Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 14, 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
Published online Nov 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374
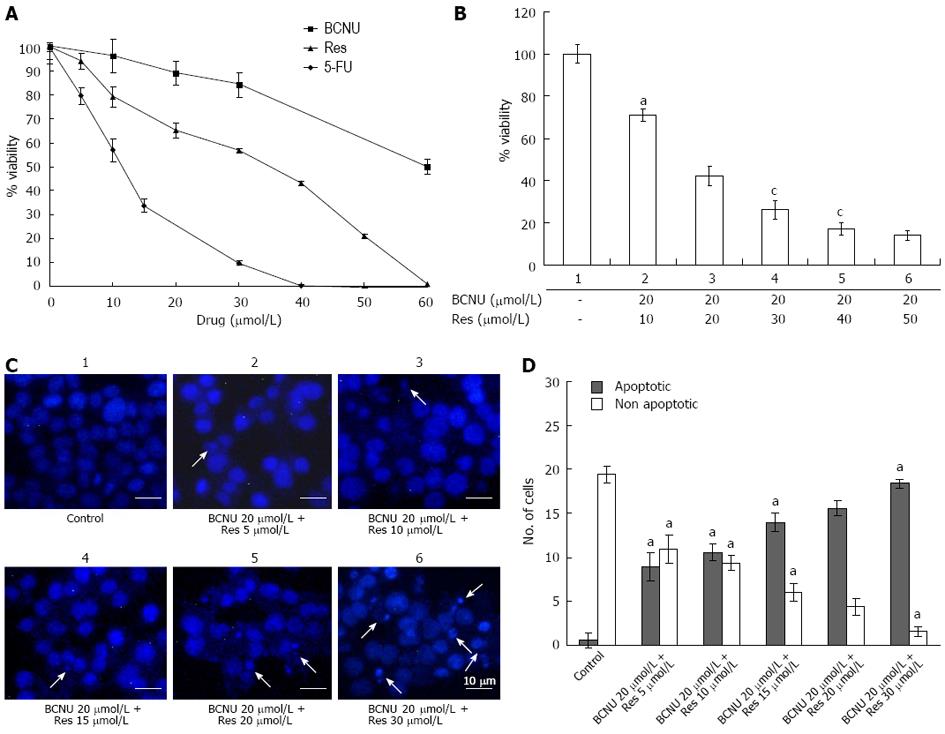
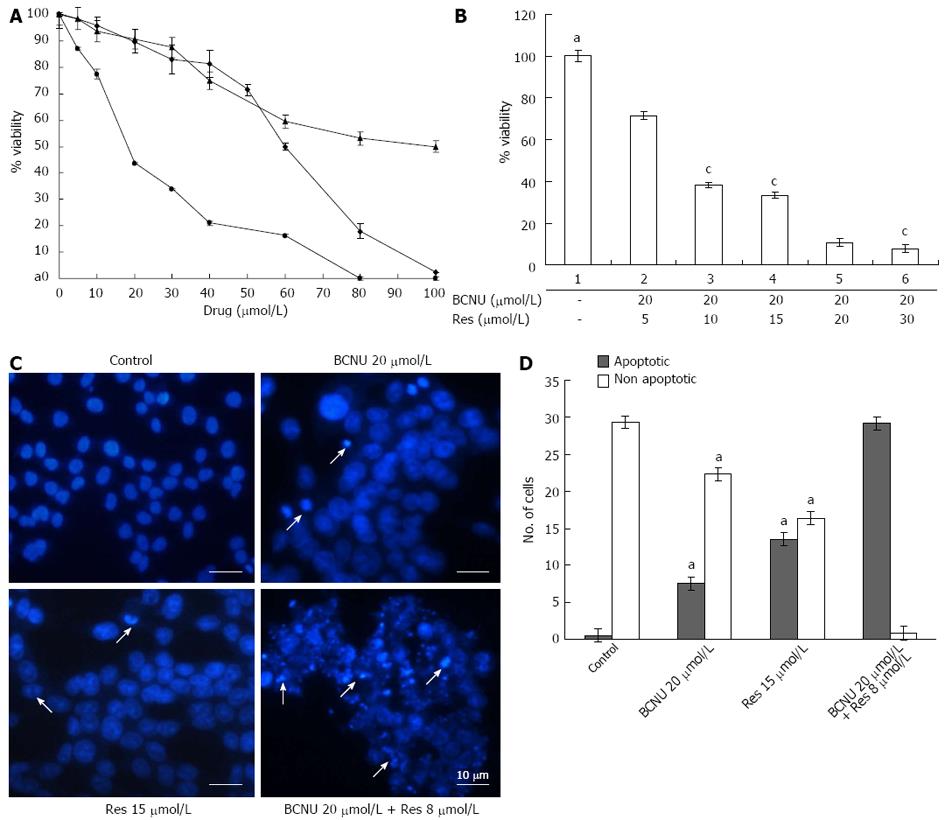
Figure 1 Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and/or resveratrol on HCT-116 colon cancer cells.
