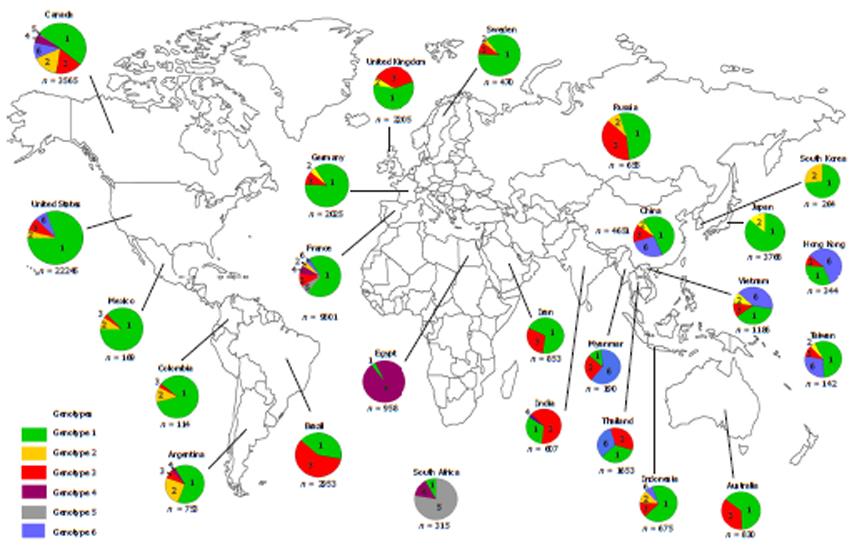
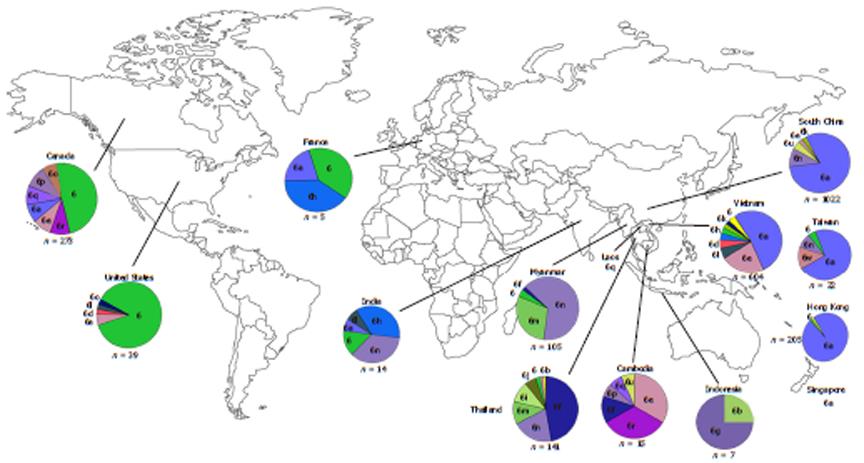
Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2014; 20(11): 2927-2940
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2927
Published online Mar 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2927
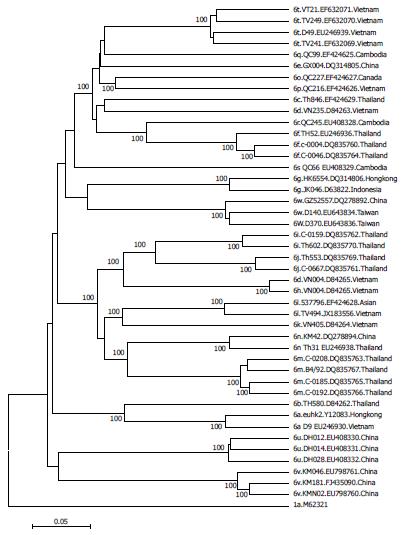
Figure 3 Phylogenetic relationships among subtypes hepatitis C virus-6.
Phylogenetic tree constructed from whole genome sequence of all hepatitis C virus-6 subtypes (subtype 6a to 6w) which was analyzed by K2P model and MEGA version.5. Bootstrap value of 1000 replicates was indicated at each node.
Figure 4 Methods used for genotyping.
The 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) and Core regions targeted by INNO-LiPA (the 5’-UTR only for INNO-LiPA I or both the 5’-UTR and core regions for INNO-LiPA II), sequencing of NS5B are used the standard methods for classifying hepatitis C virus genotype and subtype[5,78].
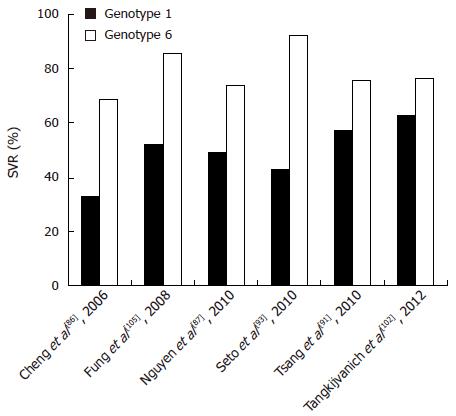
Figure 5 Sustained virological response in genotype 6 vs genotype 1.
SVR: Sustained virological response.
- Citation: Thong VD, Akkarathamrongsin S, Poovorawan K, Tangkijvanich P, Poovorawan Y. Hepatitis C virus genotype 6: Virology, epidemiology, genetic variation and clinical implication. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(11): 2927-2940
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i11/2927.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i11.2927