Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2014; 20(21): 6400-6411
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400
Published online Jun 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400
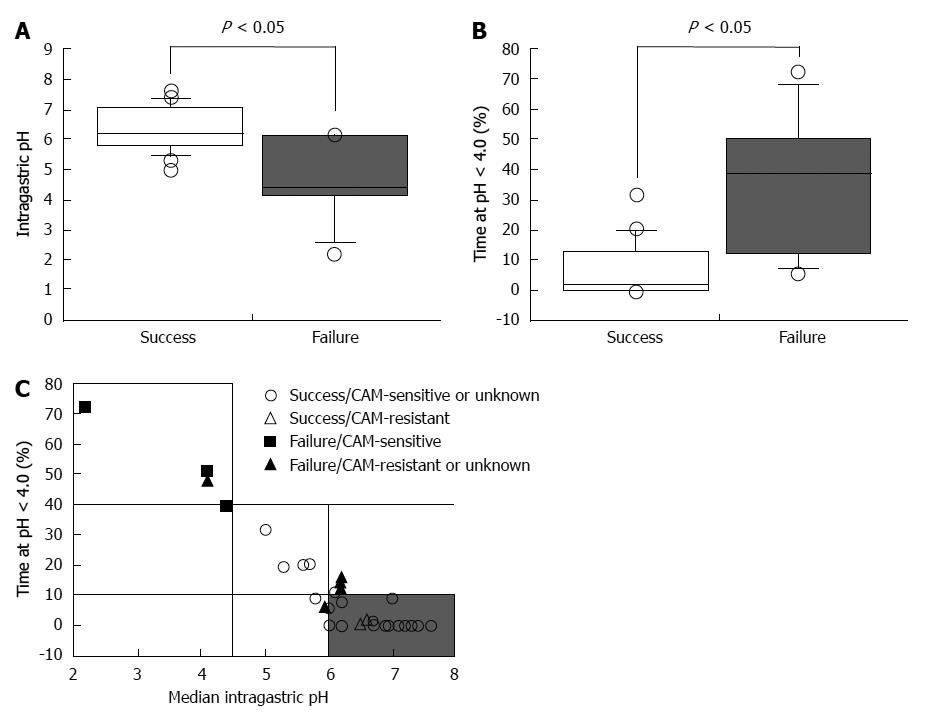
Figure 1 Success of Helicobacter pylori eradication treatment as a function of pH.
A, B: Median 24-h pH values (A) and the percentage of the times when pH < 4.0 during eradication therapy according to successful and failed treatment (B); C: Variation of pH and the percentage of time at pH < 4.0[51]. The median pH of successfully treated patients was significantly higher than compared with patients that failed treatment (A). The median percentage of the time when pH < 4.0 in successfully treated patients was significantly shorter compared with unsuccessfully treated patients (B). The majority of patients were cured using triple therapy when the percentage of time at pH < 4.0 during the 24-h post-dose period was < 10% and the 24-h pH was > 6.0 (shaded area) (C). CAM: Clarithromycin.
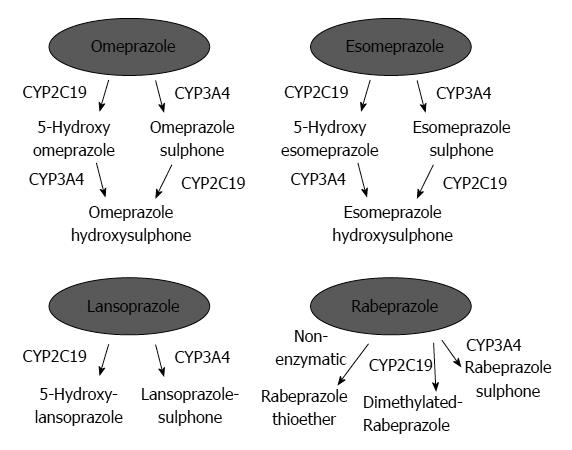
Figure 2 Metabolism of omeprazole, lansoprazole, rabeprazole, and esomeprazole by cytochrome P450 isoenzymes.
Reproduced from Chang et al[61].
