Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2014; 20(29): 10038-10049
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038
Published online Aug 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038
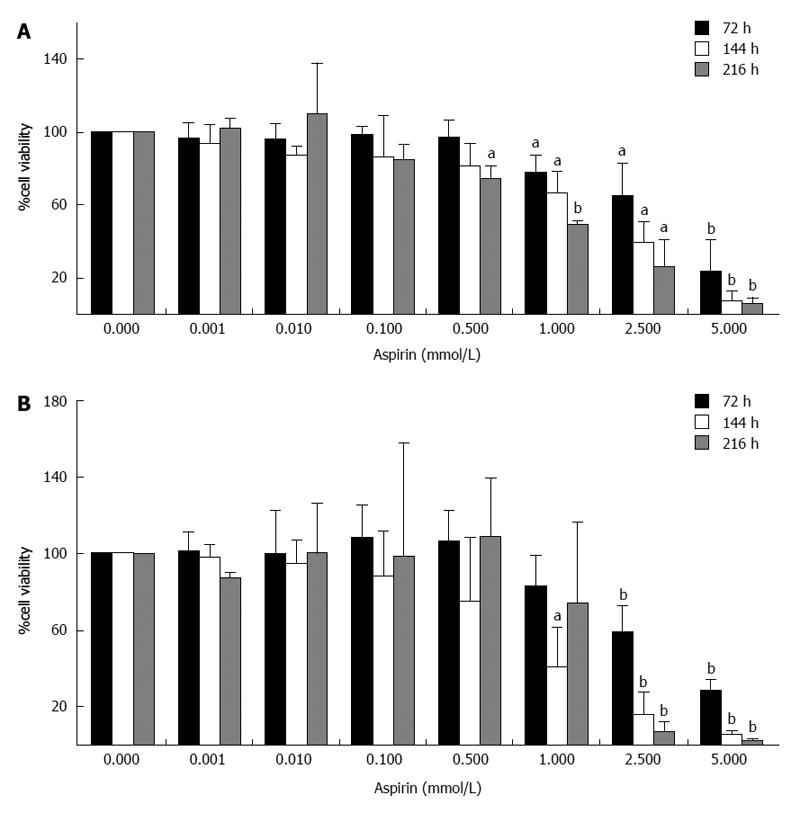
Figure 1 Inhibition of neuroendocrine BON1 cell viability by aspirin.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 72, 144 and 216 h. The viability of the cells was measured based on both metabolic activity using the Cell Titer 96 kit (Promega) (A) and DNA labeling experiments using SYBR green (Lonza) (B). The data shown are the mean ± SD of 3 independently performed experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs untreated control.
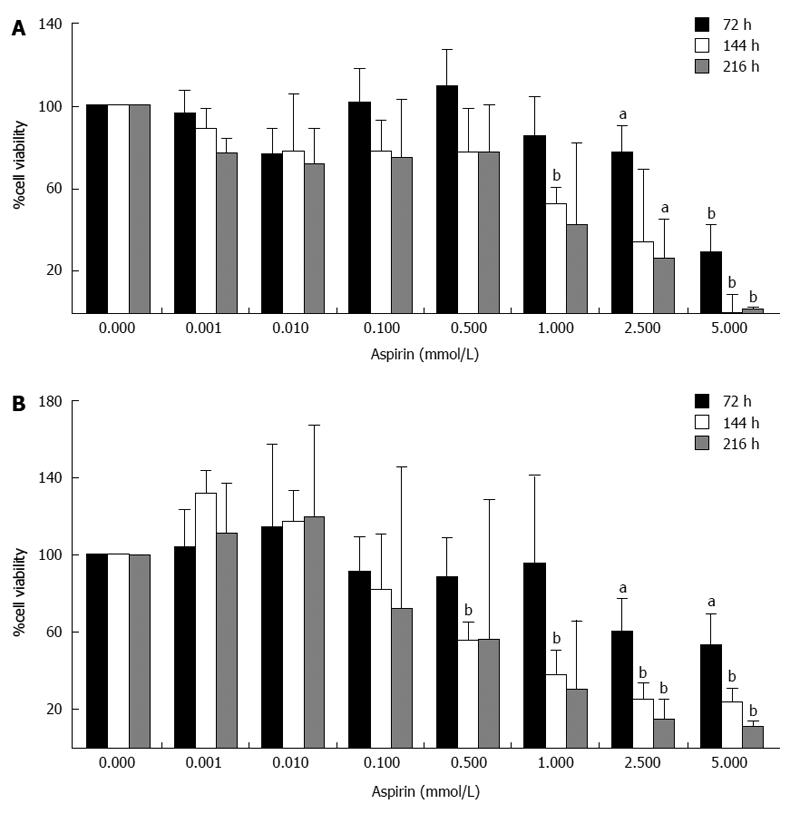
Figure 2 Inhibition of neuroendocrine NCI-H727 cell viability by aspirin.
