Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2013; 19(25): 3969-3979
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969
Published online Jul 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969
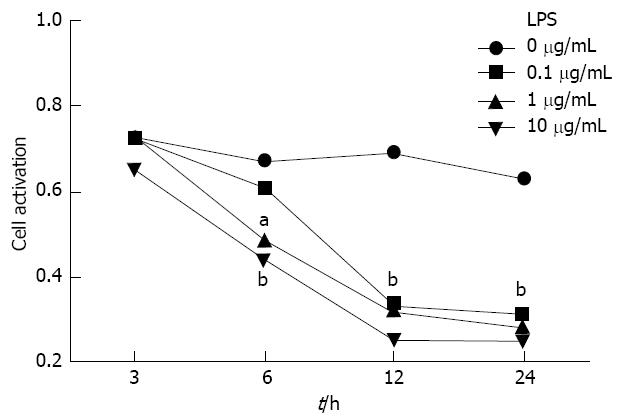
Figure 1 The optimal dose and duration of lipopolysaccharide stimulation were determined using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide method.
The cell survival rate was determined after incubation with 0 (saline) and 0.1, 1 and 10 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 3, 6, 12 and 24 h. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs the saline group.
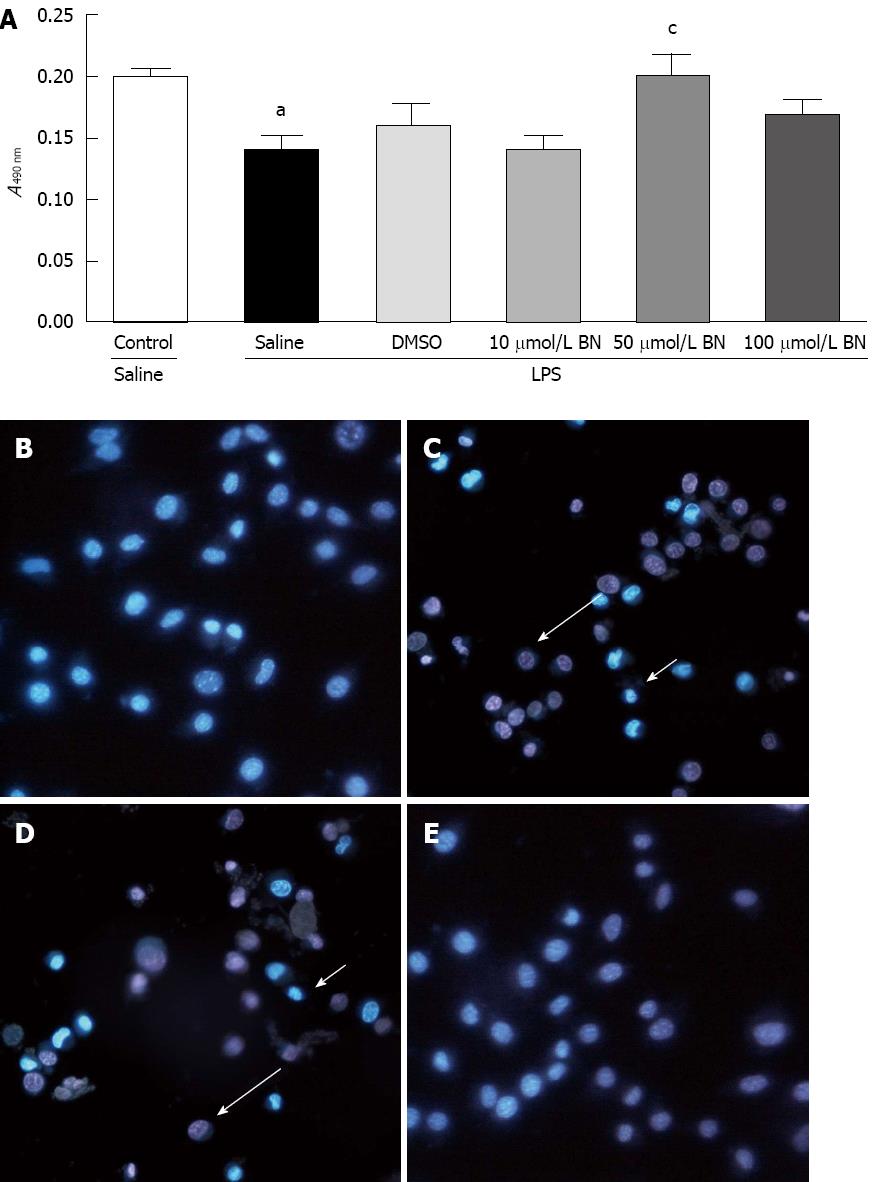
Figure 2 The dose effect of BN52021 on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation was determined by the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide method and Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide staining.