A: Anchorage-dependent cell survival of HCT-116 cells after treatment with Res, 5-FU and BCNU; B: Bar diagram representing the % viability of HCT-116 after BCNU+ Res exposure. HCT-116 cells were cultured in 96 well plates and grown to 60%-70% confluence. The cells were then treated with different compounds according to the materials and methods. Data are the mean ± SD of three different experiments. aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res; cP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 50 μmol/L Res; C: Apoptotic nuclei after 4',6'-diamidino-2-phenylindole hydrochloride staining. Images were taken using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon-Eclipse, Japan) at × 40 magnification. Arrows indicate the apoptotic nuclei. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; D: A graphical representation of apoptotic nuclei. aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea.
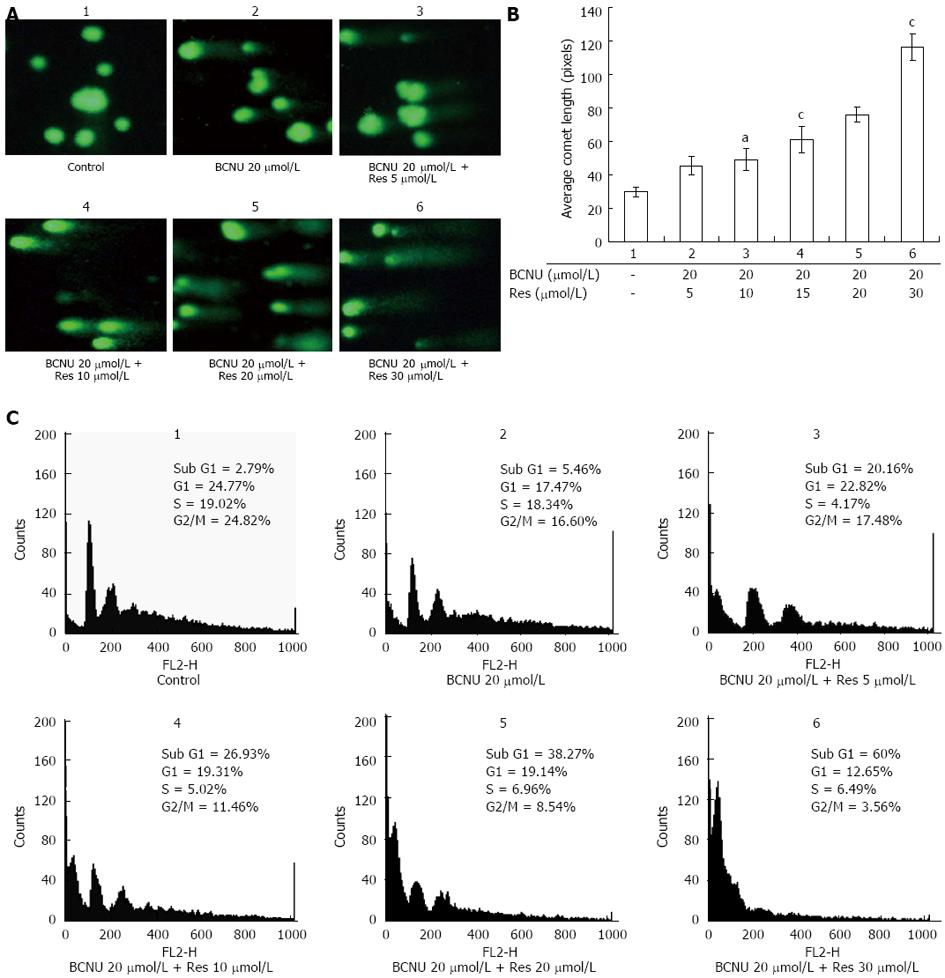
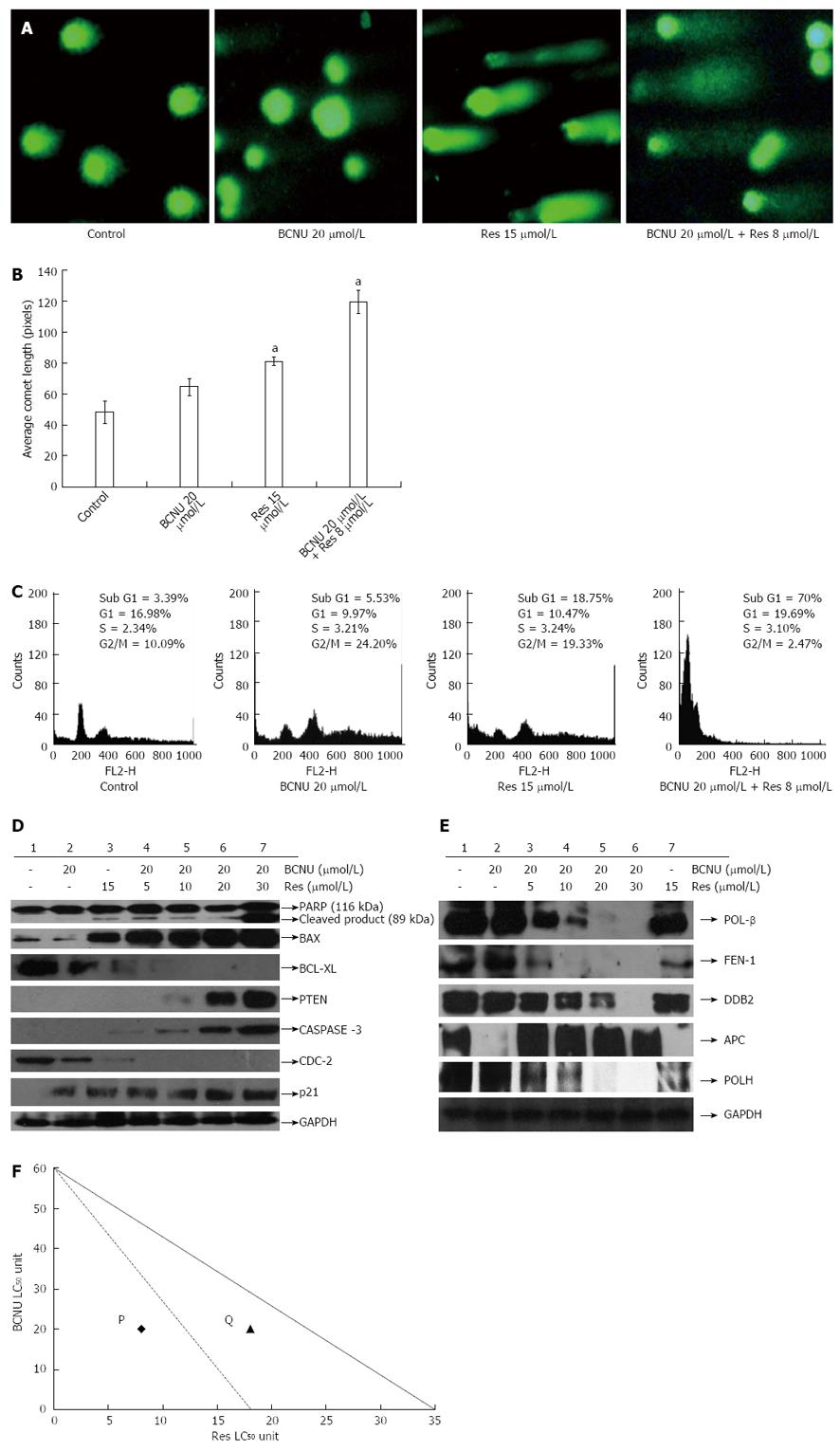
Figure 2 Regulation of cell cycle and genotoxicity of HCT-116 cells after 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and/or resveratrol treatments.
