Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2014; 20(26): 8740-8744
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8740
Published online Jul 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8740
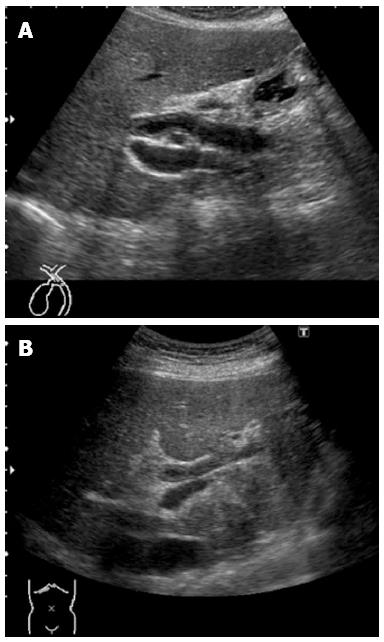
Figure 1 Abdominal ultrasonograms, showing wall thickening in the region extending from the upper bile duct (A) to the intrahepatic bile duct (B).
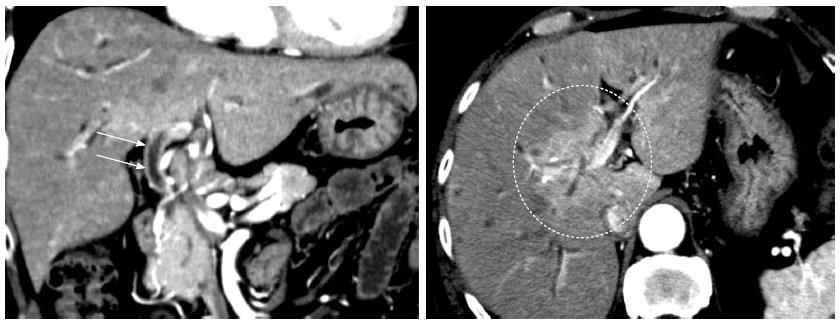
Figure 2 Early-phase, abdominal computed tomographic scans, showing wall thickening with a contrast effect in the region from the upper biliary tract to the intrahepatic bile duct (arrows) and a strong contrast effect mainly in the hepatic parenchyma in the portal region (circle).
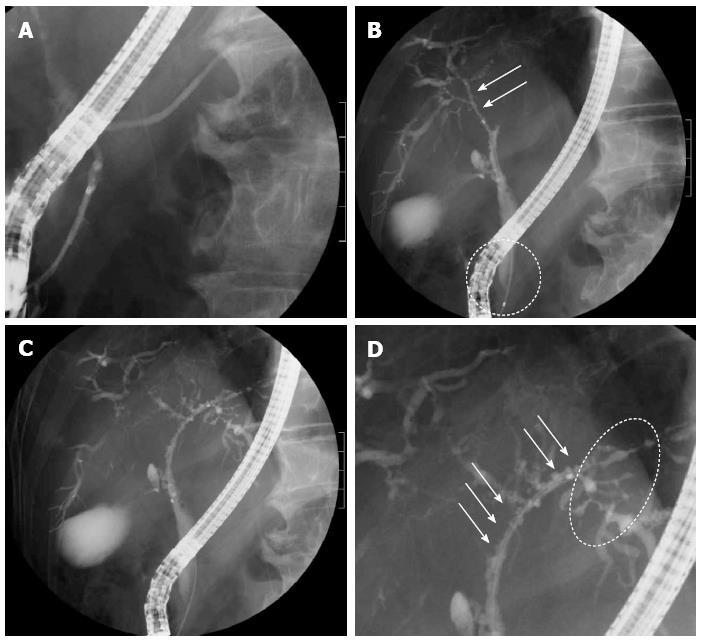
Figure 3 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography images obtained before treatment.
A: There were no abnormalities of the pancreatic ducts; B: Images of the right bile duct showed stricture and simple dilation after a relatively long confluent stricture (arrows), with no strictures of the lower common bile duct (circle); C, D: A band-like stricture was found in the left bile duct (circle), and a beaded appearance was seen from the upper bile duct to the left hepatic duct (arrows).
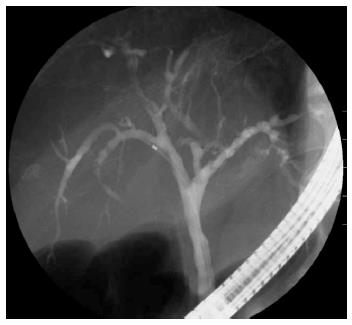
Figure 4 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography image obtained after steroid treatment, showing that the biliary stricture situated mainly in the portal region had markedly improved.
- Citation: Masutani H, Okuwaki K, Kida M, Yamauchi H, Imaizumi H, Miyazawa S, Iwai T, Takezawa M, Koizumi W. First case of IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis associated with autoimmune hemolytic anemia. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(26): 8740-8744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i26/8740.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i26.8740