Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2014; 20(39): 14263-14271
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14263
Published online Oct 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14263
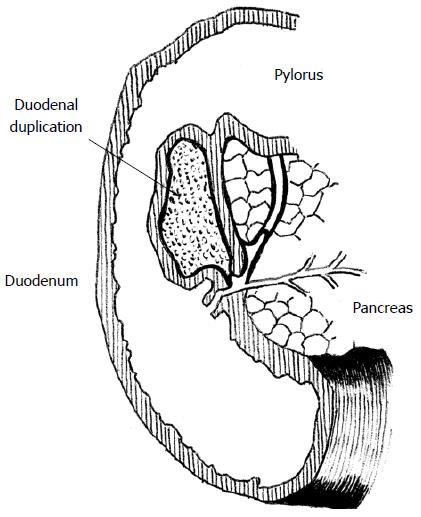
Figure 1 Duodenal duplication cyst (scheme).
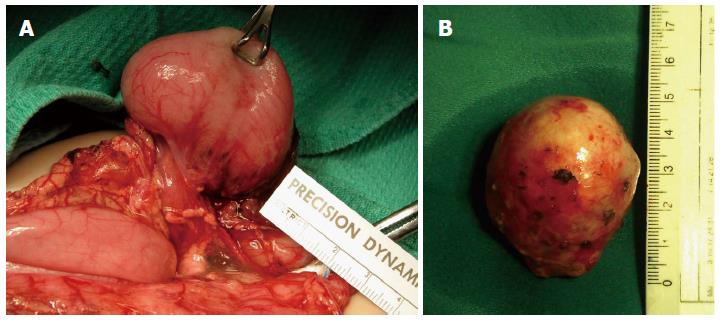
Figure 2 Gastric and duodenal duplications.
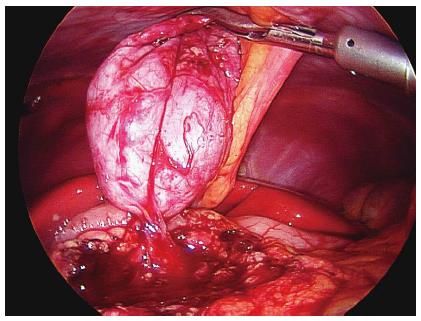
A: Isolated gastric duplication cyst; B: Duodenal duplication cyst after being shelled out laparoscopically in a 6-year-old girl.
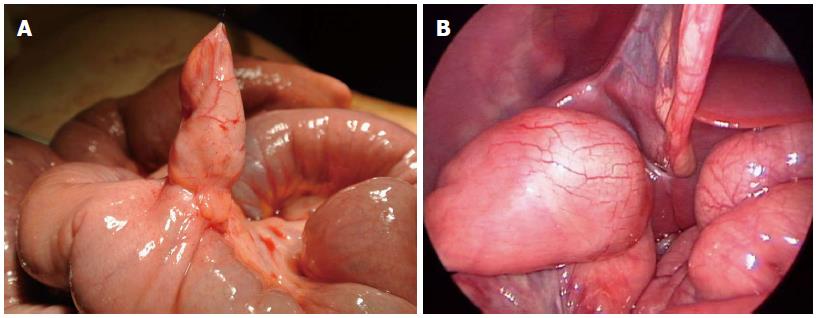
Figure 3 Small intestine duplications.
A: Ileal duplication cyst (containing heterotopic mucosa causing acute intestinal bleeding in 13-year-old girl); B: Ileal duplication cyst embedded in the muscle layer wall removed laparoscopically.
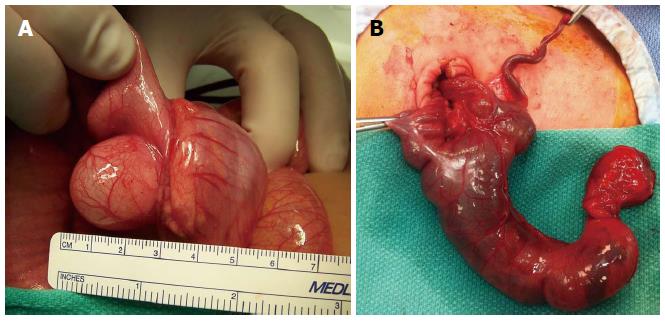
Figure 4 Colonic and rectal duplications.
A: Ileoceacal duplication cyst causing obstructive symptoms; B: Cecal tubular colonic duplication.
Figure 5 Diagnostic imaging.
A: Ultrasound of a cystic duodenal duplication; B: Magnetic resonance scan of a cystic duodenal duplication.
Figure 6 Duodenal duplication removed laparoscopically (stripping method).
- Citation: Patiño Mayer J, Bettolli M. Alimentary tract duplications in newborns and children: Diagnostic aspects and the role of laparoscopic treatment. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(39): 14263-14271
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i39/14263.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i39.14263