Human bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine NCI-H727 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 72, 144 and 216 h. The viability of the cells was measured based both metabolic activity using the Cell Titer 96 kit (Promega) (A) and DNA labeling experiments using SYBR green (Lonza) (B). The data shown are the mean ± SD of 3 independently performed experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs untreated control.
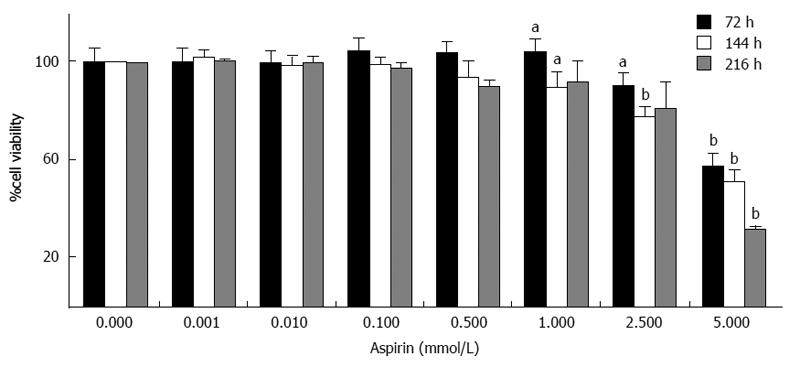
Figure 3 Inhibition of neuroendocrine GOT1 cell viability by aspirin.
Human midgut neuroendocrine GOT1 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 72, 144 and 216 h. The viability of the cells was measured based on metabolic activity using the Cell Titer 96 kit (Promega). The data shown are the mean ± SD of 4 independently performed experiments. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs untreated control.
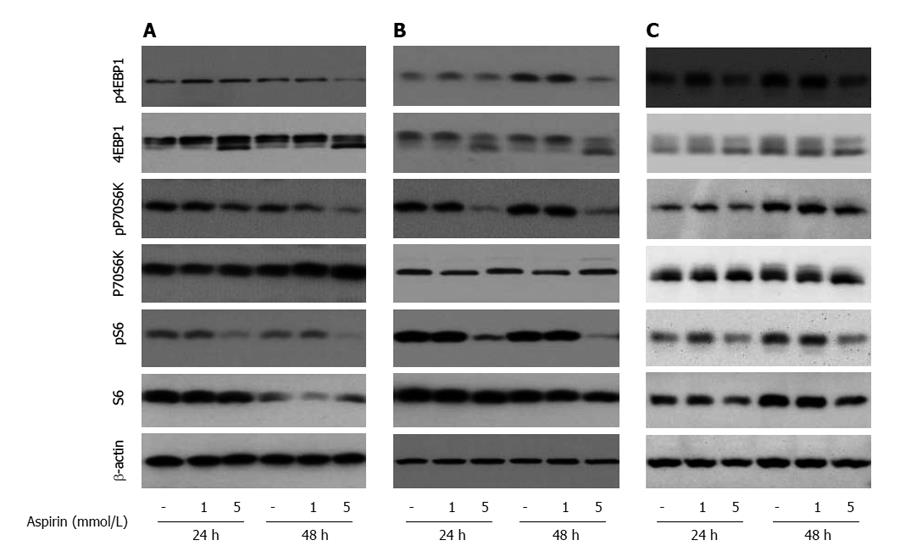
Figure 4 The effect of aspirin on mTORC1 downstream signaling in neuroendocrine BON1, NCI-H727 and GOT1 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A), bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) and midgut GOT1 (C) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of p4EBP1, 4EBP1, pP70S6K, P70S6K, pS6, S6 and a β-actin loading control was subsequently evaluated using Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