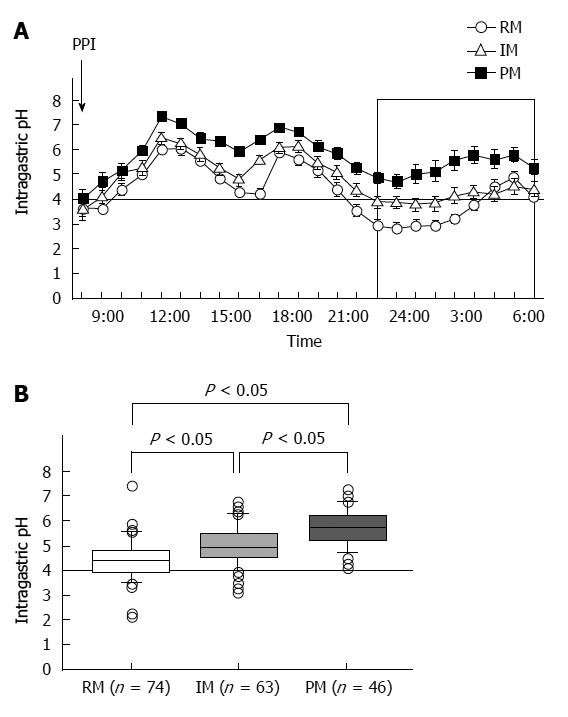
Figure 3 Median 24-h intragastric pH profiles (A) and median 24-h pH values after administering a standard dose of a proton pump inhibitor to patients with the three CYP2C19 genotypes (B).
Proton pump inhibitor (PPI) treatment of poor metabolizers (PMs) inhibited gastric acid secretion more effectively than that of rapid metabolizers (RMs) and intermediate metabolizers (IMs).
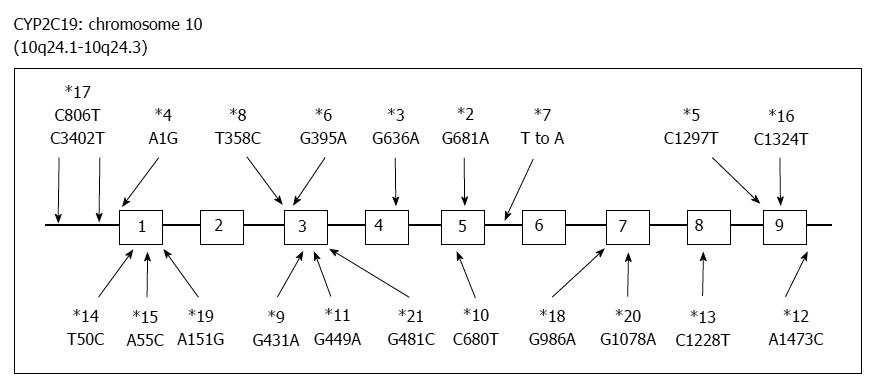
Figure 4 Genetic polymorphisms of CYP2C19.
More than 20 variants have been discovered.
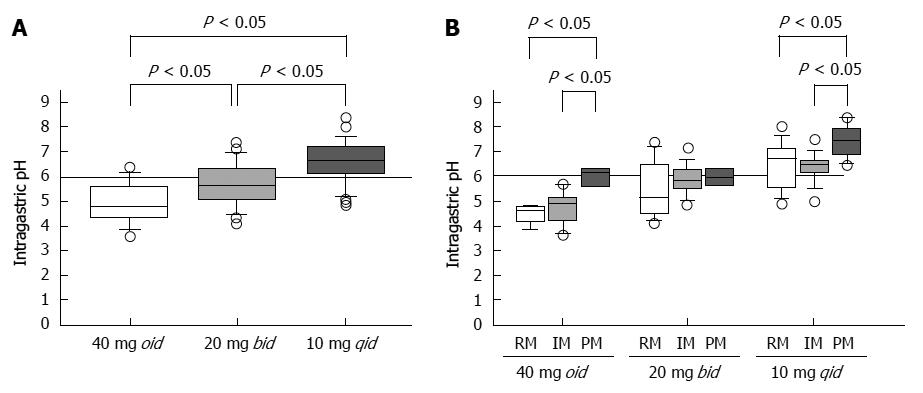
Figure 5 Median 24-h pH values as a function of dosing frequency using 40 mg of rabeprazole (A), and the pH attained using three different dosing regimens as a function of CYP2C19 genotype (B).
Reproduced from Sugimoto et al[25]. PMs: Poor metabolizers; RMs: Rapid metabolizers; IMs: Intermediate metabolizers.
