Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2014; 20(38): 14010-14017
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14010
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14010
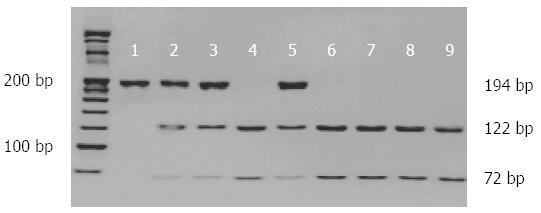
Figure 1 Genotyping of the Apolipoprotein C3 (-455T>C) polymorphism.
Polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism and polyacrylamide gel (8%) electrophoresis of the Apolipoprotein C3 (-455T>C) polymorphism illustrated the wild-type homozygote TT (122 and 72 bp), heterozygote TC (194, 122, and 72 bp), and variant-type homozygote CC (194 bp) genotypes. TT: 4, 6-9; TC: 2, 3, 5; CC: 1.
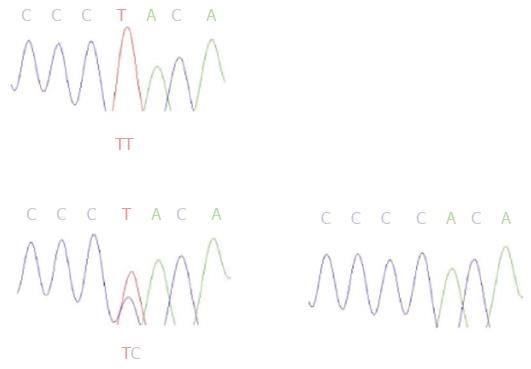
Figure 2 Sequencing analysis for genotypes of the Apolipoprotein C3 (-455T>C) polymorphism.
A: TT genotype; B: TC genotype; C: CC genotype.
-
Citation: Li MR, Zhang SH, Chao K, Liao XH, Yao JY, Chen MH, Zhong BH.
Apolipoprotein C3 (-455T>C) polymorphism confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Southern Han Chinese population. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(38): 14010-14017 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i38/14010.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.14010