Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2013; 19(47): 8831-8849
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8831
Published online Dec 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8831
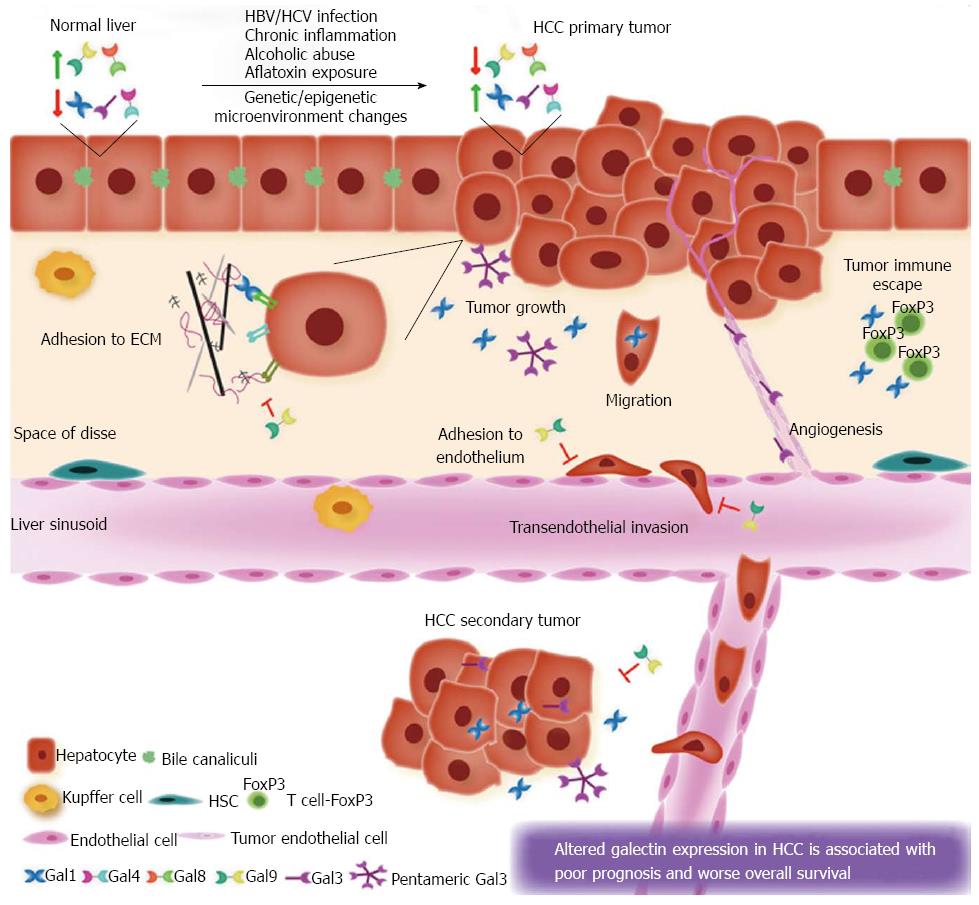
Figure 1 Galectins in hepatocellular carcinoma.
In normal liver, galectin (Gal)-8 and galectin-9 are expressed in hepatocytes whereas galectin-1, galectin-3 and galectin-4 are not detectable. This expression pattern is altered in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) as galectin-1, galectin-3 and galectin-4 are up-regulated, whereas galectin-8 and galectin-9 are down-regulated in transformed hepatocytes. This aberrant expression favors tumor growth and hepatocyte adhesion to extracellular matrix (ECM), migration, adhesion to the endothelium, transendothelial invasion and metastasis. Galectin-3, normally absent in sinusoid endothelial cells, is up-regulated in tumor capillary endothelial cells, probably promoting angiogenesis. Increased expression of galectin-1 and lack of galectin-9 expression also contribute to tumor-immune escape. HBV: Hepatitis B virus; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
- Citation: Bacigalupo ML, Manzi M, Rabinovich GA, Troncoso MF. Hierarchical and selective roles of galectins in hepatocarcinogenesis, liver fibrosis and inflammation of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(47): 8831-8849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i47/8831.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i47.8831