MS1 cell activity at A490 nm was significantly decreased 24 h after administration of 10 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS) vs the control group (aP < 0.05). Pretreatment with BN52021 for 20 min before incubation with LPS significantly improved the MS1 cell activity at A490 nmvs the group that received LPS treatment only when its concentration reached 50 μmol/L (cP < 0.05) (A). Pretreatment with 50 μmol/L BN52021 for 20 min before incubation with LPS significantly improved MS1 cell activity vs the LPS + saline group, and the LPS + dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) group as determined Hoechst 33342/propidium iodide staining (B, C, D and E). The arrows indicate the apoptosis (short) and necrosis (long) of the cells.
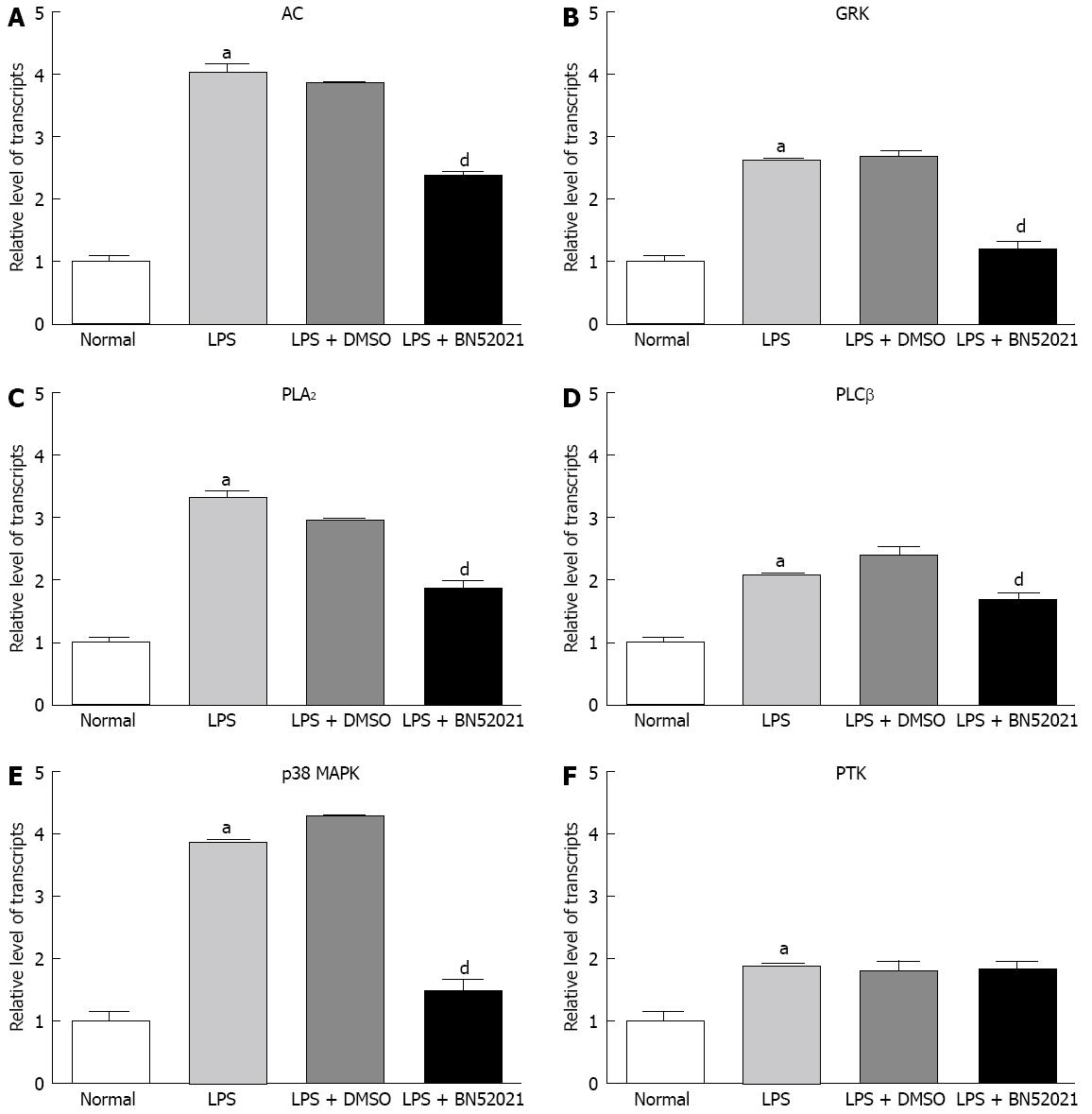
Figure 3 The effect of BN52021 on platelet-activating factor receptor signaling molecules at the mRNA level under lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.
The mRNA level of adenylate cyclase (AC) (A), G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRK) (B), phospholipase A2 (PLA2) (C), phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) (D), p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) (E) and protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) (F) was up-regulated after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. The up-regulation of AC, GRK, p38 MAPK, PLCβ and PLA2 mRNA was significantly suppressed by BN52021 except for that of PTK. aP < 0.05 vs control; dP < 0.01 vs the LPS + dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) groups.
