Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2014; 20(22): 6832-6843
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6832
Published online Jun 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6832
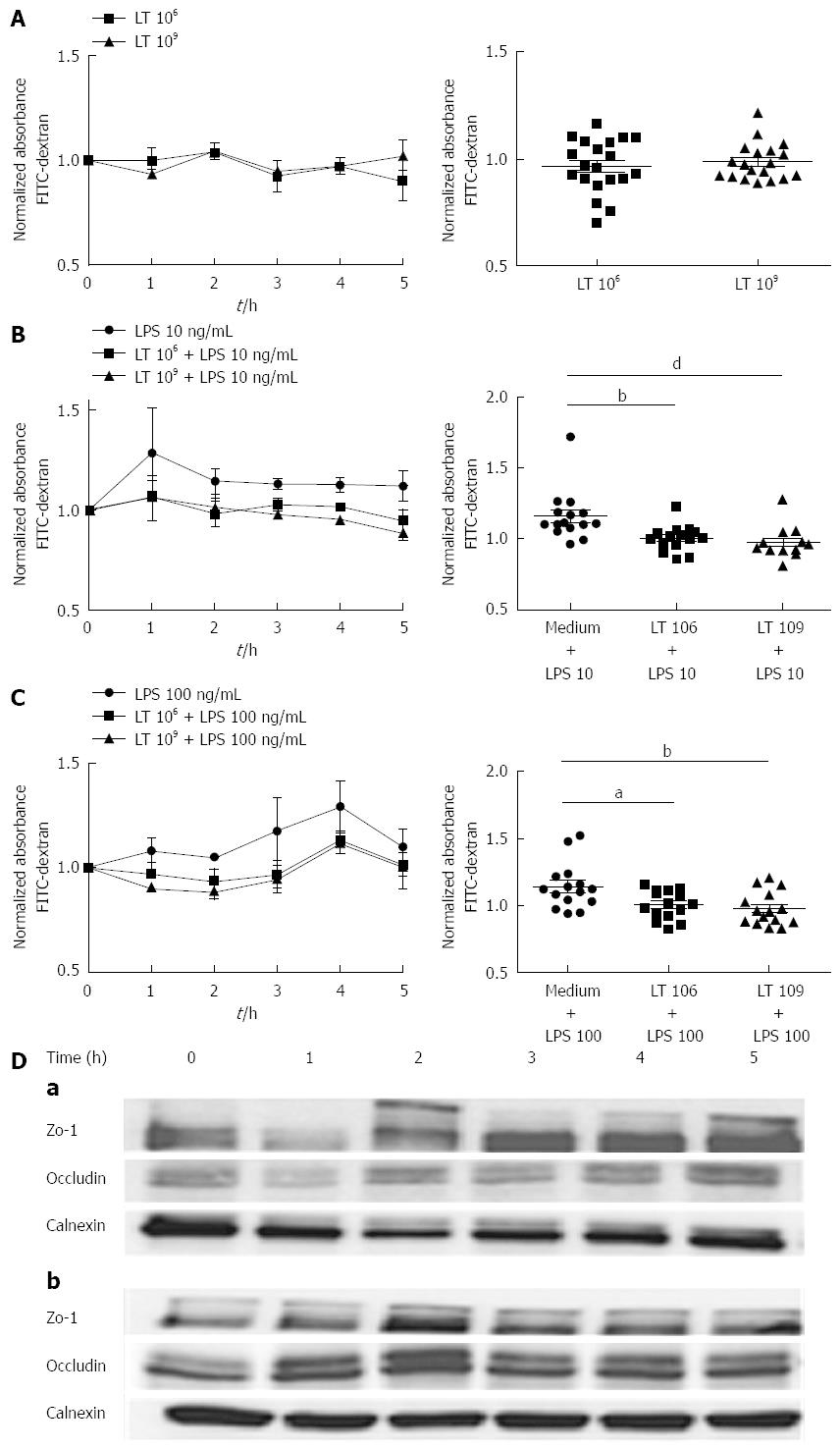
Figure 1 Effect of the Lactibiane Tolerance®.
