Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2014; 20(1): 228-234
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.228
Published online Jan 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.228
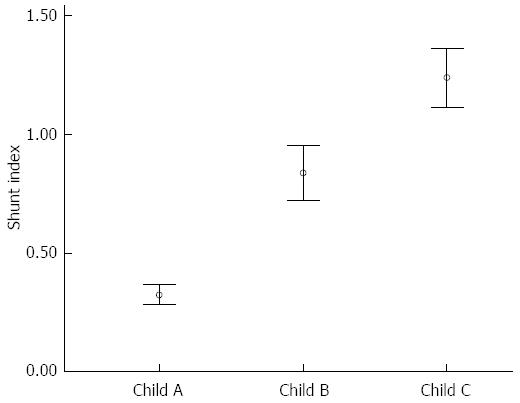
Figure 1 Correlation between Shunt index and Child-Pugh class.
Among Child-Pugh class a patients, the median thallium scan shunt index was 0.31 ± 0.24, among class B patients was 0.82 ± 0.39, and among class C patients was 1.19 ± 0.30. The thallium scan shunt index tended to increase as the Child-Pugh score became higher (P < 0.01). Shunt index: Transrectal thallium portal scan shunt index; Child: Child-Pugh class P < 0.001
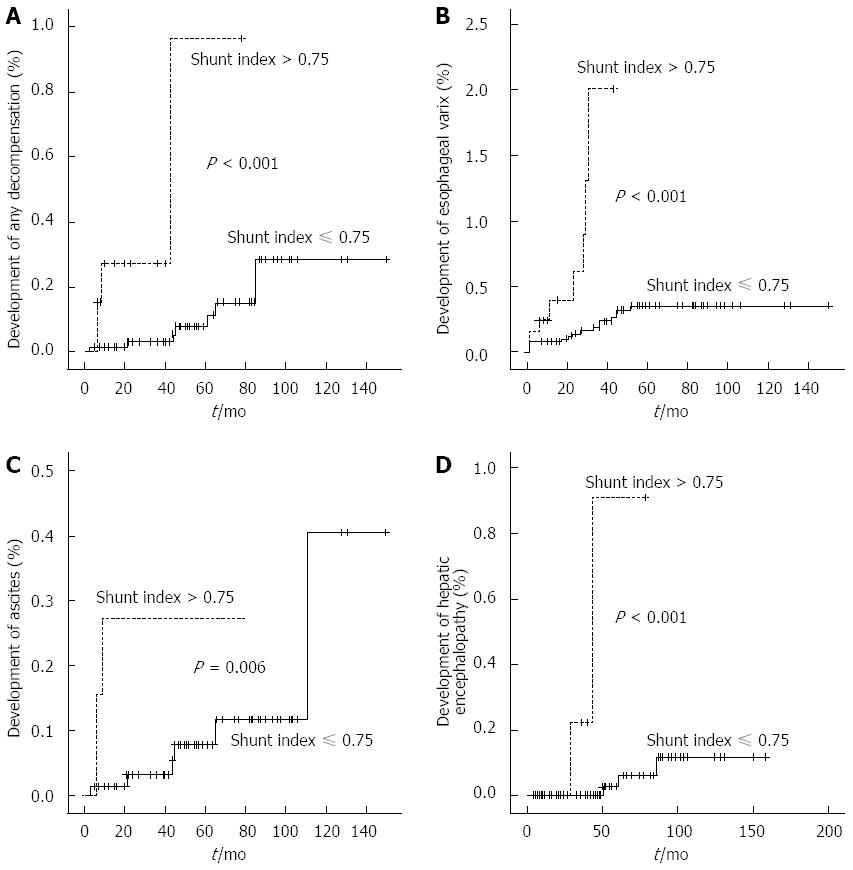
Figure 2 Cumulative incident rate for decompensation, esophageal varix, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy according to shunt index.
Reference value of shunt index was 0.75. Shunt index: Transrectal thallium portal scan shunt index
- Citation: Tae HJ, Jun DW, Choi YY, Kwak MJ, Lee MH. Assessment of risk of complications in cirrhosis using portal thallium scans. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(1): 228-234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i1/228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i1.228