Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2014; 20(37): 13306-13324
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13306
Published online Oct 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13306
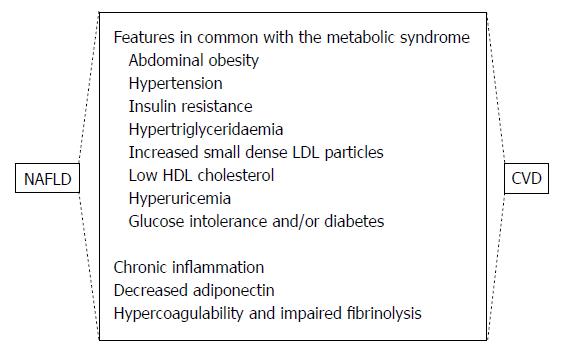
Figure 1 Common features in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease.
NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; CVD: Cardiovascular disease.
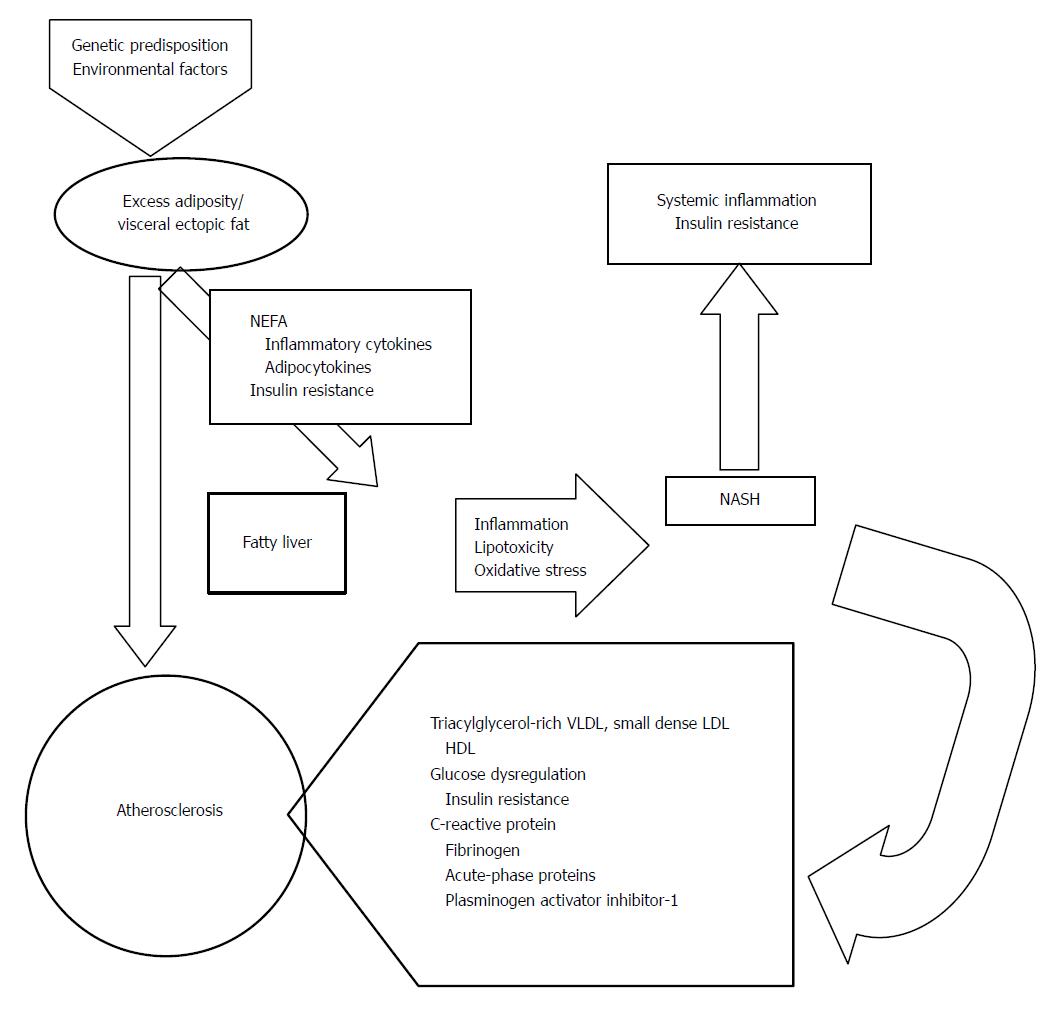
Figure 2 Mechanisms potentially responsible for atherosclerosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
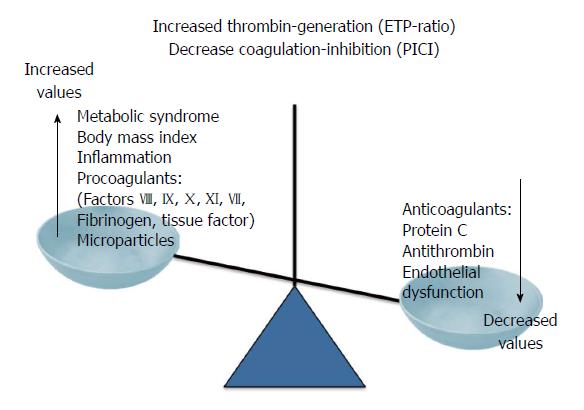
Figure 3 Causes and consequences of the procoagulant imbalance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
ETP-ratio: Ratio of the endogenous thrombin potential measured in the presence or absence of thrombomodulin; PICI: Protac®-induced coagulation inhibition.
- Citation: Fargion S, Porzio M, Fracanzani AL. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and vascular disease: State-of-the-art. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(37): 13306-13324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i37/13306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i37.13306