Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 9034-9042
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9034
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9034
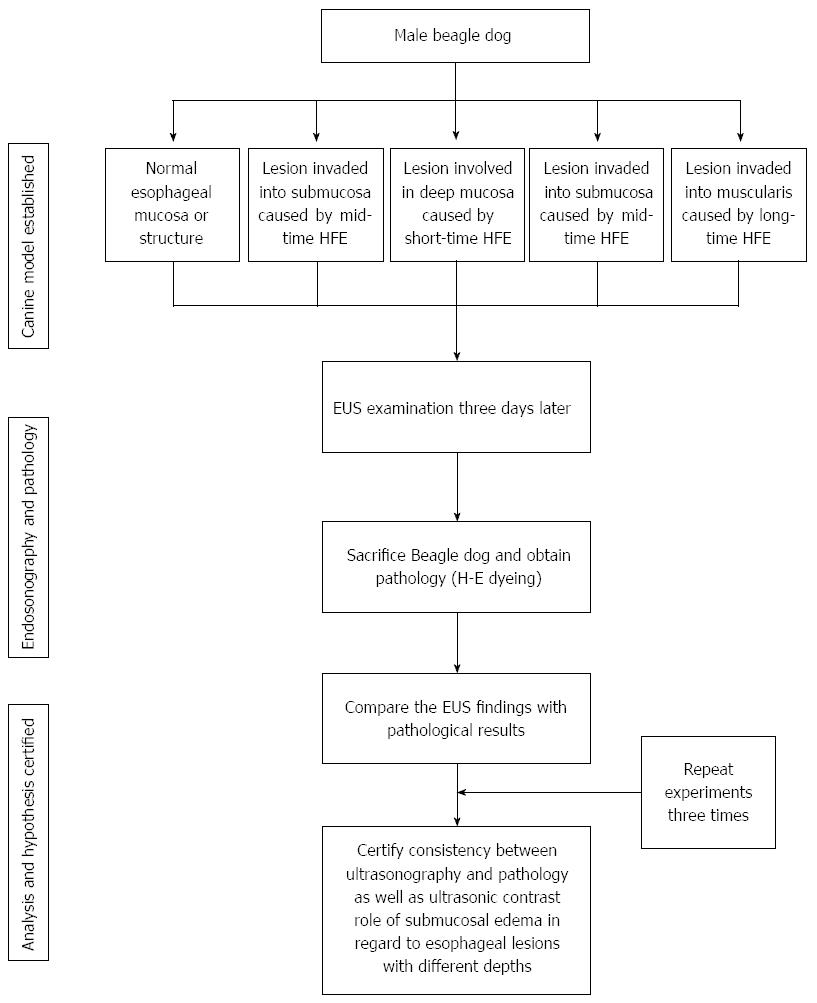
Figure 1 Flow diagram of study protocol.
EUS: Endoscopic ultrasonography; HFE: High frequency electro-coagulation generator.
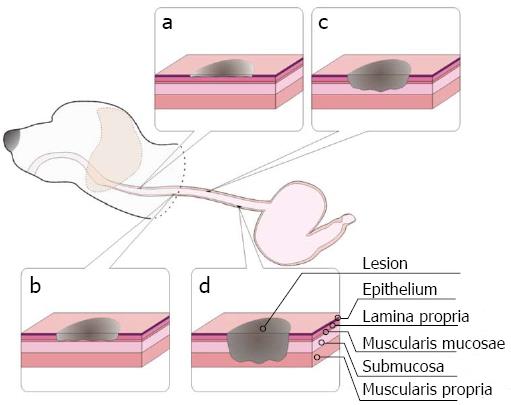
Figure 2 Schematic diagrams of superficial lesions in the esophagus with different depths in a canine model.
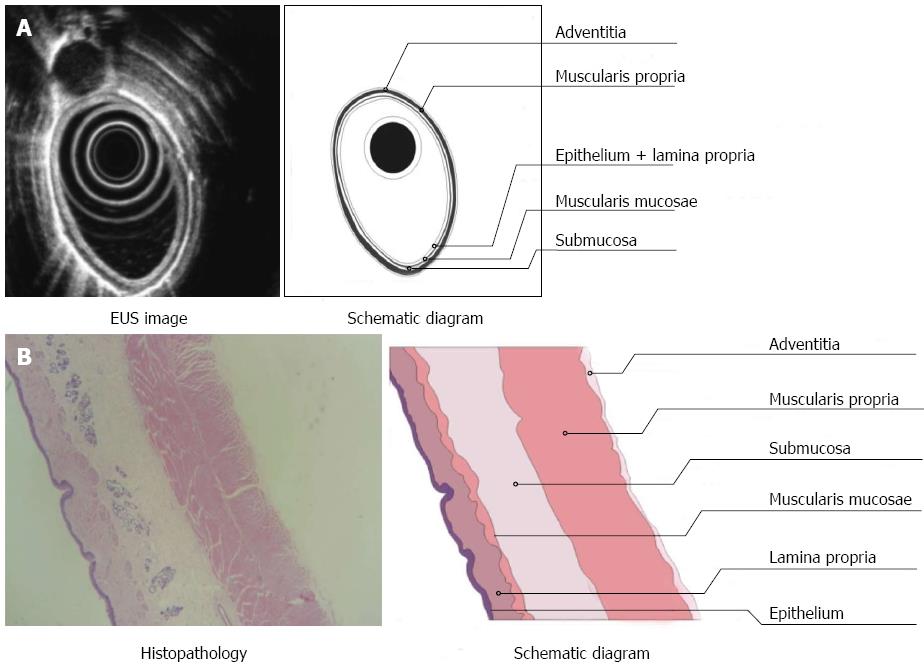
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasonography and tissue examination of the normal esophagus in a beagle dog.
