-walled gallbladder and intraluminal mass (arrow); B: Ultrasound showing right intrahepatic bile duct dilation.
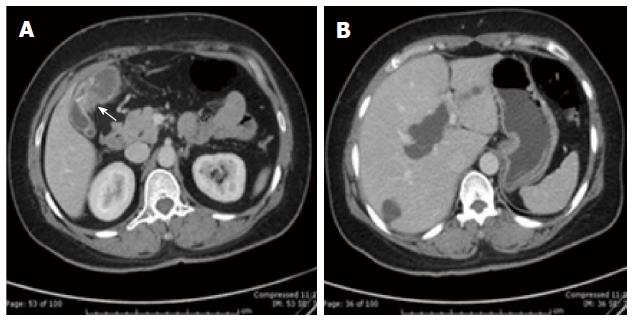
Figure 2 Computed tomography scan.
A: Computed tomography (CT) scan showing asymmetrical wall thickening of gallbladder (arrow); B: CT scan showing right intrahepatic duct dilation and small cyst in right lobe.
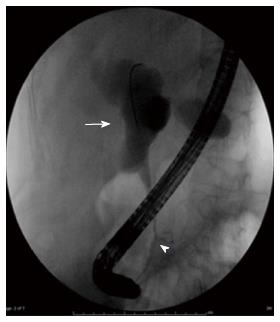
Figure 3 Abnormal junction of pancreatic duct and common bile duct (arrowhead).
Marked dilation of proximal common hepatic duct (arrow).
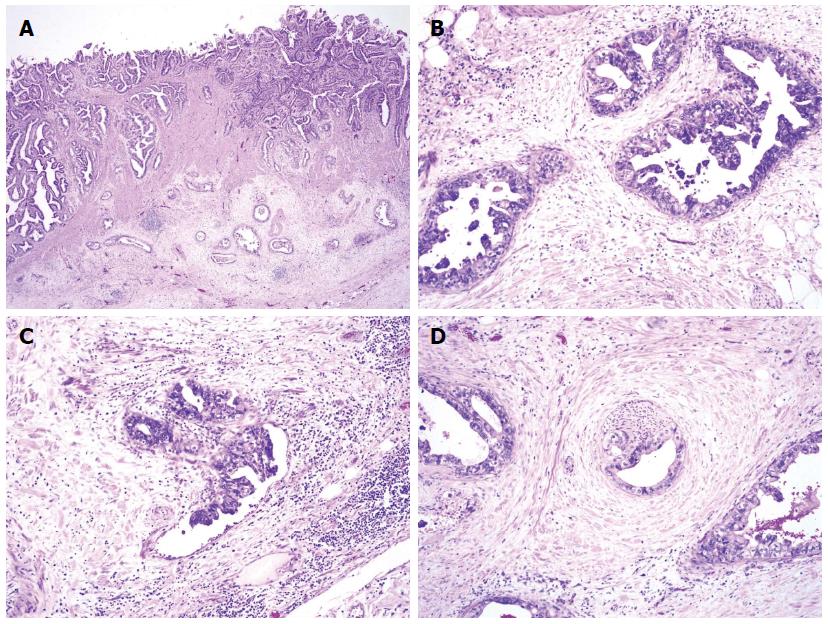
Figure 4 Adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder.
A: Tumor invades the serosa (HE, × 20); B: Tumor is well differentiated (HE, × 100); C: Lymphovascular invasions; D: Perineural invasions by the tumor are observed (HE, × 100).
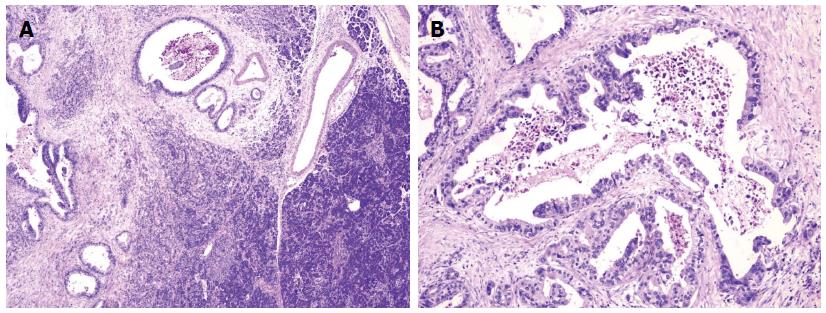
Figure 5 Adenocarcinoma of the pancreas.
A: HE, × 40; B: HE, × 100.
- Citation: Rungsakulkij N, Boonsakan P. Synchronous gallbladder and pancreatic cancer associated with pancreaticobiliary maljunction. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(39): 14500-14504
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i39/14500.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14500