Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2014; 20(25): 8229-8236
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8229
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8229
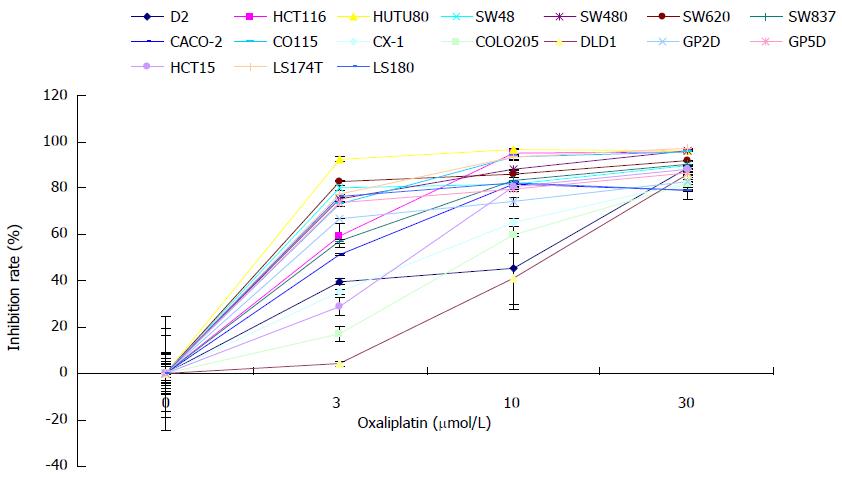
Figure 1 MTT assay.
Seventeen colorectal cancer (CRC) cell lines were treated with different concentrations of oxaliplatin, and MTT assay was used to detect cell growth inhibition as described in Materials and Methods.
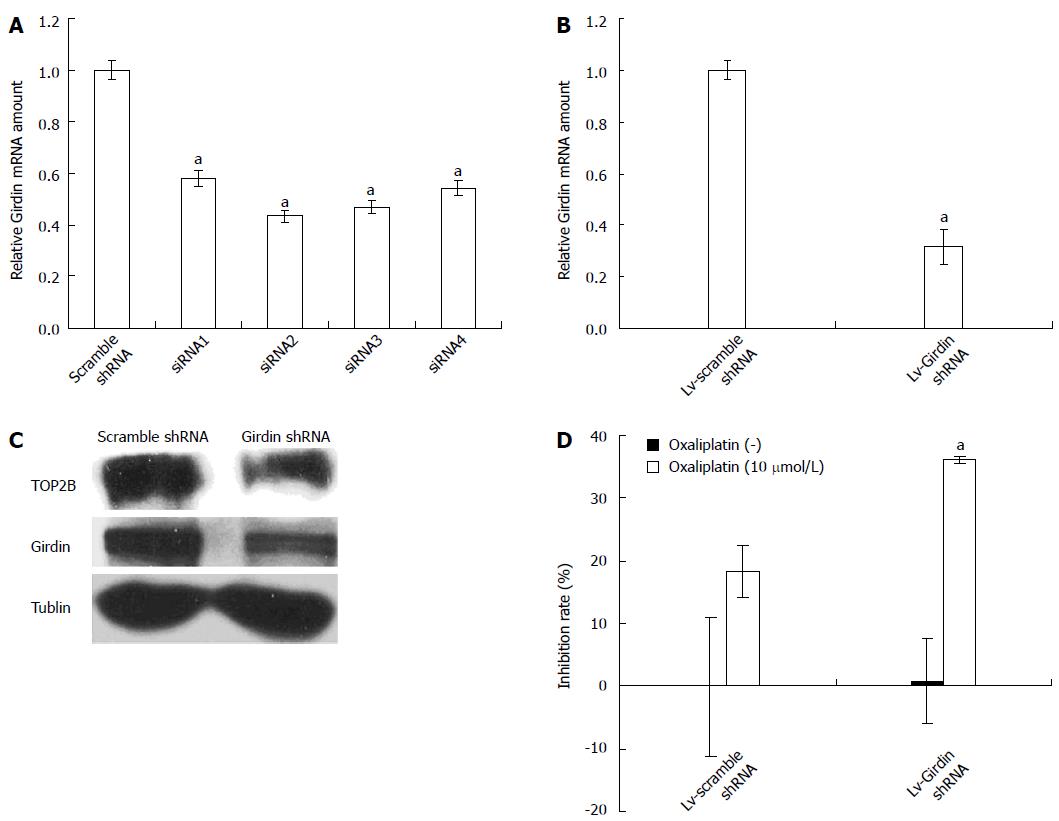
Figure 2 Effect of Girdin on DLD1 sensitivity to oxaliplatin.
