Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7298-7305
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7298
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7298
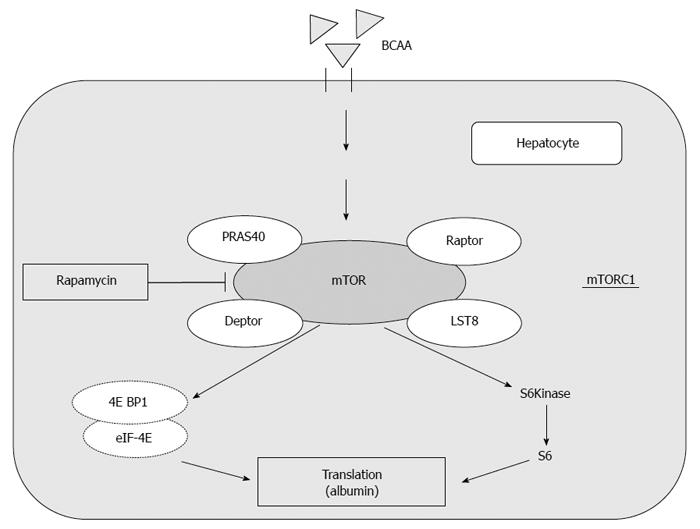
Figure 1 Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) promotes albumin synthesis through activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signal transduaction system. mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) is composed of mTOR, Raptor, LST8, PRAS40 and Deptor. Raptor: Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; LST8: Mammalian lethal with SEC13 protein 8; PRAS40: Protein-rich Akt subsrtrate of 40 kDa; Deptor; DEP domain-containing mTOR-interacting protein; eIF-4E: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; 4E BP1: Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1.
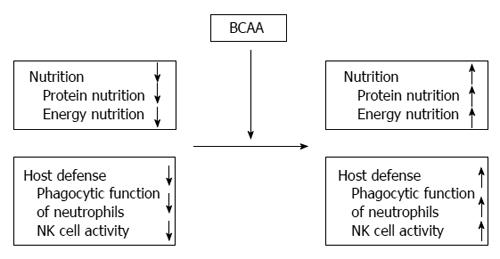
Figure 2 Restoration of nutrition state and host immune responses by branched-chain amino acids in decompensated cirrhotic patients.
Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) oral supplementation could not only improve nutrition state (protein nutrition, energy nutrition) but restore host defense mechanisms [phagocytic function of neutrophils and natural killer (NK) cell activity] in cirrhotic patients.
- Citation: Nakamura I. Impairment of innate immune responses in cirrhotic patients and treatment by branched-chain amino acids. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7298-7305
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7298