Strain combination on T84 monolayer permeability in basal conditions (A) and after stimulation with 10 ng/mL (B) or 100 ng/mL lipopolysaccharide (C). Experiments were performed in duplicate and data were normalized by comparison to control wells containing culture medium only. The results displayed on the left panels are the means of 5 experiments in basal conditions and 3 experiments with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. The right panels show the dispersion of values and statistical significance of the differences evaluated with the one-way Anova analysis followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05 and is displayed as aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 or dP < 0.01 vs culture medium + LPS; D: On ZO-1 and occludin expression in basal conditions (a) or in the presence of 10 ng/mL LPS (b). Expression of occludin (65 kDa) and ZO-1 (220 kDa) was evaluated by immunoblotting. Calnexin (95 kDa) was used as a loading control.
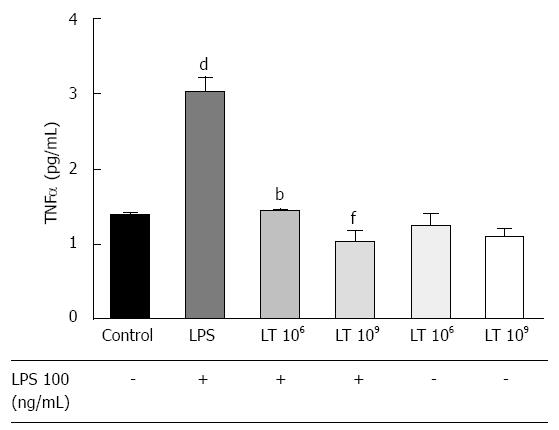
Figure 2 Comparison of the tumor necrosis factor α response to lipopolysaccharide stimulation of a confluent T84 monolayer cultured with or without the Lactibiane Tolerance® strain combination assessed by ELISA.
Experiments were performed in duplicate. Statistical significance evaluated with the one-way Anova analysis followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05 and is displayed as dP < 0.01 vs culture medium; bP < 0.01 or fP < 0.01 vs culture medium + lipopolysaccharide (LPS). TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; LT: Lactibiane Tolerance.
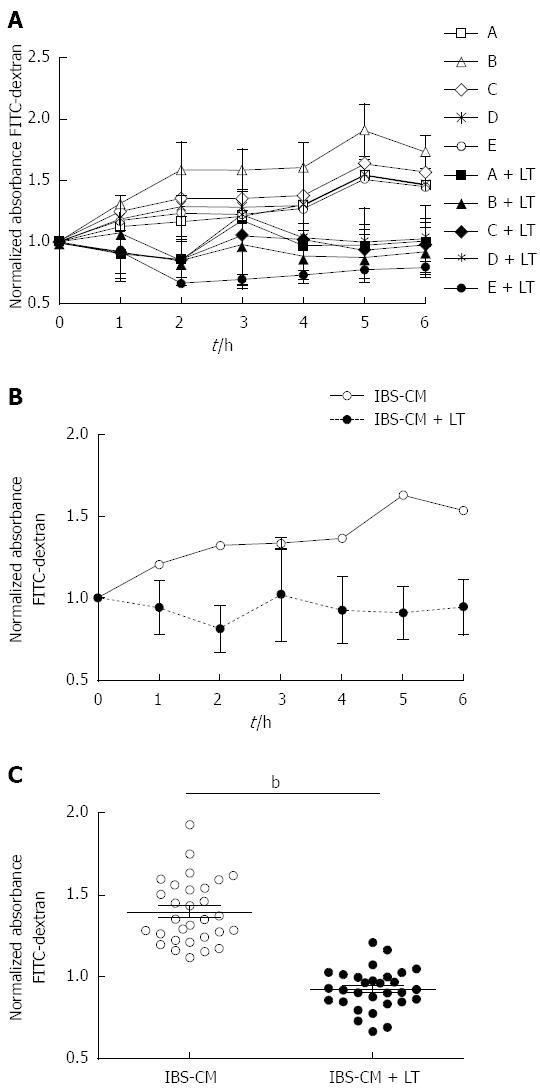
Figure 3 Effect of the Lactibiane Tolerance® strain combination on the changes in T84 monolayer permeability induced by intestinal bowel syndrome colonic biopsy conditioned medium.