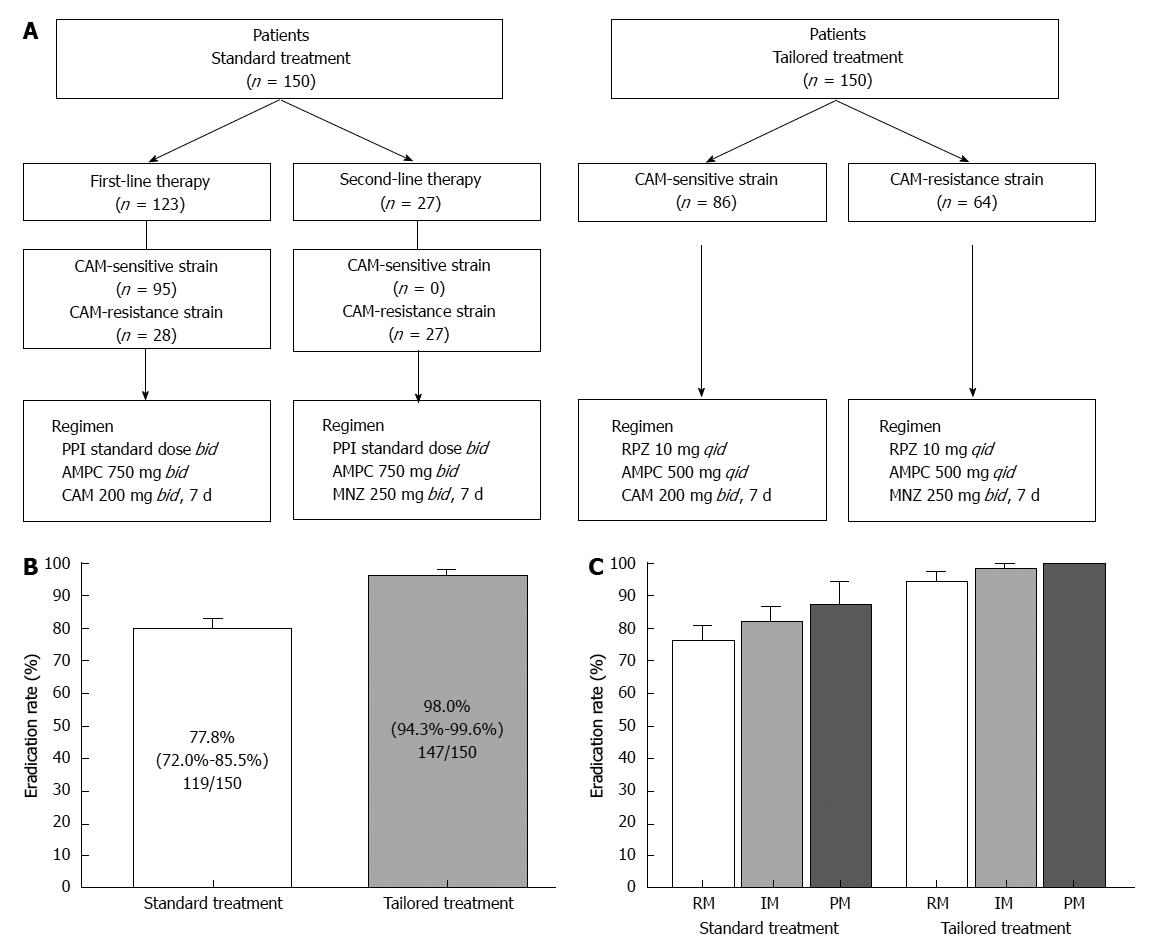
Figure 6 Study design and outcomes.
A: Patients were classified into two treatment regimens: standard treatment group (first- or second-line standard Japanese regimen) and tailored treatment group (based on clarithromycin-susceptibility); B: Eradication rates for the standard and tailored regimens for eradication of Helicobacter pylori; C: Eradication rates for the standard and tailored regimens among different CYP2C19 genotypes. CAM: Clarithromycin; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor; AMPC: Amoxicillin; MNZ: Metronidazole; RPZ: Rabeprazole.
-
Citation: Sugimoto M, Furuta T. Efficacy of tailored
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy based on antibiotic susceptibility andCYP2C19 genotype. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(21): 6400-6411 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i21/6400.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i21.6400