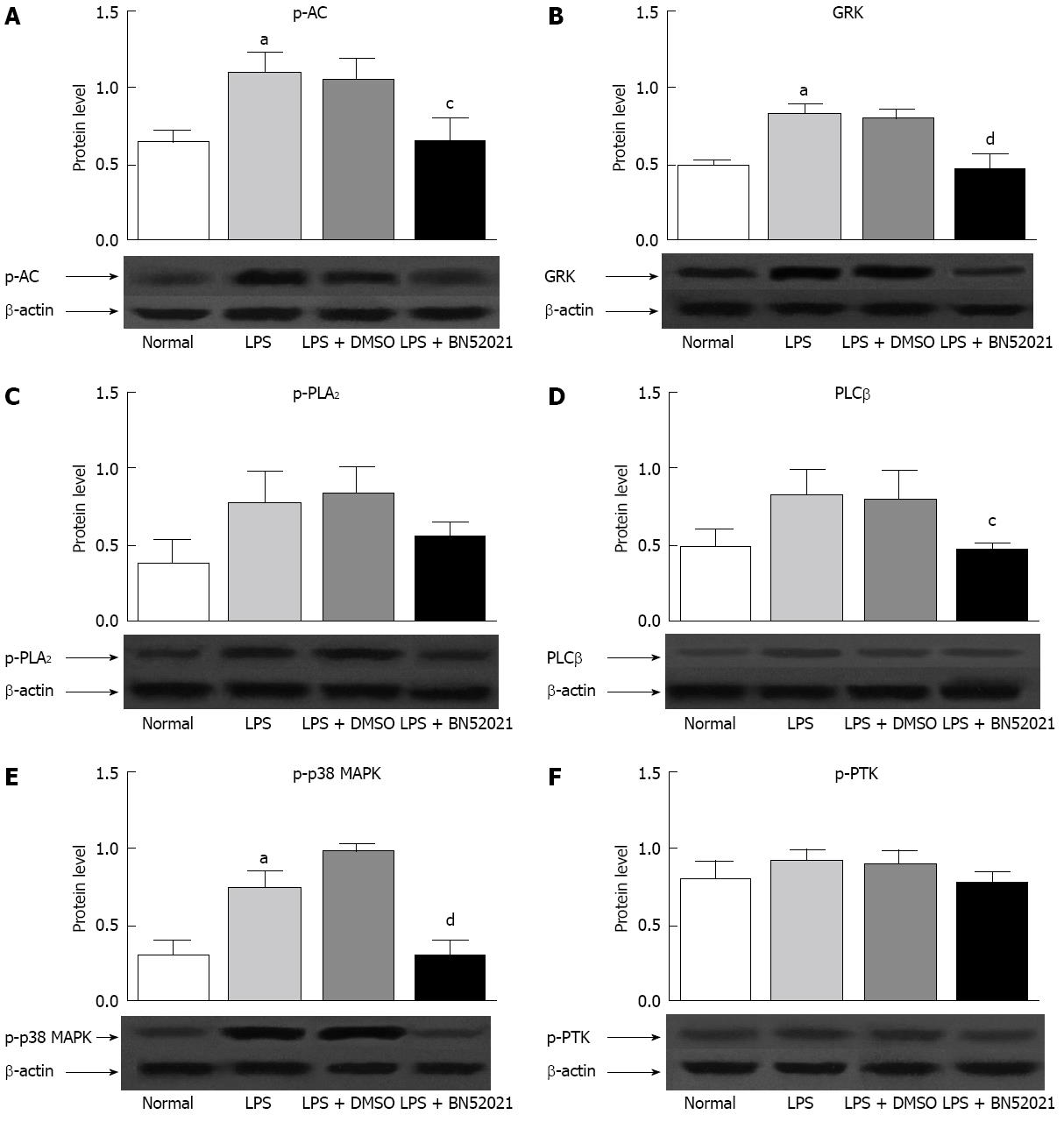
Figure 4 The effect of BN52021 on platelet-activating factor receptor signaling molecules at the protein level under lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation.
The protein level of p-adenylate cyclase (p-AC) (A), G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRK) (B), p-phospholipase A2 (p-PLA2) (C), phospholipase Cβ (PLCβ) (D) and p-p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase (p-p38 MAPK) (E) was up-regulated after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation vs the blank control (aP < 0.05). The up-regulation of p-AC, p-p38 MAPK, GRK and PLCβ protein levels was significantly suppressed by BN52021. However, p-PLA2 and phosphorylated protein tyrosine kinase (p-PTK) protein levels were insignificantly up-regulated after LPS stimulation and were not significantly changed by BN52021 (F). cP < 0.05, dP < 0.01 vs LPS + dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) groups.
- Citation: Xia SH, Xiang XH, Chen K, Xu W. Roles of BN52021 in platelet-activating factor pathway in inflammatory MS1 cells. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(25): 3969-3979
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i25/3969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i25.3969