Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2014; 20(25): 8072-8081
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8072
Published online Jul 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8072
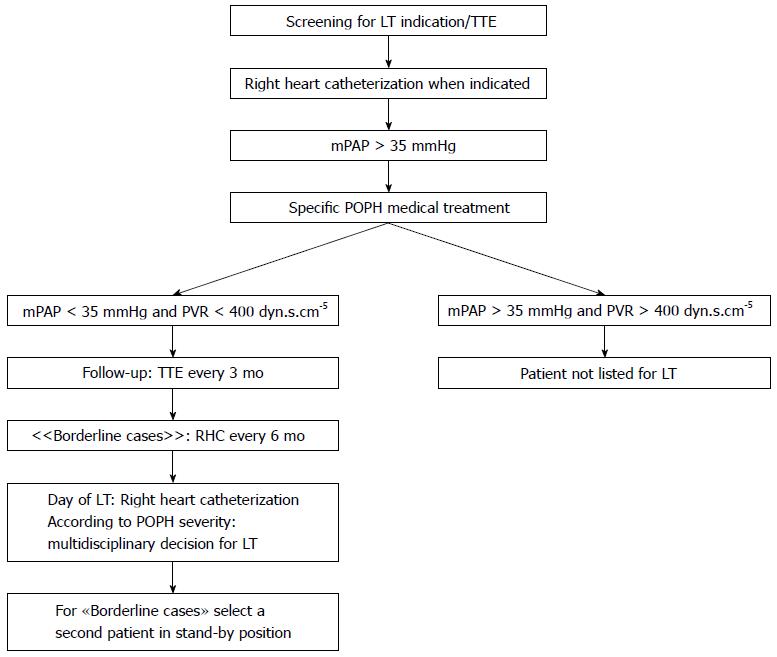
Figure 1 Portopulmonary hypertension screening and follow-up algorithm for liver transplantation candidates in Geneva.
LT: Liver transplantation; mPAP: Mean pulmonary artery pressure; POPH: Portopulmonary hypertension; PVR: Pulmonary vascular resistance; TTE: Transthoracic doppler echocardiography.
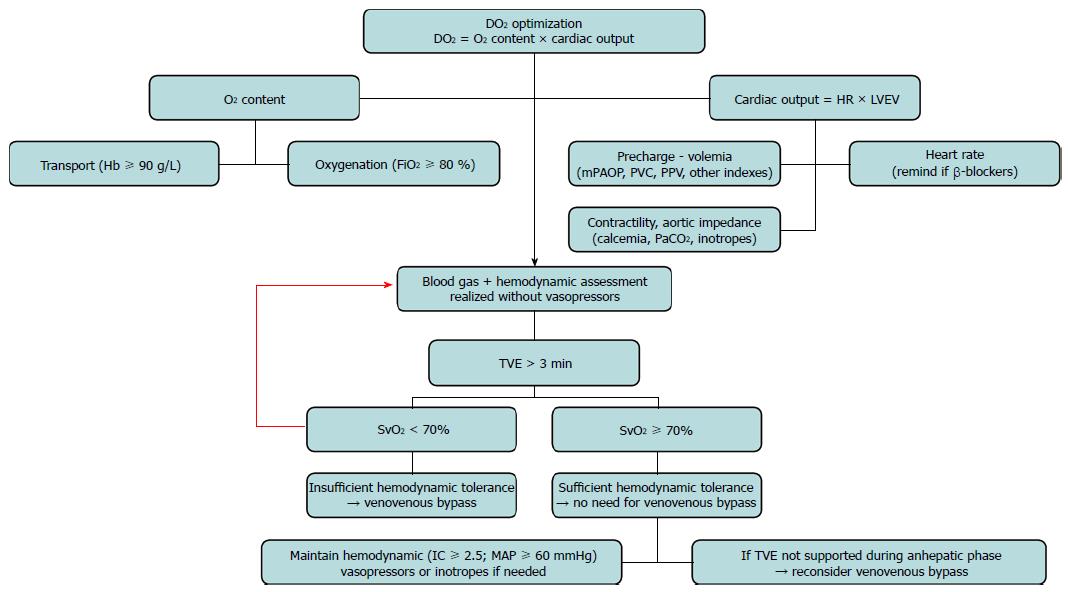
Figure 2 Challenge algorithm to total vascular exclusion of the liver.
DO2: Oxygen delivery; Hb: Hemoglobin; FiO2: Inspired oxygen fraction; HR: Heart rate; LVEV: Left ventricular ejection volume; PaCO2: Partial pressure of carbon dioxide; TVE: Total vascular exclusion of the liver; SvO2: Mixed venous oxygen blood saturation.
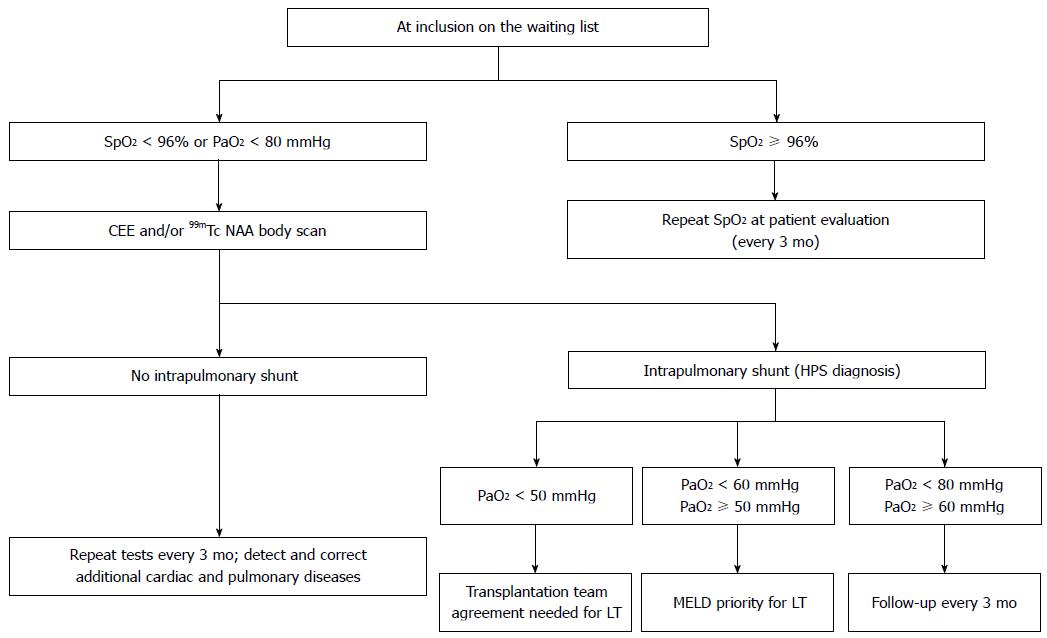
Figure 3 Hepatopulmonary syndrome screening, grading and follow-up algorithm for liver transplantation candidates.
Adapted from Pastor et al[48]. SpO2: Hemoglobin oxygen saturation; HPS: Hepatopulmonary syndrome; PaO2: Partial pressure of oxygen; MELD: Model for end-stage liver disease; LT: Liver transplantation; 99mTc NAA: Technetium macroaggregated albumin.
- Citation: Aldenkortt F, Aldenkortt M, Caviezel L, Waeber JL, Weber A, Schiffer E. Portopulmonary hypertension and hepatopulmonary syndrome. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(25): 8072-8081
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i25/8072.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i25.8072