Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2014; 20(38): 13942-13949
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13942
Published online Oct 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13942
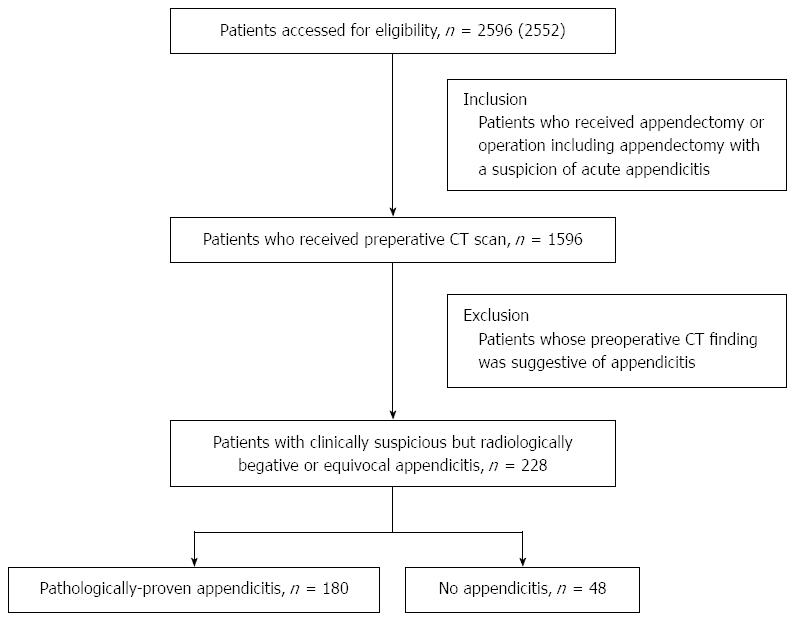
Figure 1 Patient selection flow chart.
CT: Computed tomography.
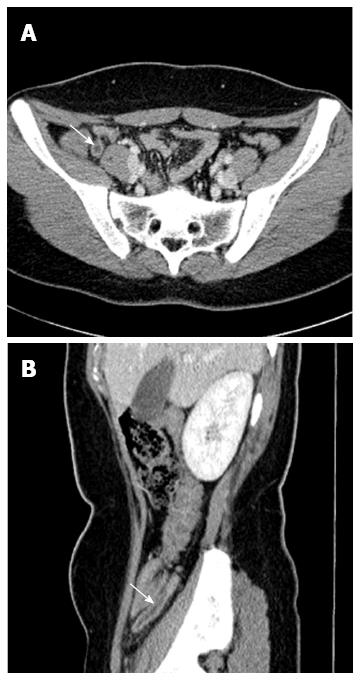
Figure 2 Enlarged appendix and appendiceal wall enhancement.
A: Cross-sectional (arrow); B: Sagittal abdominal computed tomography scans showing increased appendiceal diameter (≥ 6.0 mm) (arrow).
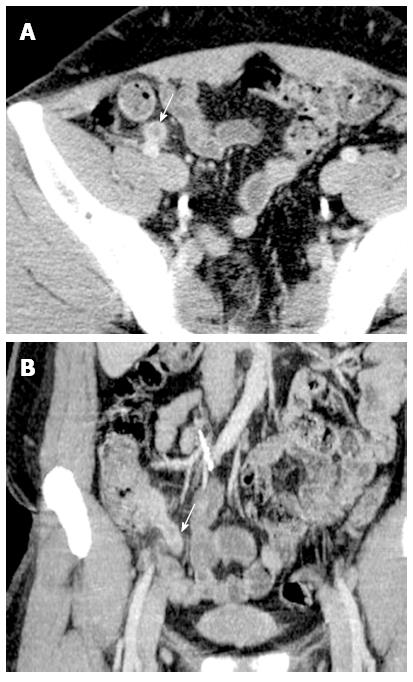
Figure 3 Appendiceal wall thickening.
A: Cross-sectional (arrow); B: Coronal abdominal computed tomography scans showing appendiceal wall thickening suggestive of acute appendicitis (arrow).
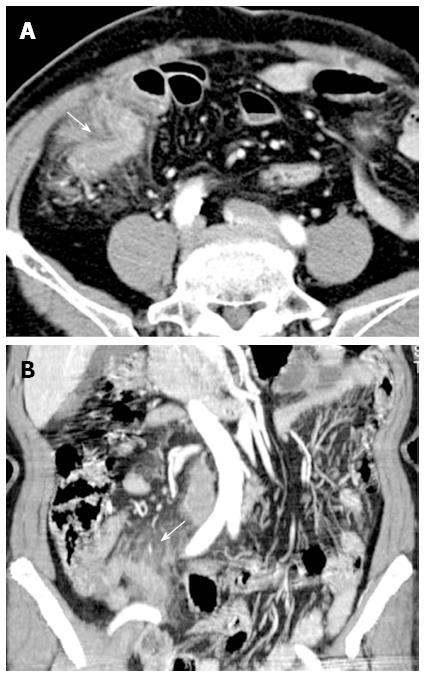
Figure 4 Fat stranding.
A: Cross-sectional (arrow); B: Coronal abdominal computed tomography scans showing periappendiceal fat stranding suggestive of acute appendicitis (arrow).
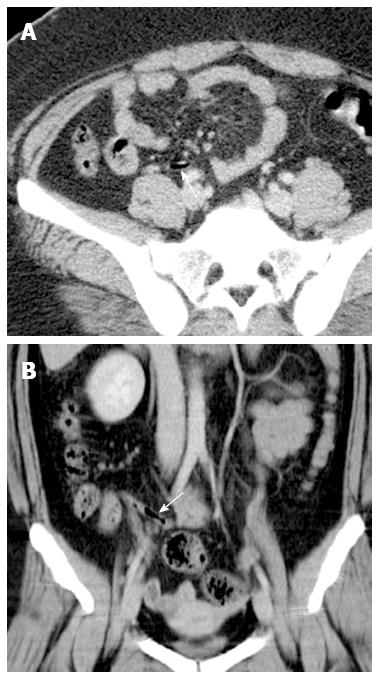
Figure 5 Appendiceal intraluminal air.
A: Cross-sectional (arrow); B: Coronal abdominal computed tomography scans showing appendiceal intraluminal air suggestive of normal appendix (arrow).
- Citation: Park G, Lee SC, Choi BJ, Kim SJ. Stratified computed tomography findings improve diagnostic accuracy for appendicitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(38): 13942-13949
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i38/13942.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13942