Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2014; 20(21): 6554-6559
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6554
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6554
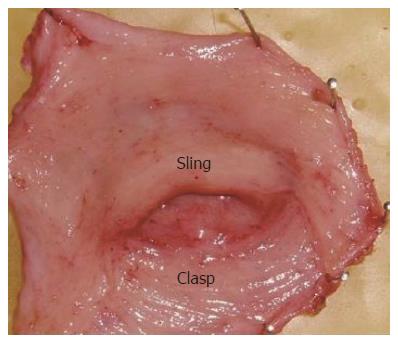
Figure 1 Arrangement of the sling and clasp muscles in the human gastroesophageal junction viewed from the distal luminal aspect after resection of the submucosa.
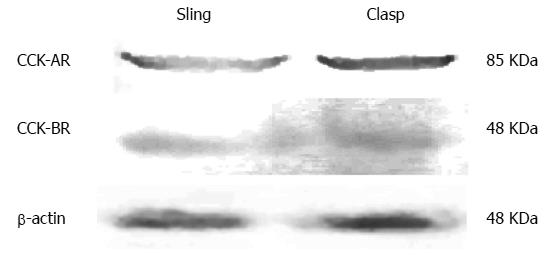
Figure 2 Western blots of the cholecystokinin-A and cholecystokinin-B receptors in the human sling and clasp muscles.
CCK: Cholecystokinin.
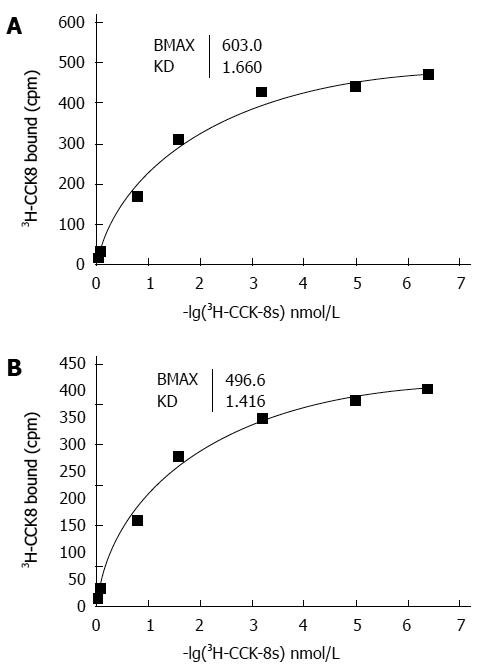
Figure 3 Representative saturation isotherms of the binding of 3H-cholecystokinin-8S to membrane proteins isolated from the human sling (A) and clasp (B) fibers.
CCK: Cholecystokinin.
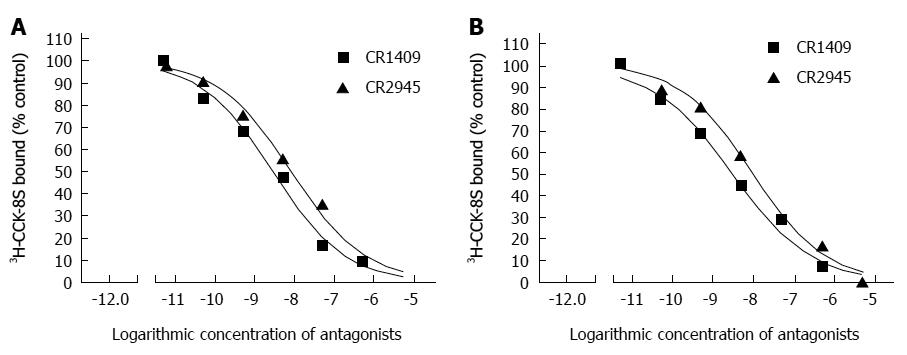
Figure 4 Representative competitive inhibition curves of the binding of 3H- cholecystokinin-8S to membrane proteins isolated from the human sling (A) and clasp (B) fibers.
The antagonists used were CR-1409 [selective for cholecystokinin (CCK)-A receptors] and CR-2945 (CCK-B receptors). Binding is expressed as the percentage of radioactivity specifically bound in the absence of antagonists.
- Citation: Liu JF, Zhang J, Liu XB, Drew PA. Investigation of cholecystokinin receptors in the human lower esophageal sphincter. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(21): 6554-6559
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i21/6554.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6554