Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 28, 2013; 19(32): 5212-5226
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5212
Published online Aug 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5212
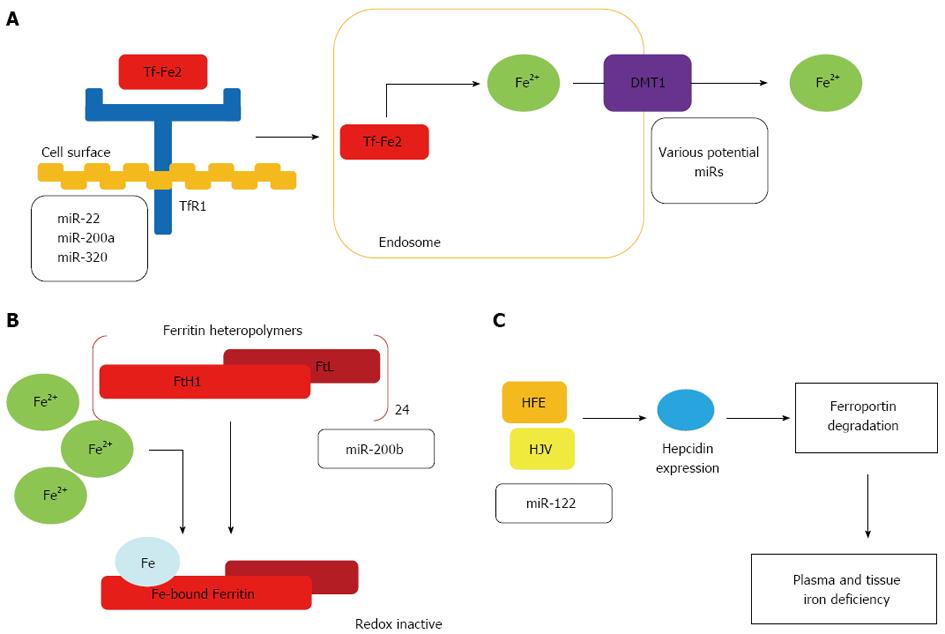
Figure 1 Effect of microRNAs on iron uptake, storage, and systemic regulation.
A: Iron-bound transferrin (Tf-Fe2) binds to the transferrin receptor TfR1 which is regulated by microRNA (miR)-22, miR-200a and miR-320. The complex is endocytosed leading to release of iron, its reduction to Fe2+ and transport to the cytoplasm via DMT1 which may be regulated by various miRNAs; B: miR-200b regulates ferritin heavy (FtH1) and light (FtL) chains. Ferritin polymers containing 24 subunits detoxify excess iron via FtH1’s ferroxidase activity and store intracellular iron; C: Levels of human haemochromatosis (HFE) protein and hemojuvelin (HJV) are regulated by miR-122, the levels of which are decreased in hereditary haemochromatosis. Reciprocal increases in HFE and HJV, in turn, enhance expression of hepcidin leading to decreased iron absorption due to degradation of ferroportin. DMT: Divalent metal transporter.
- Citation: Greene CM, Varley RB, Lawless MW. MicroRNAs and liver cancer associated with iron overload: Therapeutic targets unravelled. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(32): 5212-5226
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i32/5212.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i32.5212