Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 14, 2014; 20(34): 12062-12081
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12062
Published online Sep 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12062
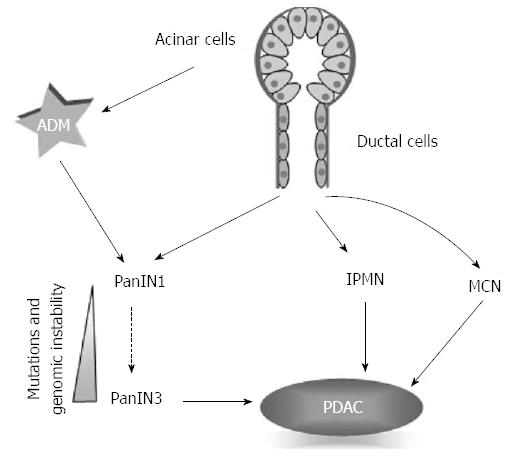
Figure 1 Origin of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.
It is widely accepted that pancreatic ductal carcinoma (PDAC) arises from precursor lesions derived from ductal cells; however, recently another model has been proposed where PDAC arises from acinar cells through a process called “acinar to ductal metaplasia” (ADM). PanIN: Intraepithelial neoplasm; IPMN: Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MCN: Mucinous cystic neoplasm.
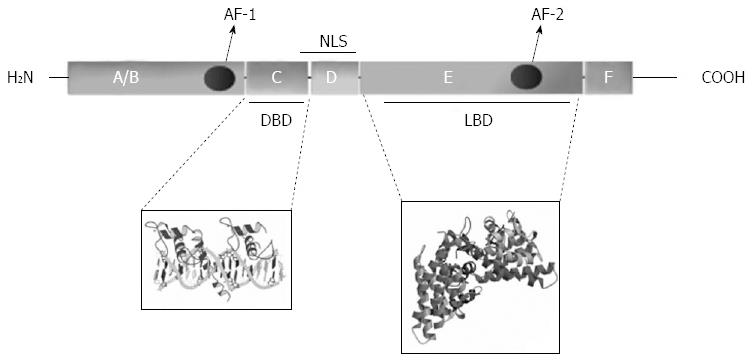
Figure 2 Domains and structural features of a classical nuclear receptor.
A typical nuclear receptor (NR) consists of 6 region (A to F); region F may or may not be present. Region D (hinge) contains the nuclear localization signal (NLS); other NLSs may be present in region E. AF-1: Activator function 1; AF-2: Activator function 2.
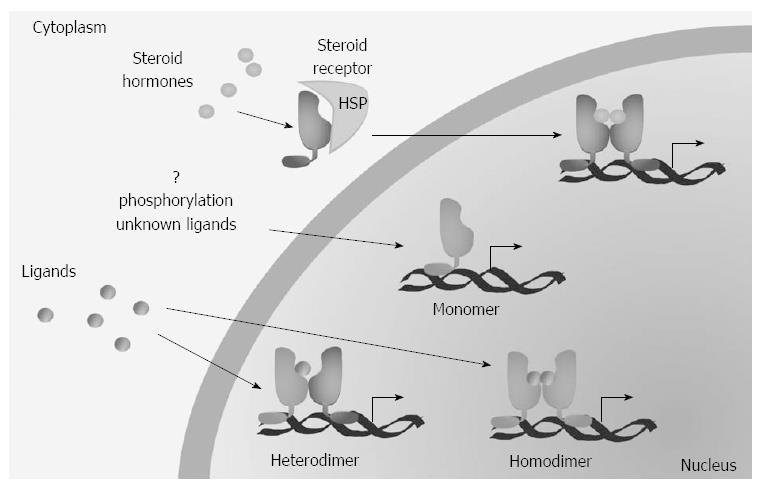
Figure 3 Mechanisms of action of nuclear receptors.
Type I nuclear receptors (NR) (steroid receptors) are complexed with heat shock proteins (HSP) and maintained in the cytoplasm in the absence of ligands. The other receptors are instead mainly nuclear and the ligands induce hetero- (for type II receptors) or homo-dimerization (for type III receptors). Furthermore, a group of receptors (type IV) whose regulation is poorly known act as monomers.
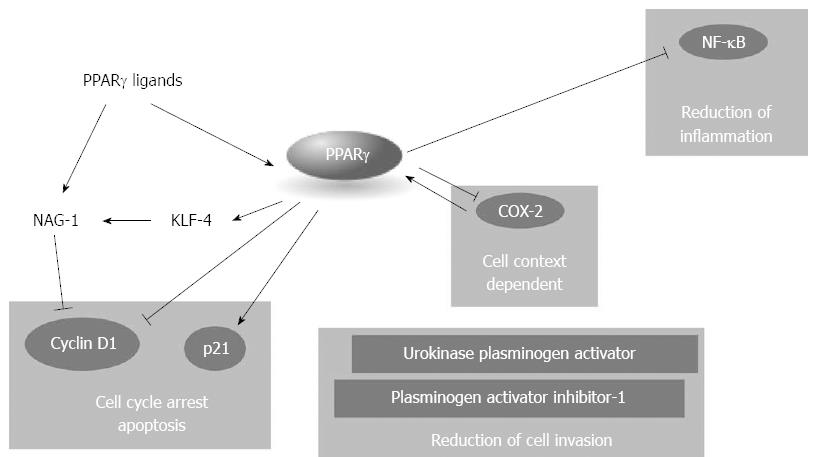
Figure 4 Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors and pancreatic ductal carcinoma.