Experiments were performed in duplicate and data were normalized to the culture medium control. A: Variations in permeability induced by each conditioned medium: Conditioned medium of intestinal bowel syndrome patient colonic biopsies (IBS-CM) “A” and “B” were obtained from patients with a constipation form of IBS and “C”,” D” and “E” with a diarrhea form; B: Mean of permeability variations induced by the five conditioned media; C: Statistical significance for differences between IBS-CM and IBS-CM + LT were evaluated with the Student’s t test set at P < 0.05 and is displayed as bP < 0.01 (IBS-CM vs IBS-CM + LT). LT: Lactibiane Tolerance.
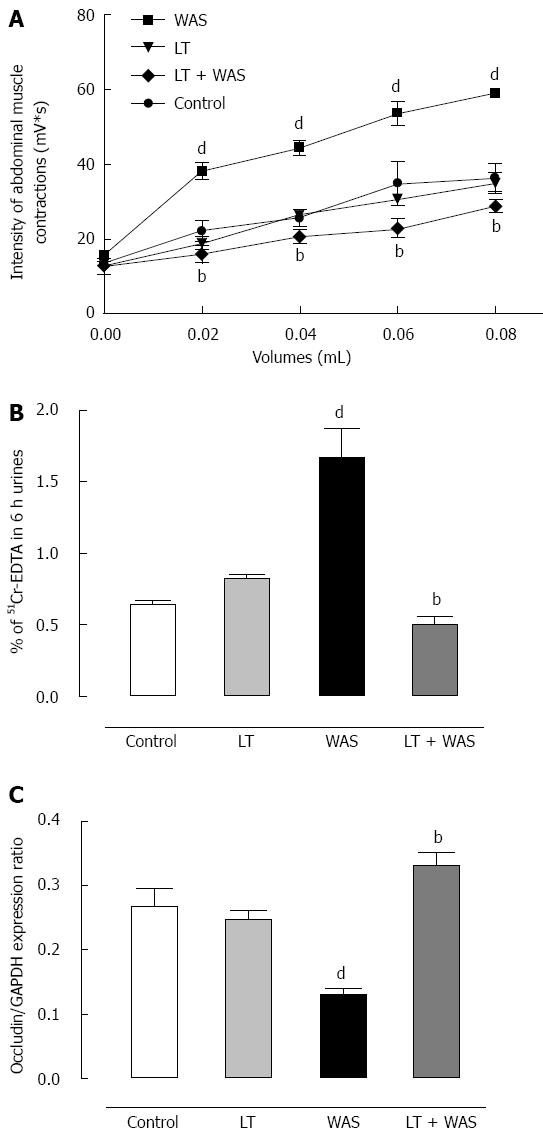
Figure 4 Effect of Lactibiane Tolerance® treatment.
A: On stress-induced visceral hypersensitivity; B: On stress-induced intestinal hyperpermeability; C: On stress-induced occludin expression. A treatment with Lactibiane Tolerance (LT) given 15 d before and for 4 d during water avoidance stress (WAS) prevented stress-induced hypersensitivity in mice as well as stress-induced hyperpermeability and the defect in occludin expression. Statistical significance for differences was evaluated with the one-way Anova analysis (hyperpermeability) or two-way Anova analysis (hypersensitivity) followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05: dP < 0.01 vs control group; bP < 0.01 vs WAS group.