A: Quantification of Girdin mRNA by real-time polymerase chain reaction to validate knockdown effect of four siRNA duplexes targeting Girdin; B: Girdin mRNA level in DLD1 cells after infection with a lentivirus expressing an shRNA targeting Girdin; C: Detection of Girdin and TOP2B proteins by Western blotting; D: Growth inhibition of DLD1 cells by oxaliplatin in combination with knockdown of Girdin. aP < 0.05 vs scramble shRNA.
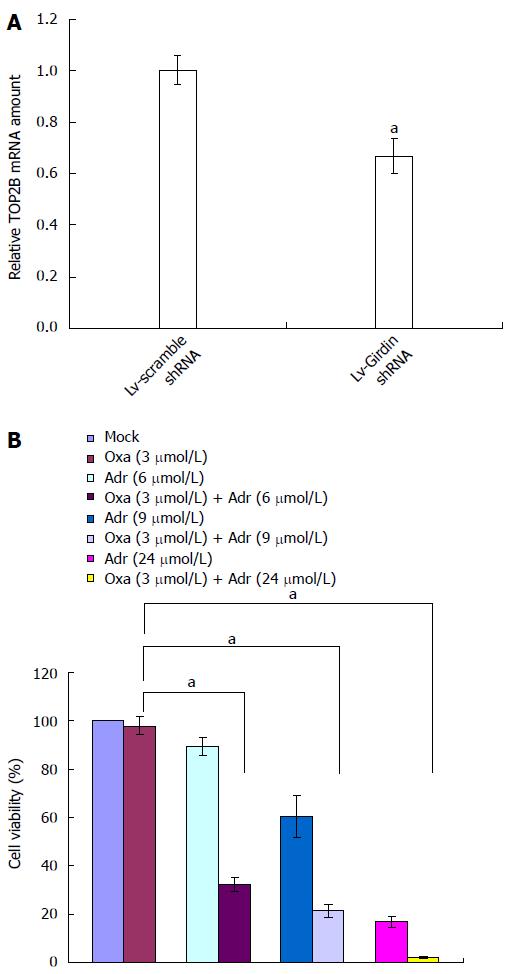
Figure 3 TOP2B as a downstream gene of Girdin is involved in the resistance of DLD1 cells to oxaliplatin.
A: TOP2B mRNA level in DLD1 cells after infection with the Lv-Girdin shRNA; B: Growth inhibition of DLD1 cells by oxaliplatin in combination with adriamycin. aP < 0.05.
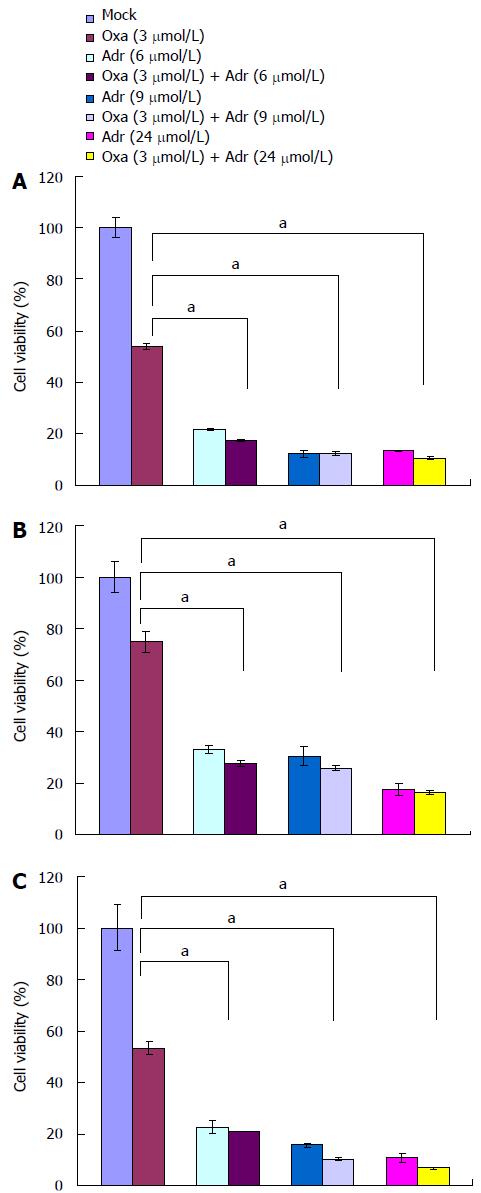
Figure 4 Growth inhibition of colorectal cancer cell lines by oxaliplatin in combination with adriamycin.
A: Growth inhibition of SW620 cells; B: Growth inhibition of SW480 cells; C: Growth inhibition of HCT116 cells. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Zhang YJ, Li AJ, Han Y, Yin L, Lin MB. Inhibition of Girdin enhances chemosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(25): 8229-8236
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i25/8229.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8229