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR)γ acts as a tumor inhibitor at multiple levels, blocking cell cycle progression, inflammation, and cell invasion. NAG-1: Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-activated gene-1; Cox-2: Ciclooxigenase-2; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
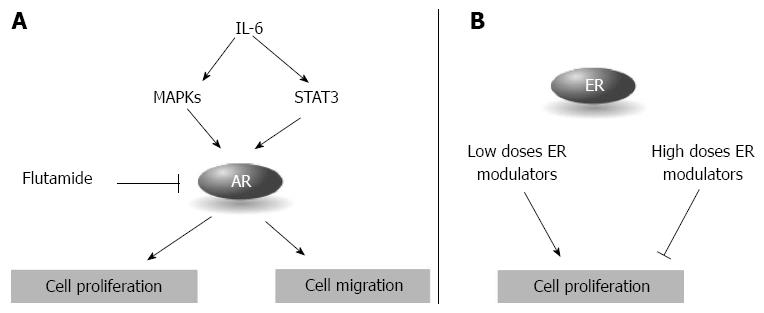
Figure 5 Steroid receptors in pancreatic ductal carcinoma.
A: Androgen receptor (AR) regulates cell proliferation and migration and it is activated by the inflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6); B: The effect of estrogen receptors (ER) on cell proliferation depends on the concentrations of the ER modulators.
Figure 6 Clustal sequence alignment of human NR4As.
Shaded sequences correspond to the DNA binding domain where homology among NR4A1-3 is very high.
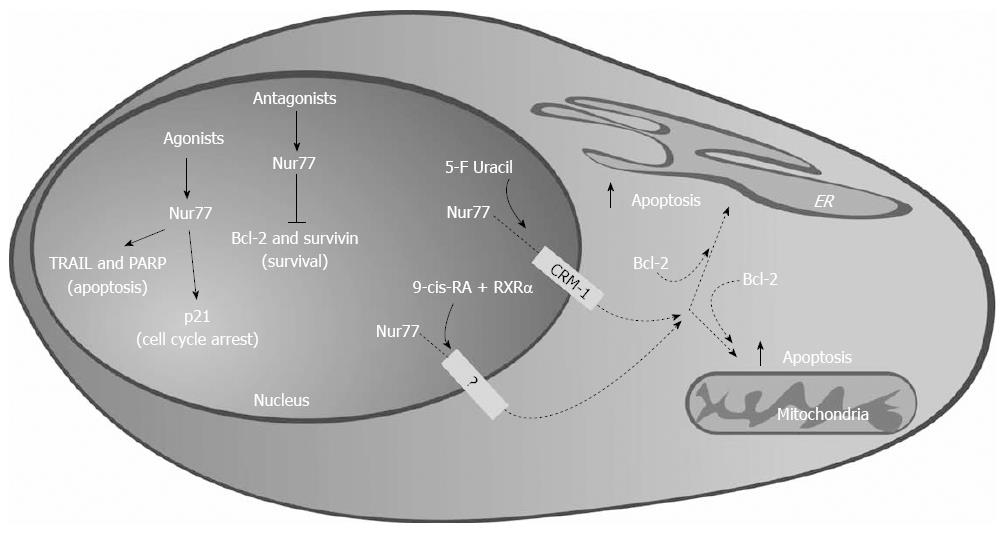
Figure 7 Nur77 acts as a tumor suppressor and as tumor promoting gene in pancreatic ductal carcinoma, inducing pro-apototic and anti-proliferative genes or repressing pro-survival genes.
Dashed lines: Effects yet to be demonstrated in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). TRAIL: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand; PARP: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase; RXR: Retinoid X receptor; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum.
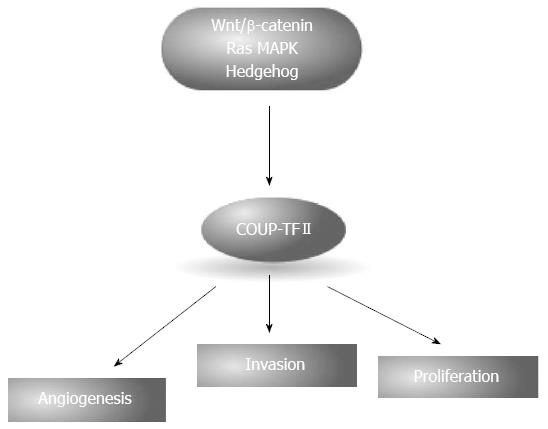
Figure 8 Chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II is involved in the regulation of angiogenesis, invasion and tumor proliferation.
Expression of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor II (COUP-TFII) is induced by several pathways altered in pancreatic ductal carcinoma, including Wnt/β-catenin, RAS-MAPK and Hedgehog.
- Citation: Polvani S, Tarocchi M, Tempesti S, Galli A. Nuclear receptors and pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(34): 12062-12081
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i34/12062.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12062