Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2014; 20(25): 8221-8228
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8221
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8221
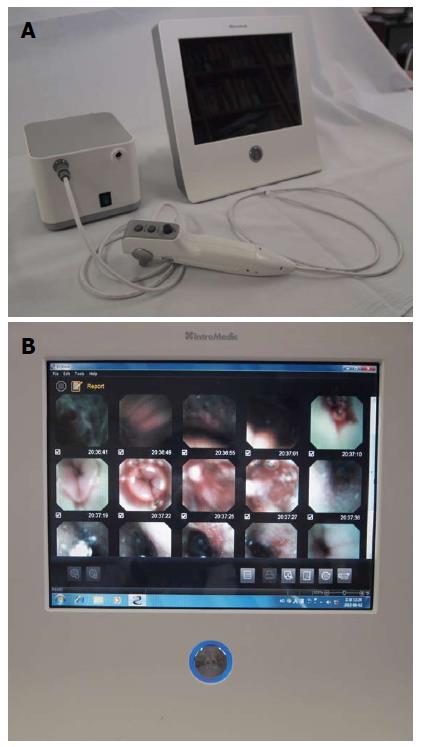
Figure 1 EG scan machine (A) and a display monitor (B).
Figure 2 Comparison of the diameters of conventional endoscopy (A, GIF-XQ260, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan), the EG scan (B), and 16F nasogastric tube (C).
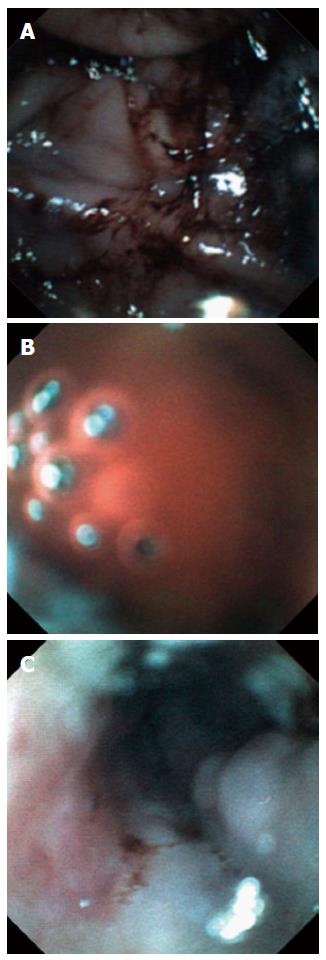
Figure 3 Images of EG scan.
A: Dark, coffee-ground colored blood clot; B: bright red fresh blood; C: multiple bluish colored esophageal varices.
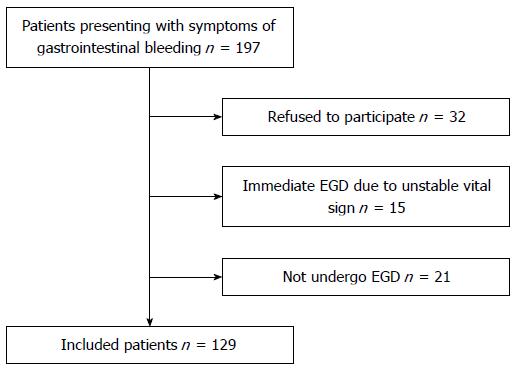
Figure 4 Flow diagram illustrating patients enrolled in the study.
EGD: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy.
- Citation: Choi JH, Choi JH, Lee YJ, Lee HK, Choi WY, Kim ES, Park KS, Cho KB, Jang BK, Chung WJ, Hwang JS. Comparison of a novel bedside portable endoscopy device with nasogastric aspiration for identifying upper gastrointestinal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(25): 8221-8228
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i25/8221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8221