Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 9049-9056
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9049
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9049
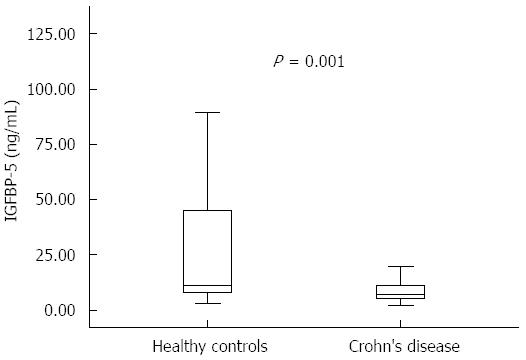
Figure 1 Serum Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 concentrations in Crohn’s disease patients and healthy controls.
Serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) (ELISA) levels were significantly decreased in patients with Crohn’s disease compared to healthy controls (P < 0.001). P value from Mann-Whitney test.
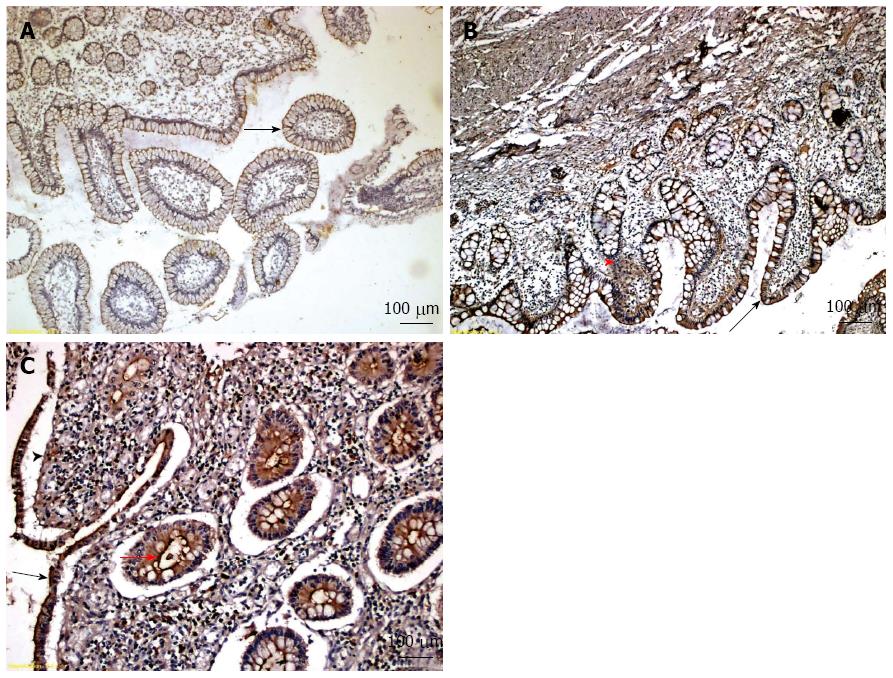
Figure 2 Representative examples of different immunohistochemical staining intensity scores for Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 expression.
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) was diffusely expressed in the intestinal tissue. A: Weak staining (score = 1) (arrow) in epithelial cells in a Crohn’s disease (CD) patient without stricture formation (ileal sample); B: Moderate staining (score = 2) both in epithelial (arrow) and stromal cells (arrowhead) in a CD patient with stricture formation (ileal sample); C: Strong staining (score = 3) in epithelial cells (arrow), stromal cells (arrowhead) and crypt lumen (red arrow) in a CD patient with active disease (colonic sample). Bar = 100 μm. Images were obtained using a light-field microscope, and edited using Adobe Photoshop CS5 (Adobe Systems Incorporated).
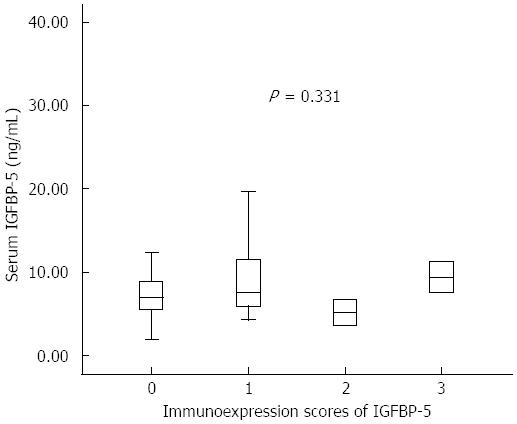
Figure 3 Serum Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 concentrations in patients with different immunohistochemical staining intensity scores for Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 expression.
Serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 (IGFBP-5) concentrations were not significantly different for individuals with absent/very weak, weak, moderate, or strong IGFBP-5 staining intensity scores (P = 0.331). P value from Kruskal-Wallis test.
- Citation: Adali G, Yorulmaz E, Ozkanli S, Ulasoglu C, Bayraktar B, Orhun A, Colak Y, Tuncer I. Serum concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 9049-9056
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/9049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9049