Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2014; 20(11): 3044-3049
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3044
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3044
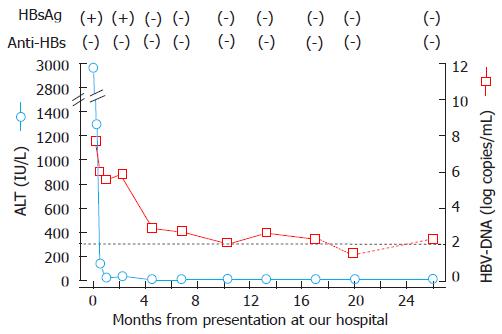
Figure 1 Clinical course of the patient infected with the genotype H strain.
The dotted line indicates the detection limit of HBV-DNA (2.1 log copy/mL); the titer of the HBV-DNA was below the lower limit at 18 mo. HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; Anti-HBs: Antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
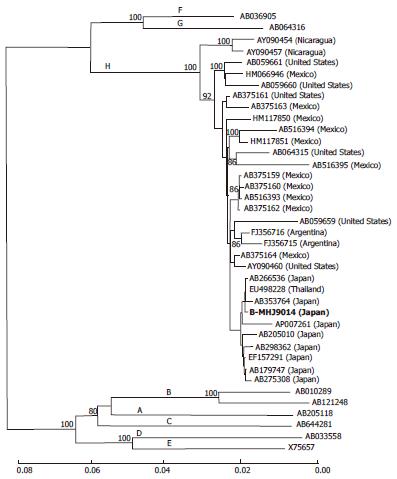
Figure 2 A phylogenetic trees constructed using the neighbor-joining method with the full hepatitis B virus genome sequence of the isolated and reference strains.
The strain isolated in this case (B-MHJ9014) is shown in bold. The horizontal bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions per site. The reference sequences are shown with the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession numbers. The HBV genotypes are indicated on each branch. The bootstrap values (> 80%) are indicated at the nodes as a percentage of the data obtained from 1000 resamplings. HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
- Citation: Yamada N, Shigefuku R, Sugiyama R, Kobayashi M, Ikeda H, Takahashi H, Okuse C, Suzuki M, Itoh F, Yotsuyanagi H, Yasuda K, Moriya K, Koike K, Wakita T, Kato T. Acute hepatitis B of genotype H resulting in persistent infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(11): 3044-3049
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i11/3044.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.3044