Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2014; 20(13): 3712-3715
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3712
Published online Apr 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3712
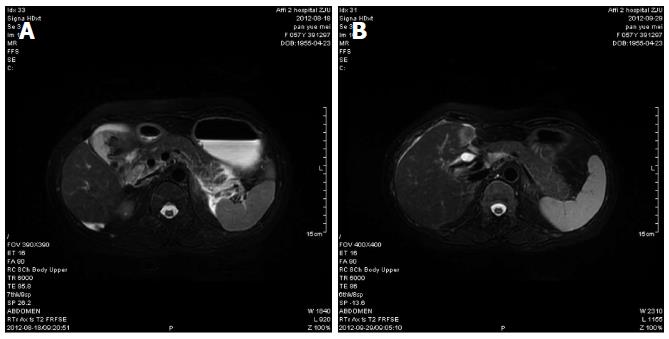
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) revealed pancreatitis, cholecystolithiasis, cholecystitis, and cholangiectasis and abnormal signals that were considered to indicate muddy stone or hematocele in the common bile duct and hepatic duct; B: After treatment, MRCP showed there was little exudation in the gallbladder fossa, and bile ducts in the left liver were thickened.
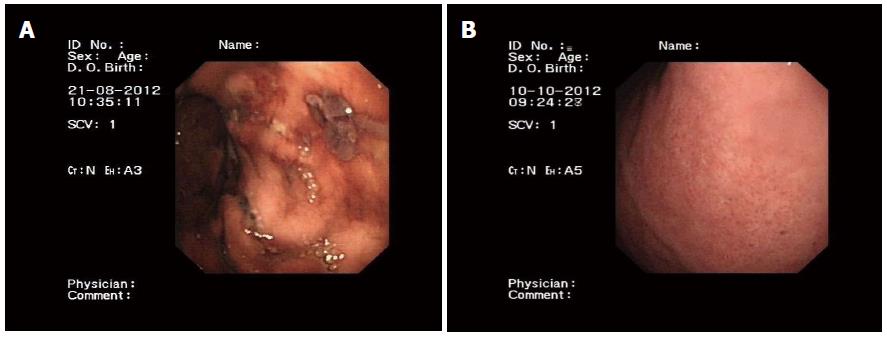
Figure 2 Gastroscopy.
A: Gastroscopy showed multiple gastric ulcers; B: After treatment, gastroscopy revealed chronic superficial gastritis, and no gastric ulcers.
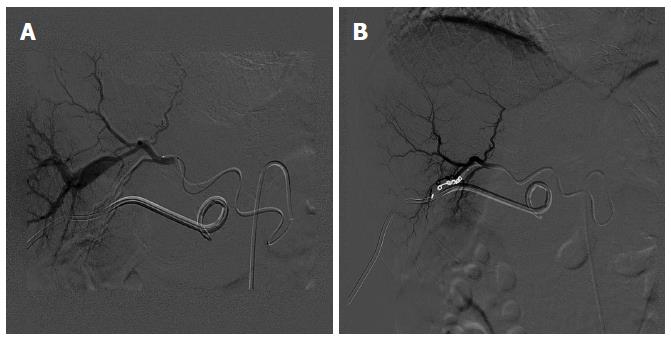
Figure 3 Digital subtraction angiography.
A: Digital subtraction angiography showed obvious arteriovenous fistula of the right liver; B: There was no obvious arteriovenous fistula of the right liver after the hepatic artery was selected and embolized by spring orbs.
- Citation: Zhou HB. Hemobilia and other complications caused by percutaneous ultrasound-guided liver biopsy. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(13): 3712-3715
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i13/3712.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i13.3712