A: The three layers of a normal esophagus, as visualized by endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS); B: Tissue examination showed that the esophageal wall is composed of the mucosa (including squamous epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa), submucosa, and muscularis propria and adventitia.
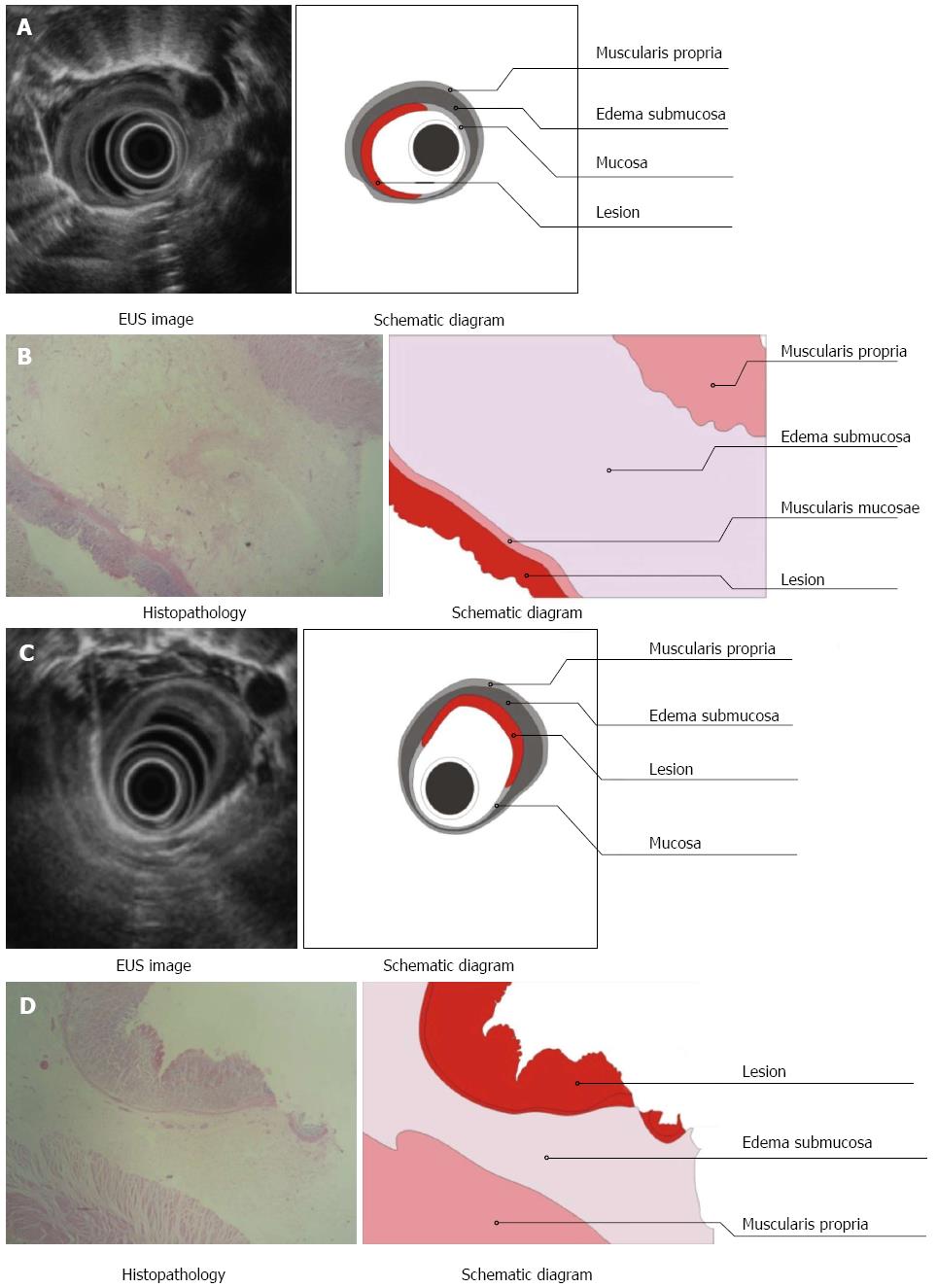
Figure 4 Endoscopic ultrasonography and tissue examination of esophageal lesions located in the superficial mucosa (A, B) and deep mucosa (C, D).