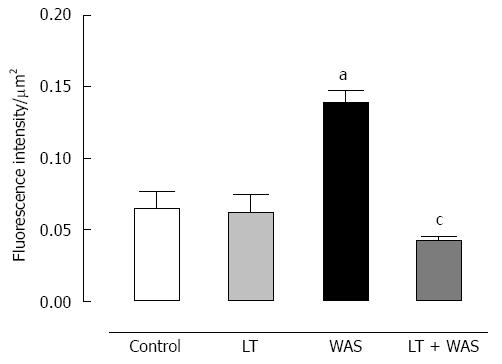
Figure 5 Effect of Lactibiane Tolerance® treatment on toll-like receptor-4 immunoreactivity in colonic sections of control or stressed (water avoidance stress) mice.
The Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4) staining intensity was increased in colonic epithelial cells in stressed mice (arrows). Lactibiane Tolerance (LT) treatment decreased TLR-4 expression in stressed animals. Statistical significance for differences was evaluated with the two-way Anova analysis followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05: aP < 0.05 vs control group; cP < 0.05 vs water avoidance stress (WAS) group.
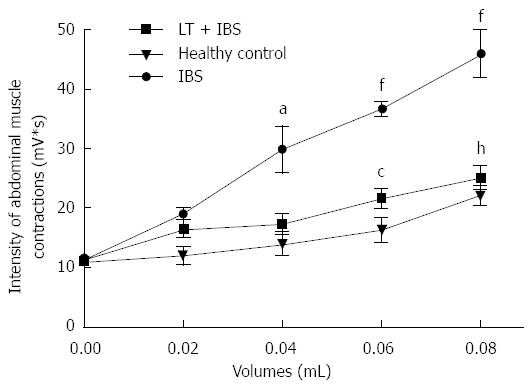
Figure 6 Effects of Lactibiane Tolerance® treatment on changes to the visceral sensitivity induced by intracolonic infusion of intestinal bowel syndrome fecal supernatants.
Intestinal bowel syndrome fecal supernatants (IBS FSN) (from 4 IBS patients) infusion in naive mice induced visceral hyersensitivity in response to colorectal distension (from 0.04 to 0.08 mL). Lactibiane Tolerance® treatment during 15 d before IBS FSN infusion prevented the IBS FSN-induced hypersensitivity at the highest volumes of distension applied. Statistical significance for differences was evaluated with Two-way Anova analysis followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05: aP < 0.05 vs healthy control (0.04 mL); fP < 0.01 vs healthy control (0.06 and 0.08 mL); cP < 0.05 vs IBS (0.04 mL); hP < 0.01 vs IBS (0.08 mL).
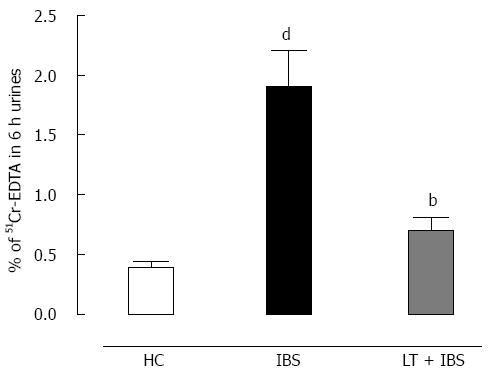
Figure 7 Effect of Lactibiane Tolerance® treatment on changes to the intestinal paracellular permeability induced by intracolonic infusion of intestinal bowel syndrome fecal supernatants.
Intestinal bowel syndrome fecal supernatants (IBS FSN) (from 4 IBS patients) infusion in naive mice increased intestinal paracellular permeability. The 15-d treatment with Lactibiane Tolerance® (LT) before IBS FSN infusion totally prevented this effect. Statistical significance for differences was evaluated with the one-way Anova analysis followed by the Bonferroni post-test set at P < 0.05: dP < 0.01 vs healthy control; bP < 0.01 vs IBS.
- Citation: Nébot-Vivinus M, Harkat C, Bzioueche H, Cartier C, Plichon-Dainese R, Moussa L, Eutamene H, Pishvaie D, Holowacz S, Seyrig C, Piche T, Theodorou V. Multispecies probiotic protects gut barrier function in experimental models. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(22): 6832-6843
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i22/6832.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i22.6832