Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2013; 19(26): 4146-4154
Published online Jul 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4146
Published online Jul 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4146
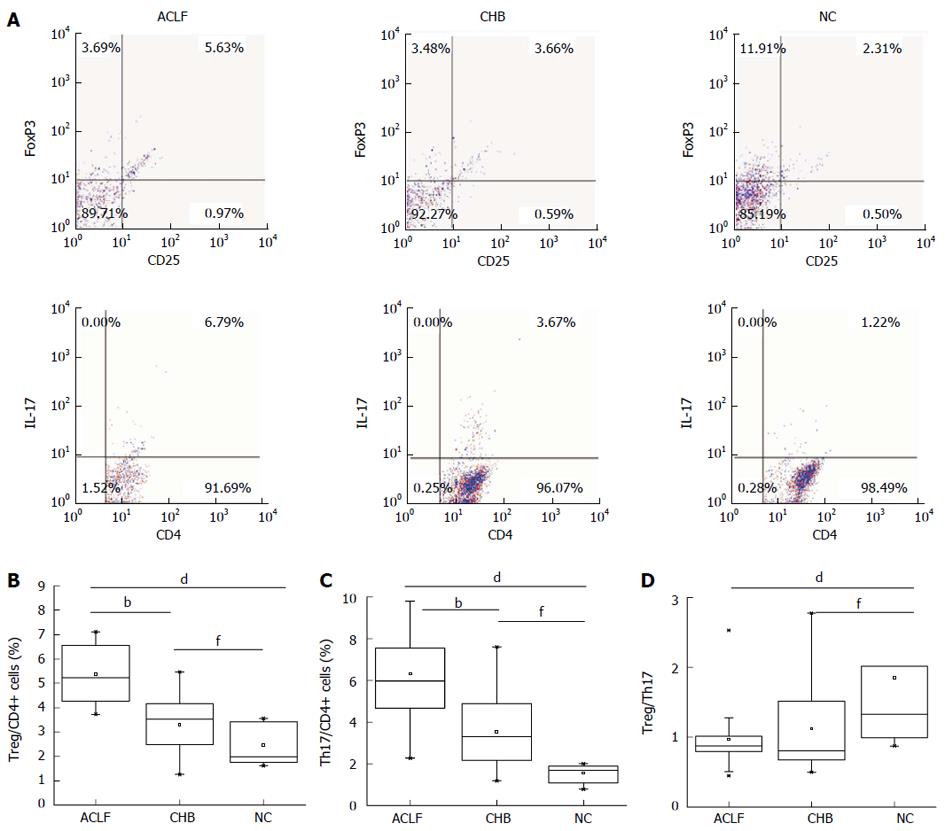
Figure 1 Percentages of T helper 17 cells and regulatory T cells, and the ratio of regulatory T cells to T helper 17 cells in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure, chronic hepatitis B, and normal control groups.
Typical four-quadrant graphs of CD25+FoxP3+ cells [regulatory T (Treg)] and IL17+ cells [T helper 17 (Th17)] in CD4+ cells were divided into three groups (A). The proportion of Treg cells (B) and Th17 cells (C) among CD4+ cells, and the Treg cell to Th17 cell ratios (D) were shown as box plot graphs. Acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) vs chronic hepatitis B group (CHB) bP < 0.01; ACLF vs normal control group (NC) dP < 0.01; CHB vs NC fP < 0.01.
Figure 2 Correlation between T helper 17 cells and regulatory T cells counts and clinical parameters in hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure group.
The percentage of regulatory T (Treg) cells was significantly correlated with alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (A), total bilirubin (TBIL) (B), and international normalized ratio (INR) (C). The percentage of T helper 17 (Th17) cells was significantly correlated with ALT (D), TBIL (E), and Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) scores (F).The percentage of Treg cells was significantly correlated with that of Th17 cells (G).
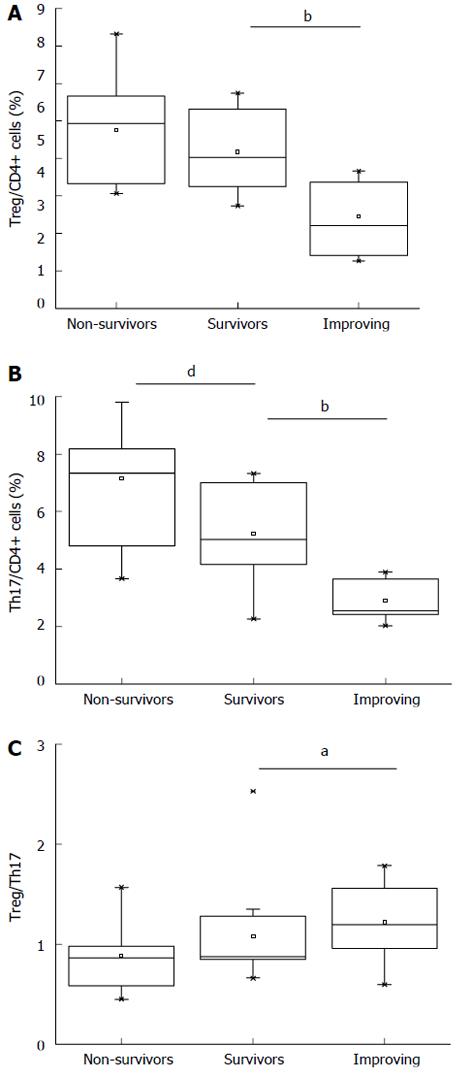
Figure 3 Comparison of regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cell counts, and the regulatory T cell to T helper 17 cell ratio between acute-on-chronic liver failure survivors and non-survivors, as well as those during the peak of acute-on-chronic liver failure severity (total bilirubin peak) and those during the 8th week of follow-up.
Regulatory T (Treg) cell counts (A), T helper 17 (Th17) cell counts (B), and the Treg cell to Th17 cell ratios (C) of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF) non-survivors, as well as those of ACLF survivors during the total bilirubin (TBIL) peak and during the 8th week of follow-up. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the 8th week of follow-up in ACLF survivors, dP < 0.01 vs non-survivors. Non-survivors: The non-survivors in ACLF group; Survivors: The survivors in ACLF group during the TBIL peak; Improving: The survivors in ACLF group during the 8th week of follow-up.
Figure 4 Changes in regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cell counts, and regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cell ratios of acute-on-chronic liver failure survivors.
Changes in regulatory T (Treg) cell counts (A), T helper 17 (Th17) cell counts (B), and the Treg cell to Th17 cell ratio (C) of six acute-on-chronic liver failure survivors (5 males and 1 female).
- Citation: Niu YH, Yin DL, Liu HL, Yi RT, Yang YC, Xue HA, Chen TY, Zhang SL, Lin SM, Zhao YR. Restoring the Treg cell to Th17 cell ratio may alleviate HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(26): 4146-4154
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i26/4146.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i26.4146