Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2013; 19(27): 4300-4308
Published online Jul 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4300
Published online Jul 21, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4300
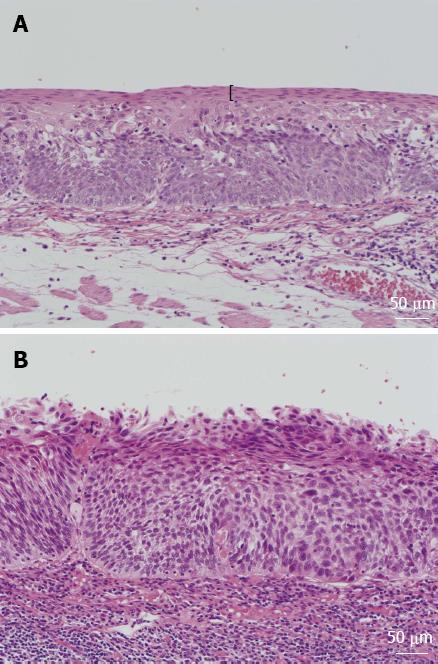
Figure 1 Histologic findings of esophageal lesions.
A: Esophageal lesion with keratinous layers, shown by black parentheses; B: Esophageal lesion without keratinous layers.
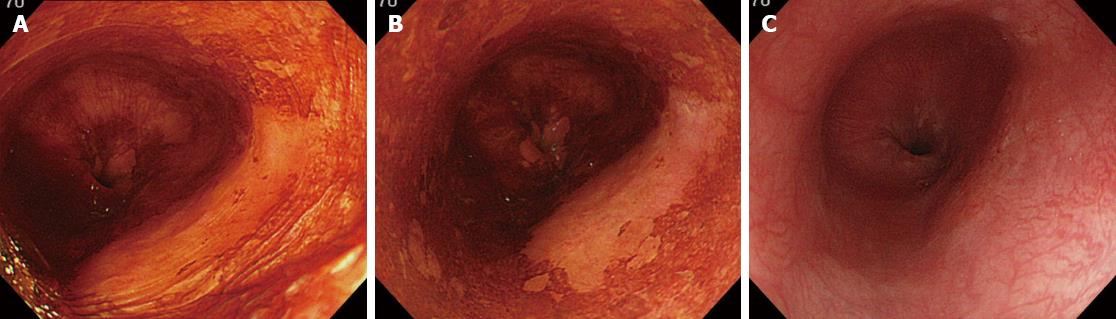
Figure 2 Endoscopic image of type IIc esophageal cancer.
A: Endoscopic image of type IIc esophageal cancer immediately after iodine staining; B: Endoscopic image of type IIc esophageal cancer 2 min after iodine staining. The pink-color sign is observed on the right side of the lesion; C: Endoscopic image of type IIc esophageal cancer 3 min after sodium thiosulfate spraying.
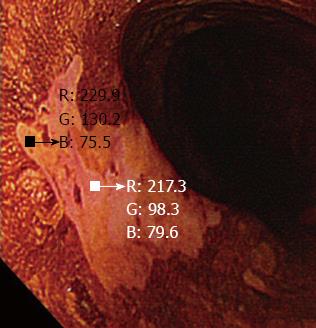
Figure 3 A small region of interest was chosen in both the pink-color sign positive and pink-color sign negative areas.
These regions of interest were carefully chosen to be of similar size in each area. The red-green-blue components of each region of interest were calculated using Image J software.
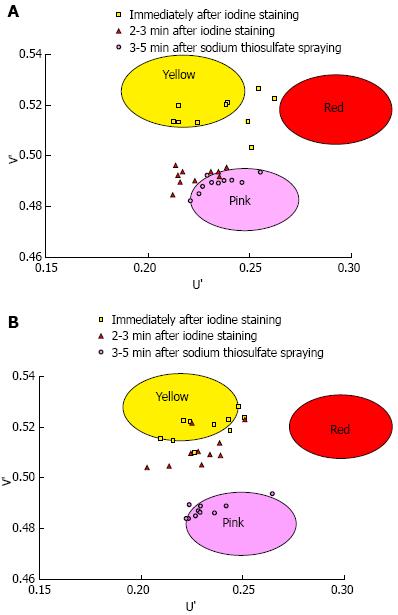
Figure 4 The U’ and V’ values of the pink-color sign positive mucosa and negative mucosa in the early, late and final phases were plotted on a color diagram.
A: Pink-color sign positive mucosa; B: Pink-color sign negative mucosa.
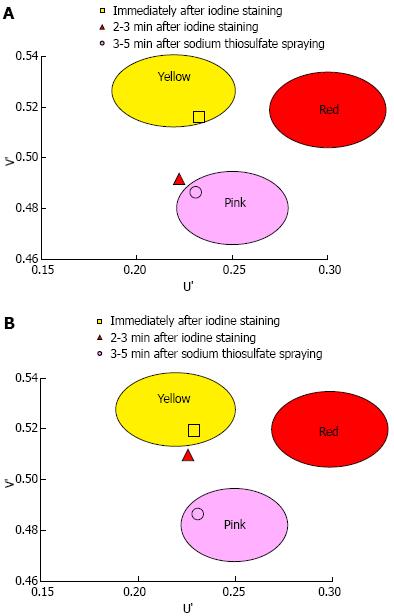
Figure 5 Mean U’ and V’ values of the mucosa in the early, late and final phases were plotted on a color diagram.
A: Pink-color sign positive mucosa had a lower mean V’ value in the late phase (pinkish color) than in the early phase (yellowish color), suggesting that the pink-color sign positive mucosa underwent a color change from yellow to pink. The mucosa had similar mean U’ and V’ values in the late and final phases, suggesting that the color of pink-color sign positive mucosa in the late stage was similar to the color of mucosa after complete fading of iodine staining; B: Pink-color sign negative mucosa had similar mean U’ and V’ values in the early and late phases (yellowish color), suggesting that pink-color sign negative mucosa did not change in color during this time period.
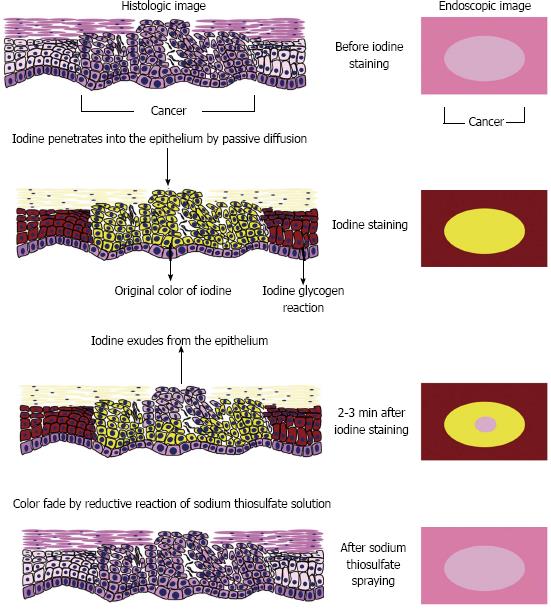
Figure 6 Speculated mechanism of the pink-color sign.
- Citation: Ishihara R, Kanzaki H, Iishi H, Nagai K, Matsui F, Yamashina T, Matsuura N, Ito T, Fujii M, Yamamoto S, Hanaoka N, Takeuchi Y, Higashino K, Uedo N, Tatsuta M, Tomita Y, Ishiguro S. Pink-color sign in esophageal squamous neoplasia, and speculation regarding the underlying mechanism. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(27): 4300-4308
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i27/4300.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i27.4300