Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2014; 20(22): 7055-7060
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.7055
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.7055
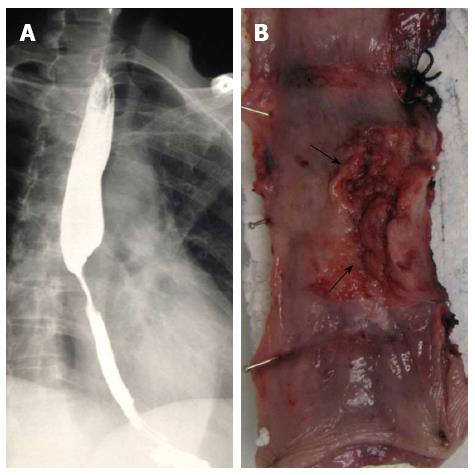
Figure 1 Clinical features.
A: Contrast swallow with mid-esophageal stenosis; B: Partially ulcerated annular tumor (arrows).
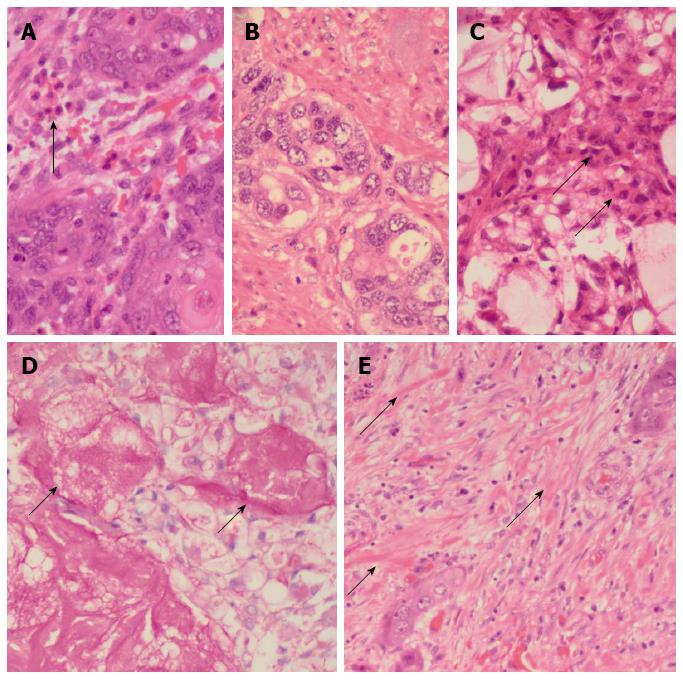
Figure 2 Pathological features.
A: Islands of malignant squamoid cells with surrounding stromal eosinophils (arrow) [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), × 480]; B: Glandular foci (HE, × 480); C: Foci of intermediate (arrows) and clear cells and of the cystically dilated mucinous component (HE, × 480); D: Southgate mucicarmine stain demonstrating the luminal (arrows) and intracytoplasmic mucin (southgate mucicarmine, × 480); E: Sclerotic stroma with keloid-like areas (arrows) (HE, × 480).
- Citation: Mewa Kinoo S, Maharaj K, Singh B, Govender M, Ramdial PK. Primary esophageal sclerosing mucoepidermoid carcinoma with “tissue eosinophilia”. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(22): 7055-7060
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i22/7055.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.7055