Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2014; 20(34): 12233-12240
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12233
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12233
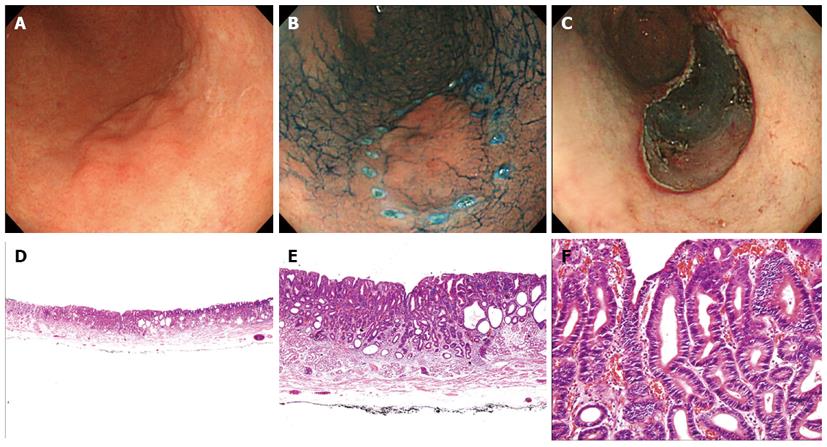
Figure 1 Endoscopic and pathologic findings in a 66-year-old female patient with low-grade neoplasia.
In this case, forceps biopsy specimens showed high-grade neoplasia, but endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) revealed low-grade neoplasia. A, B: A 22-mm, type 0-IIb lesion was observed in the greater curvature aspect of the antrum. This lesion had a nodular change; C: There was artificial ulceration after successful ESD; D-F: The pathologic findings in the ESD specimen showed a tubular adenoma with low-grade neoplasia. The glands had a similar shape and were slightly crowded with a regular arrangement, and the nuclei were basally oriented, spindle-shaped, and mildly hyperchromatic (D: HE stain, × 12.5; E: HE stain, × 40; F: HE stain, × 200).
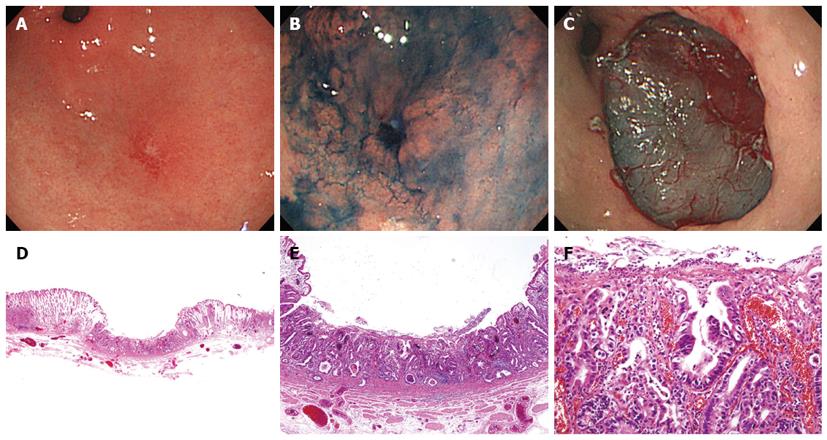
Figure 2 Endoscopic and pathologic findings in a 51-year-old male patient with mucosal cancer.
In this case, forceps biopsy specimens showed high-grade neoplasia, but endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) revealed adenocarcinoma. A, B: An 8-mm, type 0-IIc lesion was observed in the greater curvature aspect of the antrum. This lesion had a smooth surface, red color change, and mucosal ulceration; C: There was artificial ulceration after successful ESD; D-F: The pathologic findings in the ESD specimen showed a tubular adenocarcinoma with focal areas of invasion into the lamina propria. The carcinoma cells have hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular nuclear membranes and prominent nuclei (D: HE stain, × 12.5; E: HE stain, × 40; F: HE stain, × 200).
- Citation: Kim JH, Kim YJ, An J, Lee JJ, Cho JH, Kim KO, Chung JW, Kwon KA, Park DK, Kim JH. Endoscopic features suggesting gastric cancer in biopsy-proven gastric adenoma with high-grade neoplasia. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(34): 12233-12240
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i34/12233.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12233