Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7252-7259
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7252
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7252
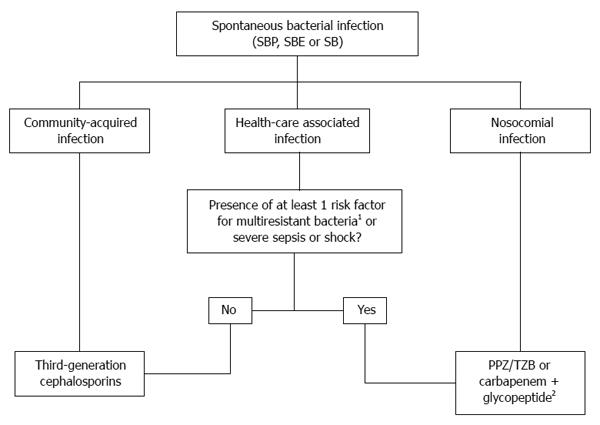
Figure 1 Proposed algorithm for the empirical treatment of infections in cirrhosis.
1Risk factors for multiresistant bacteria in Health care associated infections are long-term norphloxacin prophylaxis or previous infection by multiresistant (MR) bacteria within 6 mo; 2Piperaziline/tazobactam in areas of low MR bacteria but high Enterococcus faecalis prevalence. Meropenem and glycopeptides in areas with high prevalence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. SBP: Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; SBE: Spontaneous bacterial empyema; SB: Spontaneous bacteremia; PPZ/TZB: Piperaziline/tazobactam.
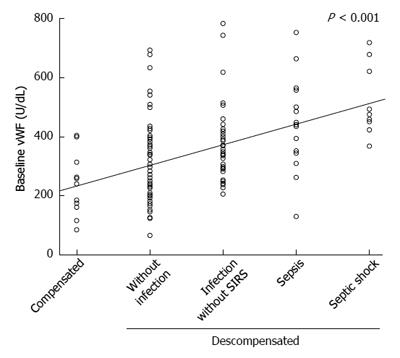
Figure 2 Correlation between von Willebrand factor and degree of sepsis.
SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome. (thanks Hepatology journal for permission to reproduce the figure).
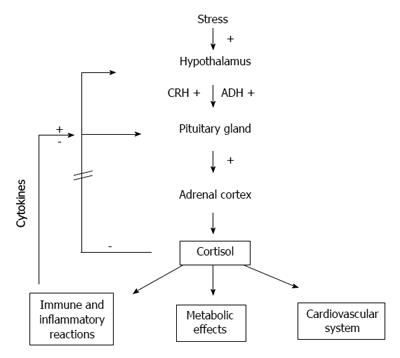
Figure 3 Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in the critical illness.
CRH: Corticotrophin releasing hormone; ADH: Antidiuretic hormone; ACTH: Adrenocorticotropic hormone. Original work of the authors.
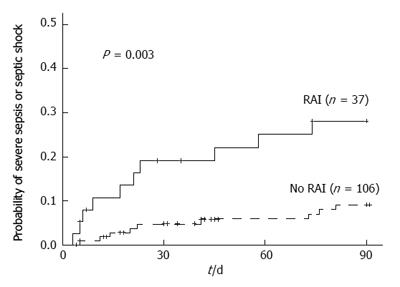
Figure 4 Probability of development of severe sepsis and septic shock in patients with and without relative adrenal insufficiency.
Probability of developing new episodes of severe sepsis or septic shock in patients with relative adrenal insufficiency (RAI) (continuous line) or with normal adrenal function (doted line) during 3 mo follow-up. Probability was significantly higher in patients with RAI. (thanks Hepatology journal for permission to reproduce the figure).
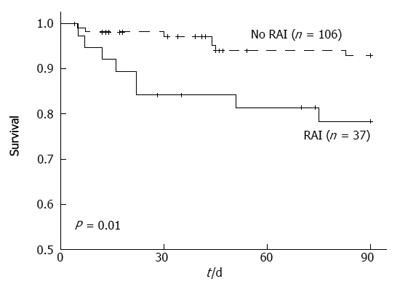
Figure 5 Probability of survival at 3 mo in patients with and without relative adrenal insufficiency.
Probability of survival at 3 mo in patients with relative adrenal insufficiency (RAI) (continuous line) or with normal adrenal function (doted line). Probability was significantly higher in patients with RAI. (thanks Hepatology journal for permission to reproduce the figure).
- Citation: Acevedo J, Fernández J. New determinants of prognosis in bacterial infections in cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7252-7259
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7252