Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2014; 20(30): 10628-10636
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10628
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10628
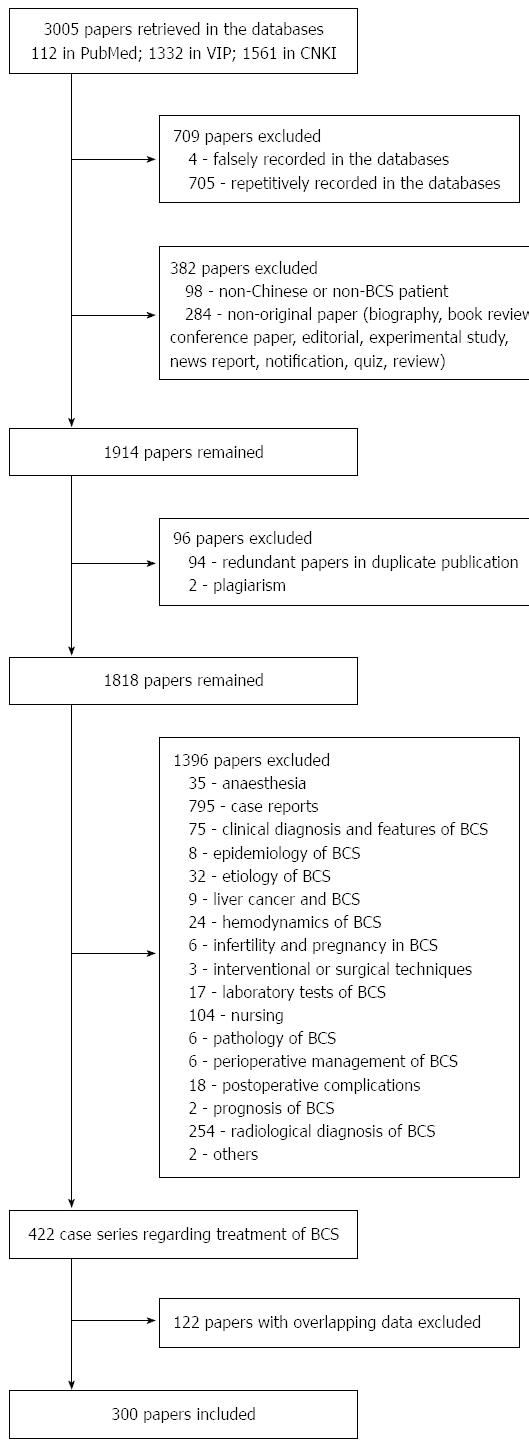
Figure 1 Flow chart for literature identification.