A, C: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) imaging: high echoic lesions located in the mucosa (A) and relatively high echoic lesion (C) located in the mucosa with obvious submucosal edema, as visualized by EUS; B, D: Pathology: tissue examination showed that the lesions were located in the mucosa with complete (B) and incomplete (D) squamous epithelium, intact muscularis mucosa, and obvious submucosal edema.
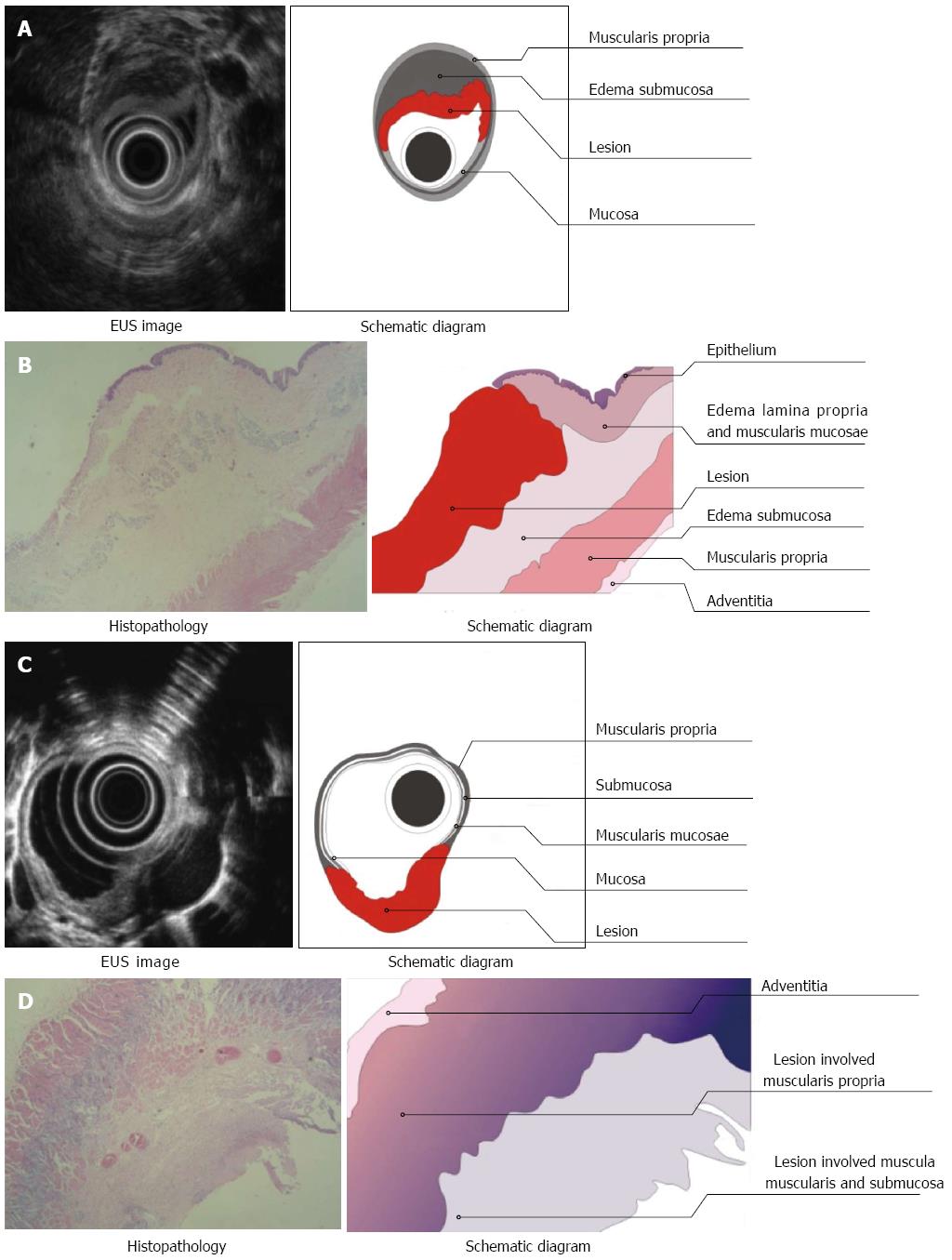
Figure 5 Endoscopy, endoscopic ultrasonography, and tissue examination of an esophageal lesion invading into the submucosa (A, B) and muscularis propria (C, D).
A, C: Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS) imaging: Middle echoic lesion (A) and low echoic lesion (C) invading the submucosa with obvious submucosal edema, as visualized by EUS; B, D: Pathology: Lesion invading into the submucosa (B) and muscularis propria (D) was characterized as squamous epithelium with disappearing muscularis mucosa and submucosal edema, as revealed by pathological examination.
- Citation: Li JJ, He LJ, Shan HB, Wang TD, Xiong H, Chen LM, Xu GL, Li XH, Huang XX, Luo GY, Li Y, Zhang R. Superficial esophageal lesions detected by endoscopic ultrasound enhanced with submucosal edema. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 9034-9042
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/9034.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.9034