Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2014; 20(23): 7242-7251
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7242
Published online Jun 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7242
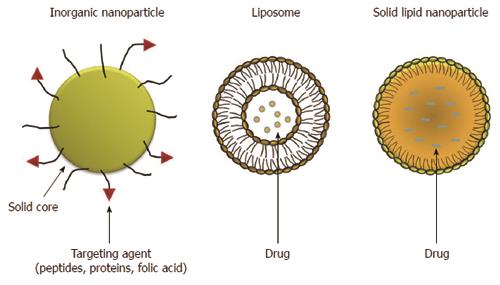
Figure 1 Major types of nanoparticles including: inorganic nanoparticles, liposomes and solid lipid nanoparticles.
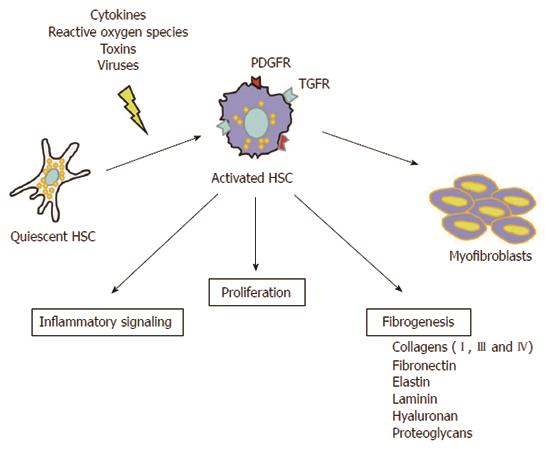
Figure 2 Quiescent stellate cell activation is initiated by different types of stimulus (cytokines, reactive oxygen species, toxins, viruses).
The activated cell is transformed into myofibroblasts which contain contractile filaments. Activation of hepatic stellate cells is associated with a gradual replacement of the extracellular matrix (ECM) by the collagen rich fibers and the production of fibrous bands. In advanced stages of fibrosis, the liver contains more ECM components than normal, including collagens (I, III and IV), fibronectin, elastin, laminin, hyaluronan, and proteoglycans. PDGFRs: Platelet-derived growth factor receptors; TGFR: Transforming growth factor receptor.
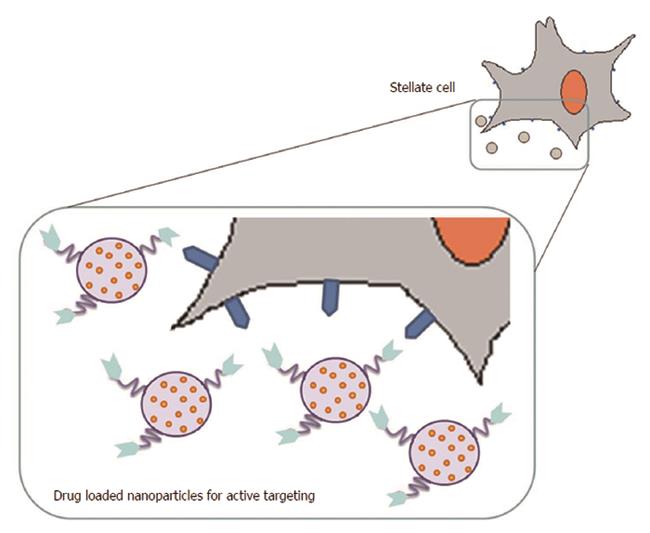
Figure 3 Nanoparticles are loaded with drugs to actively target the disease site by using cell-specific homing devices.
- Citation: Giannitrapani L, Soresi M, Bondì ML, Montalto G, Cervello M. Nanotechnology applications for the therapy of liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(23): 7242-7251
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i23/7242.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i23.7242