BCS: Budd-Chiari syndrome.
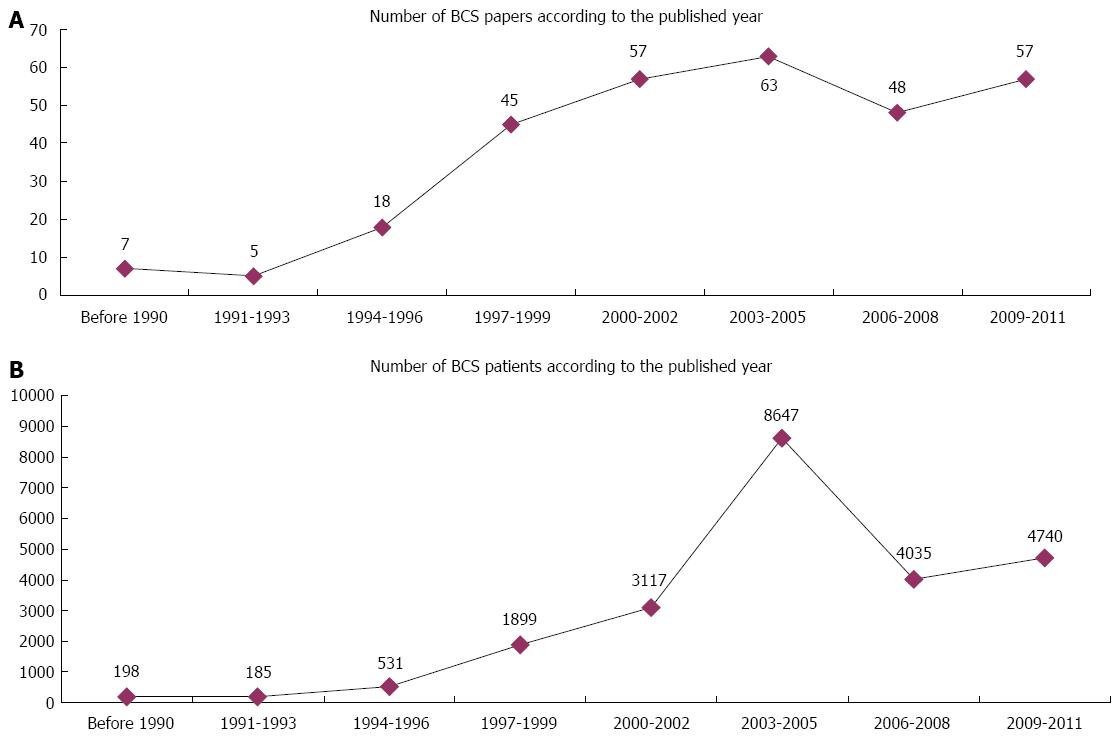
Figure 2 Numbers of Budd-Chiari syndrome papers (A) and patients (B) according to the year of publication.
BCS: Budd-Chiari syndrome.
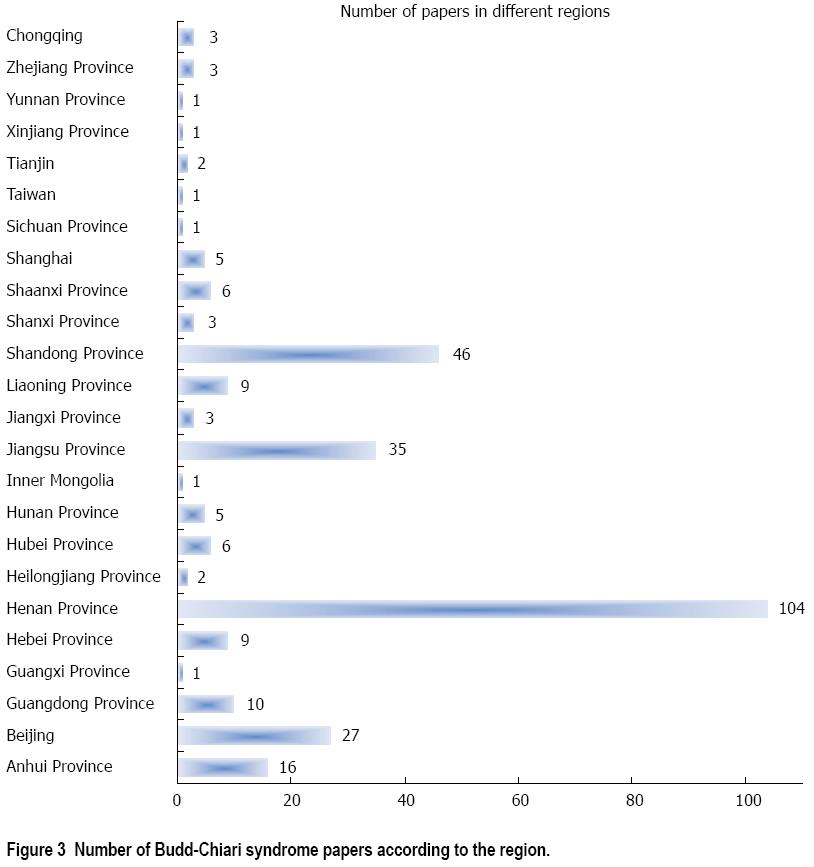
Figure 3 Number of Budd-Chiari syndrome papers according to the region.