A: Comet assay showing the DNA damaging effect of the drugs in HCT-116 cells. Images were taken using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon-Eclipse, Japan) at × 20 magnification. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; B: Bar diagram represents the average comet - length in pixels as obtained from TriTek CometScore™ software. Data are the mean ± SD of three different experiments, aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 5 μmol/L Res; cP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res; C: Effect of the drugs on cell cycle regulation. After treatment as mentioned in the materials and method fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis was performed and the DNA content of the cell was measured by Cell Quest Software (Becton and Dickinson, CA). Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea.
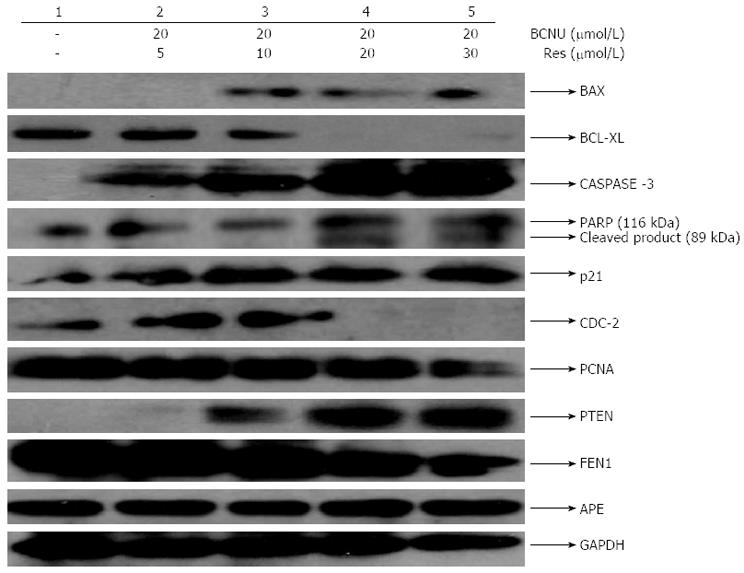
Figure 3 Combined effects of 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and resveratrol on various cellular markers in HCT-116 colon cancer cells.