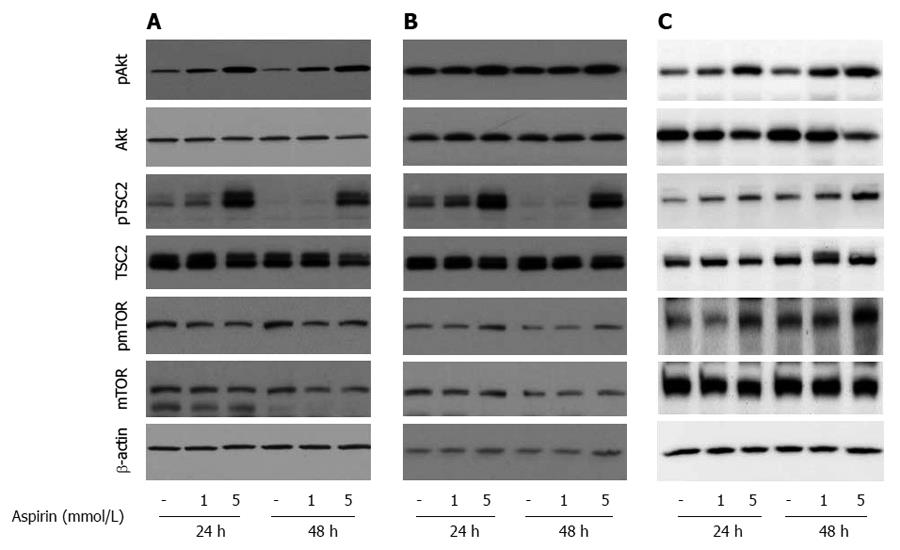
Figure 5 The effect of aspirin on AKT/mTOR signaling in neuroendocrine BON1, NCI-H727 and GOT1 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A), human bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) and midgut GOT1 (C) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of pAkt, Akt, pTSC2, TSC2, pmTOR, mTOR and a β-actin loading control was subsequently evaluated using Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
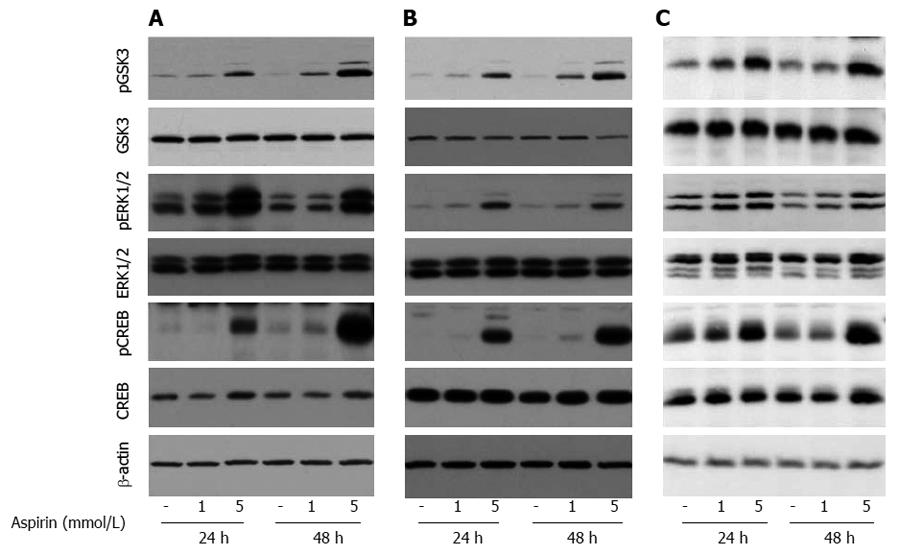
Figure 6 The effect of aspirin on GSK3 and ERK1/2 signaling in neuroendocrine BON1, NCI-H727 and GOT1 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A), human bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) and midgut GOT1 (C) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of pGSK3, GSK3, pERK1/2, ERK1/2, pCREB, CREB and a β-actin loading control was subsequently evaluated by Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
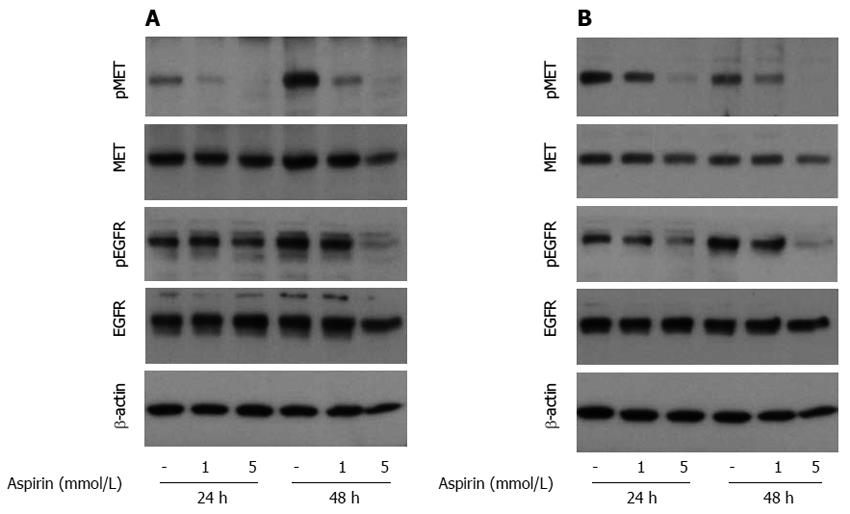
Figure 7 The effect of aspirin on EGFR and c-MET signaling in neuroendocrine BON1 and NCI-H727 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A) and bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of pMET, MET, pEGFR, EGFR and a β-actin loading control was evaluated using Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
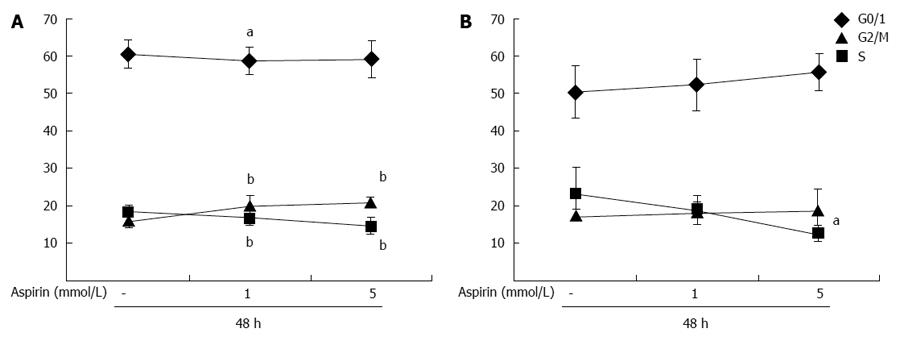
