Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2013; 19(45): 8203-8210
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8203
Published online Dec 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8203
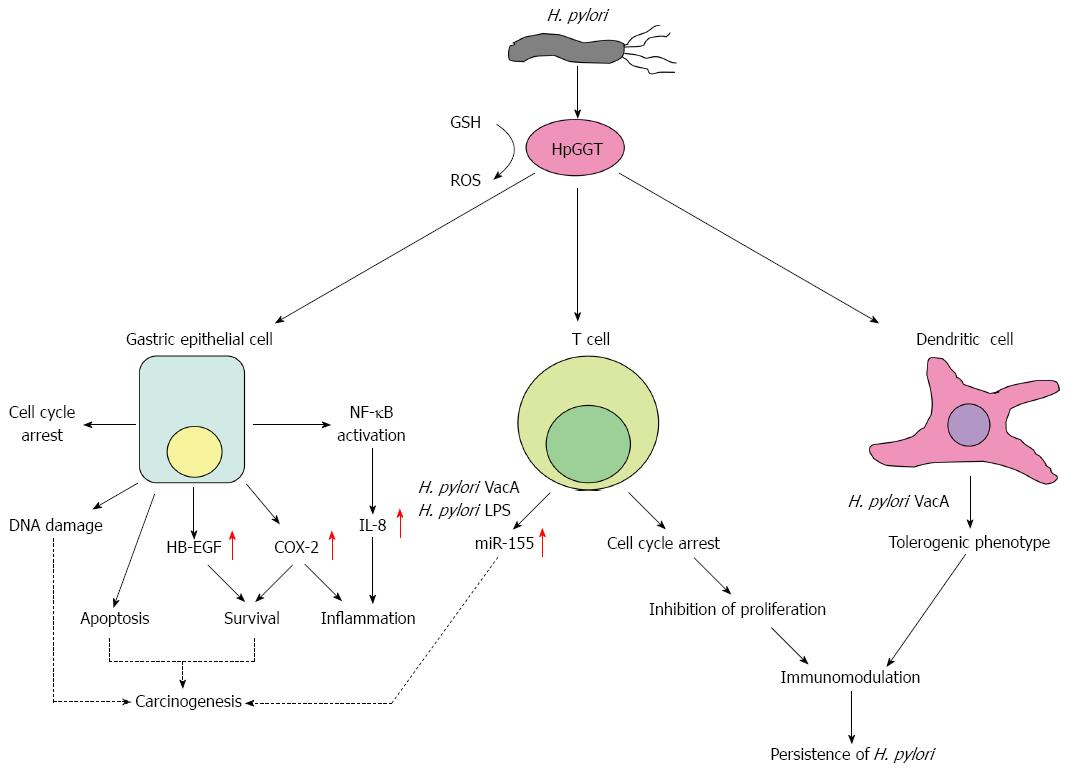
Figure 1 Schematic diagram highlighting important effects of Helicobacter pyloriγ-glutamyl transpeptidase on both gastric epithelial and immune cells and their implications on carcinogenesis and persistence of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucosa.
COX-2: Cyclooxygenase-2; HpGGT: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) γ-glutamyl transpeptidase; GSH: Glutathione; HB-EGF: Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor; IL-8: Interleukin-8; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; miR-155: microRNA-155; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; VacA: Vacuolating cytotoxin. Red arrows indicate upregulation of the respective molecules.
-
Citation: Ling SSM, Yeoh KG, Ho B.
Helicobacter pylori γ-glutamyl transpeptidase: A formidable virulence factor. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(45): 8203-8210 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i45/8203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i45.8203