Expression pattern of apoptotic, DNA damage/repair and cell cycle regulatory proteins after drug treatment. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments. Glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) served as a loading control. BAX: Bcl-2-associated X protein; BCL-XL: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; PTEN: Phosphatase and tensin homolog; FEN1: Flap endonuclease 1; CDC-2: Cyclin dependent kinase-1; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea; APE: Apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) endonuclease.
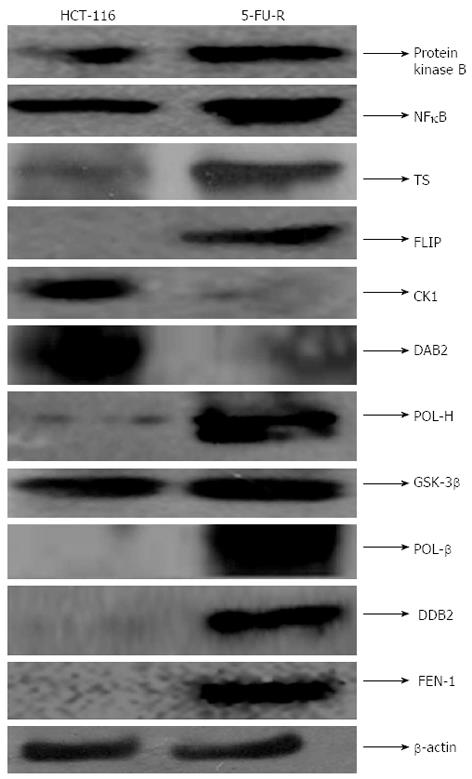
Figure 4 Characterization of 5-fluorouracil-resistant cells.
The cell lysates of HCT-116 and 5-FU-R cells were immunoblotted using specific antibody. The lower panel shows the expression of β-actin, which was the loading control (to ensure the same amount of protein loaded in each lane). Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments. CK1: Casein kinase 1; FLIP: FLICE-like inhibitory protein; NFκB: nuclear factor κB; POL-β: DNA polymerase beta; POLH: DNA polymerase eta; protein Flap FEN1: Endonuclease 1; DDB2: DNA damage-binding protein 2; 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea; TS: Thymidylate synthase.
Figure 5 Anti-proliferative and apoptotic effect of 3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and/or resveratrol on 5-fluorouracil-R cells.
A: Anchorage-dependent cell survival of 5-FU-R cells after treatment with 5-FU, Res and BCNU; B: Bar diagram representing the % viability of 5-FU-R cells after BCNU + Res exposure. Data are the mean ± SD of three different experiments, aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 5 μmol/L Res; cP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 20 μmol/L Res; C: Apoptotic nuclei after DAPI staining. Images were taken using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon-Eclipse, Japan) at ×40 magnification. An arrow indicates the apoptotic nuclei. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; D: A graphical representation of apoptotic nuclei, aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU + 8 μmol/L Res. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea.
Figure 6 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea and Res synergistically increased apoptosis in 5-fluorouracil-resistance cells.
A: Comet assay. Images were taken using a fluorescent microscope (Nikon-Eclipse, Japan) at × 20 magnification. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; B: Bar diagram representing the average comet score of the treated and untreated 5-FU-R cells in pixels, as obtained from TriTek CometScore™ software. Data are the mean ± SD of three different experiments, aP < 0.05 vs 20 μmol/L BCNU; C: Regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis by BCNU, Res and their combination in 5-FU-R cells. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis was done after the desired treatment and then the DNA content was measured by Cell Quest Software. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; D, E: Western blotting of 5-FU-R cell lysate after treatment with BCNU and Res individually, as well as in combination. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase was used as the loading control. Data are the representation of one of the replicates of three different experiments; F: Isobolograms for combinations of BCNU and Res in HCT-116 and 5-FU-R cells. The bold line represents the isobologram of BCNU and Res in HCT-116 and dotted lines represents the isobologram of BCNU and Res in 5-FU-R cells. The point P and Q represent the 50% cell death of the combined drug in case of 5-FU-R and HCT-116 cells, respectively. 5-FU: 5-fluorouracil; Res: Resveratrol; BCNU: 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea.
- Citation: Das D, Preet R, Mohapatra P, Satapathy SR, Kundu CN. 1,3-Bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea enhances the inhibitory effect of Resveratrol on 5-fluorouracil sensitive/resistant colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(42): 7374-7388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i42/7374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i42.7374