Figure 8 The effect of aspirin on cell cycle distribution of neuroendocrine BON1 and NCI-H727 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A) and bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) cells were cultured in serum-free medium (0.2% BSA) for 24 h and then treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 48 h. The mean ± SDs of 8 independently performed experiments in duplicates are shown; aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs untreated control.
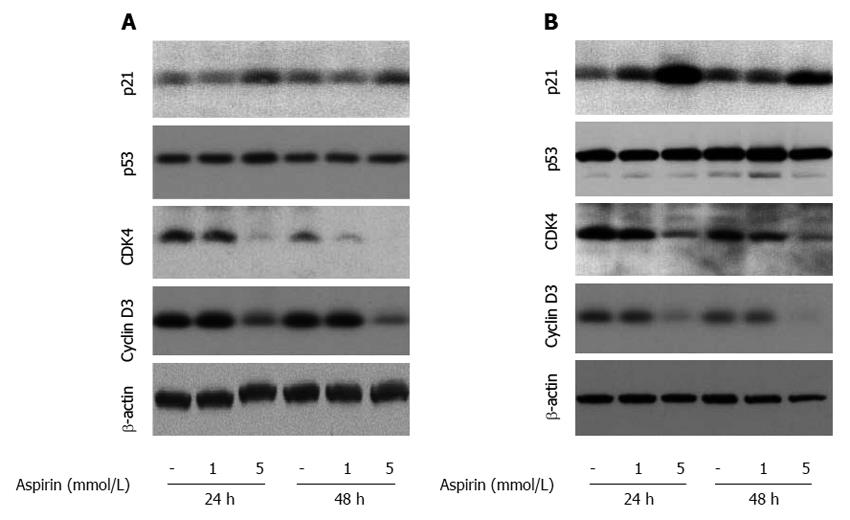
Figure 9 The effect of aspirin on proteins involved in cell cycle progression in neuroendocrine BON1 and NCI-H727 tumor cells.
Human pancreatic neuroendocrine BON1 (A) and human bronchopulmonary NCI-H727 (B) cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of aspirin for 24 and 48 h. The expression of p21, CDK4, p53, cyclin D3 and a β-actin loading control was subsequently evaluated by Western blot analysis. A representative blot from 3 independently performed experiments is shown.
- Citation: Spampatti M, Vlotides G, Spöttl G, Maurer J, Göke B, Auernhammer CJ. Aspirin inhibits cell viability and mTOR downstream signaling in gastroenteropancreatic and bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine tumor cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(29): 10038-10049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i29/10038.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i29.10038