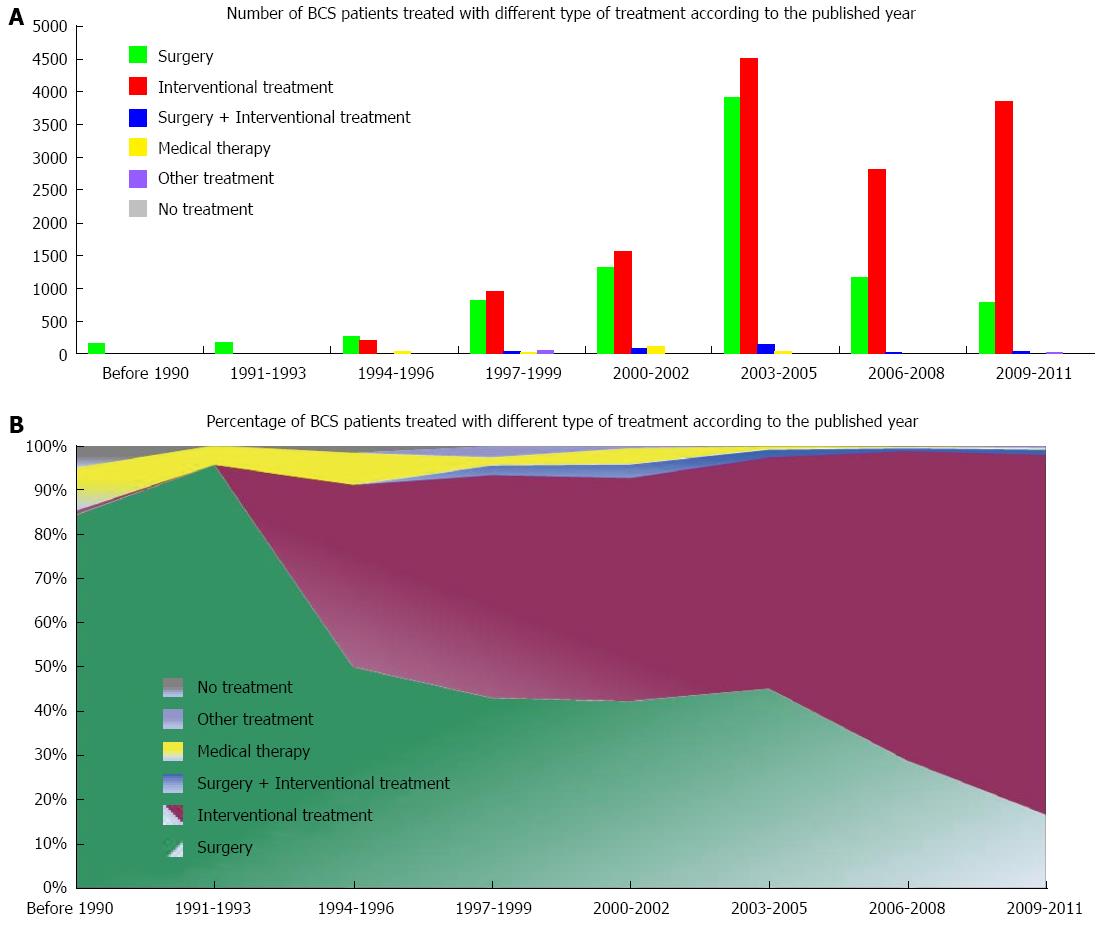
Figure 4 Number (A) and percentage (B) of Budd-Chiari syndrome patients treated with different type of treatment modalities according to the year of publication.
BCS: Budd-Chiari syndrome.
