Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2013; 19(27): 4334-4343
Published online Jul 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4334
Published online Jul 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4334
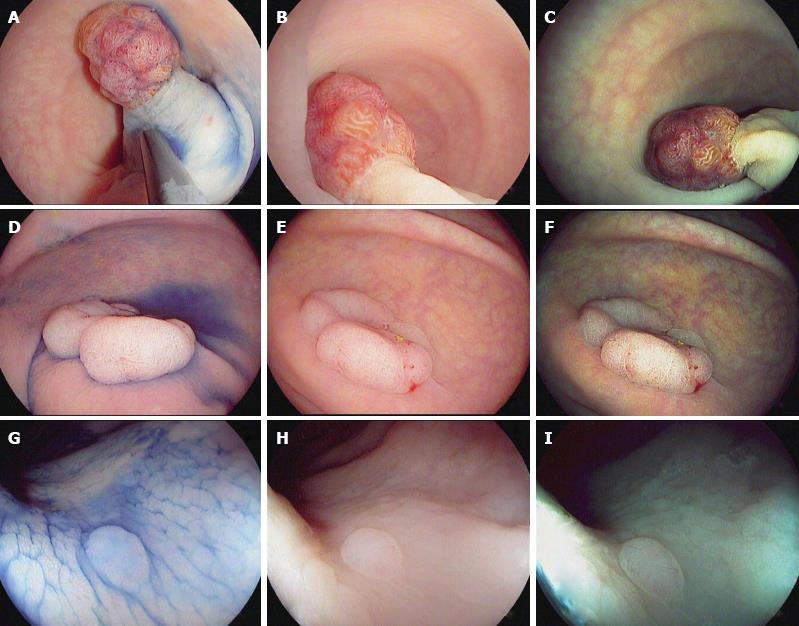
Figure 1 Characterization of colorectal polyps using chromoendoscopy with indigo carmine 0.
4% (A, D and G) and high-definition i-scan, surface enhancement (B, E and H)/tone enhancement (C, F and I), the i-scan classification for endoscopic diagnosis. A-C: 20 mm sized pedunculated polyp (Paris Ip). Image enhanced endoscopy shows reddish color, prominent vessels and a type IV pit pattern of the epithelial surface. Histopathology showed a tubulovillous adenoma with low-grade dysplasia; D-F: 40 mm sized non-polypoid (Paris IIa) lesion. Image enhanced endoscopy shows reddish color, dilated, irregular vessels and a type IV pit pattern of the epithelial surface. Histopathology showed a tubulovillous adenoma with high-grade dysplasia; G-I: 3 mm sized non-polypoid (Paris IIa) lesion. Image enhanced endoscopy shows pale color, isolated, lacy vessels and a type II pit pattern. Histopathology showed a hyperplastic polyp.
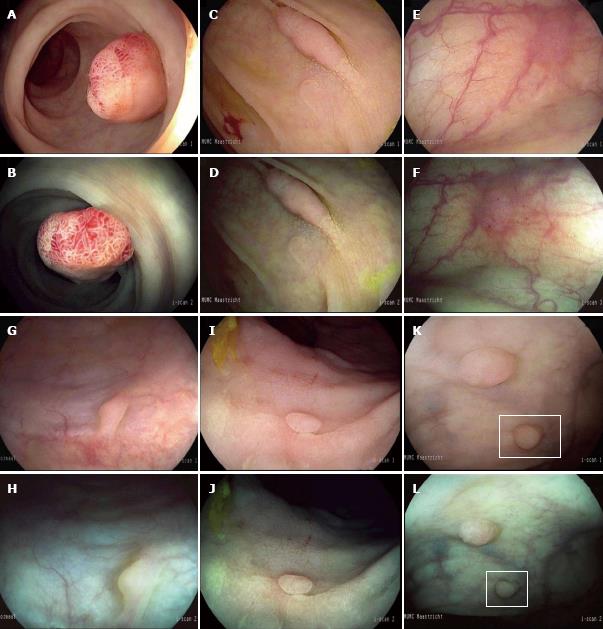
Figure 2 Endoscopic features of non-adenomatous and adenomatous polyps.
High-definition (HD) i-scan surface enhancement (SE) (A) and tone enhancement (TE) (B) of a 12 mm pedunculated polyp located in the rectum characterized by a reddish color, prominent vessels and a branch-like (type IV) pit pattern. All endoscopists diagnosed this lesion as adenomatous with high confidence. Histopathology showed a tubulovillous adenoma with low-grade dysplasia. HD i-scan SE (C) and TE (D) of a 20 mm non-polypoid lesion in the ascending colon characterized by a reddish color, irregular vessels and a tubular (type IIIs) pit pattern. Adenomatous histology was predicted by all endoscopists with high confidence. Histopathology showed a tubular adenoma with low-grade dysplasia. HD i-scan SE (E) and TE (F) of a 4 mm non-polypoid lesion located in the proximal colon characterized by a reddish color, surface epithelium different from the surrounding mucosa and indiscrete borders while the vascular pattern could not be clearly observed. Polyp histology was predicted with low confidence by 6 of the 11 endoscopists. Histopathology showed a tubular adenoma with low grade dysplasia. SE (G) and TE (H) of a 3 mm sessile lesion in the sigmoid characterized by a pale color, no vessels and no definite pit pattern. Non-adenomatous histology was predicted with high confidence by 10 of the 11 endoscopists. Histopathology showed normal mucosa. SE (I) and TE (J) of a 3 mm non-polypoid lesion in the rectum characterized by a pale color, no vessels and round pits of uniform size. Non-adenomatous histology was predicted with high confidence by all endoscopists. Histopathology showed a hyperplastic polyp. SE (K) and TE (L) of a 3 mm sessile lesion in the rectum characterized by a pale color and epithelium similar to the adjacent mucosa while the surface pattern and vessel pattern are unclear. Histopathology was predicted with low confidence by 5 out of 11 endoscopists. Histopathology showed a hyperplastic polyp.
- Citation: Bouwens MW, de Ridder R, Masclee AA, Driessen A, Riedl RG, Winkens B, Sanduleanu S. Optical diagnosis of colorectal polyps using high-definition i-scan: An educational experience. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(27): 4334-4343
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i27/4334.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4334