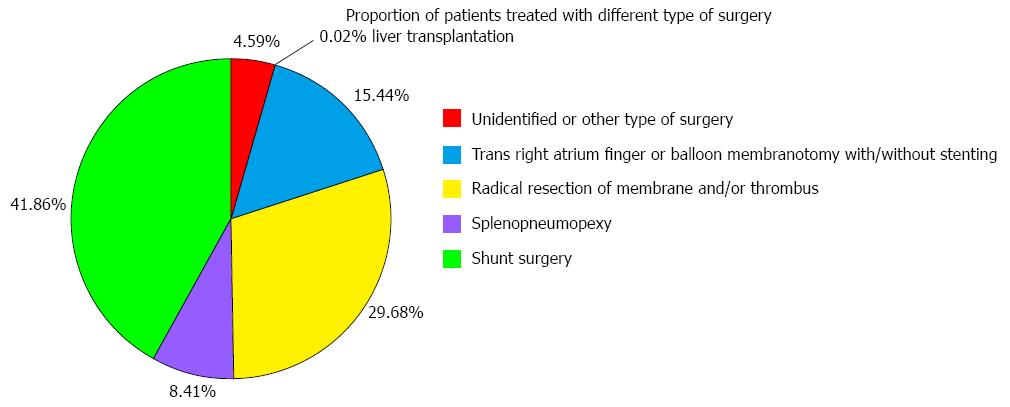
Figure 5 Proportion of patients treated with different types of surgery.
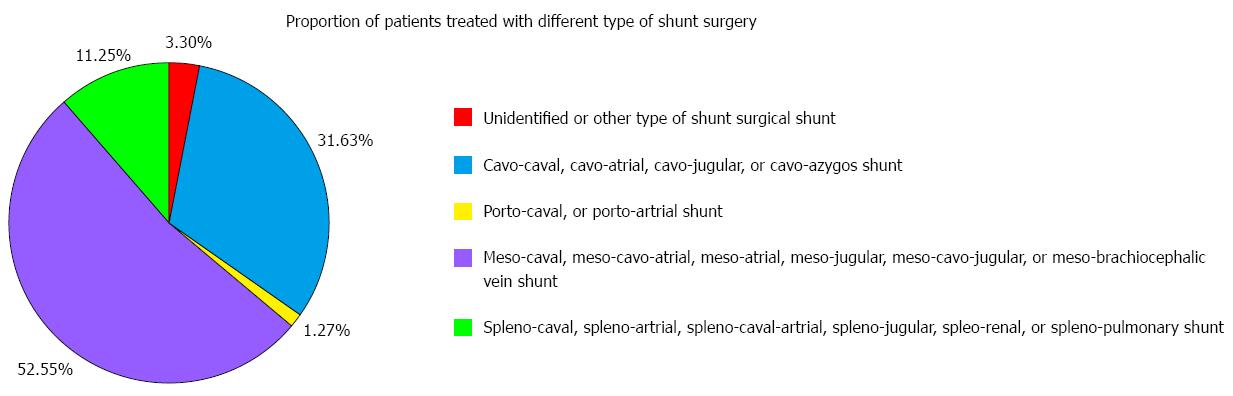
Figure 6 Proportion of patients treated with different types of shunt surgery.
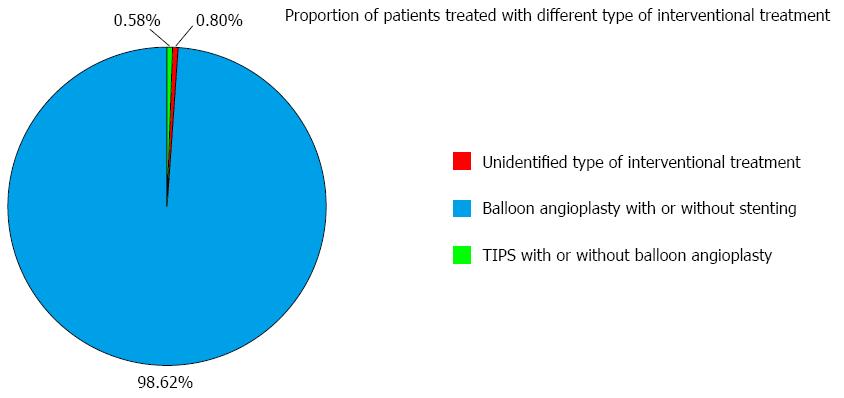
Figure 7 Proportion of patients treated with different types of interventional treatment.
TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Qi XS, Ren WR, Fan DM, Han GH. Selection of treatment modalities for Budd-Chiari Syndrome in China: A preliminary survey of published literature. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(30): 10628-10636
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i30/10628.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10628