Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2013; 19(21): 3332-3338
Published online Jun 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3332
Published online Jun 7, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3332
Figure 1 p.
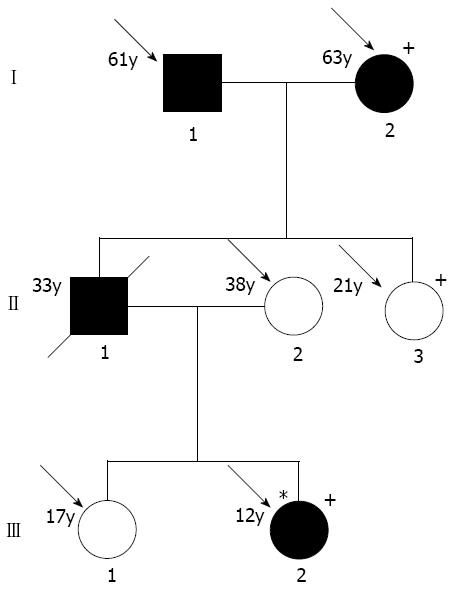
L81M mutation of the protease serine 1 gene in autoimmune pancreatitis family. Hatched symbols: Patients with chronic pancreatitis; Striped symbols: Individuals with suspected chronic pancreatitis; Arrows: Subjects who were available for genetic analysis; Plus: Presence of heterozygous mutation; Asterisk: Index patient.
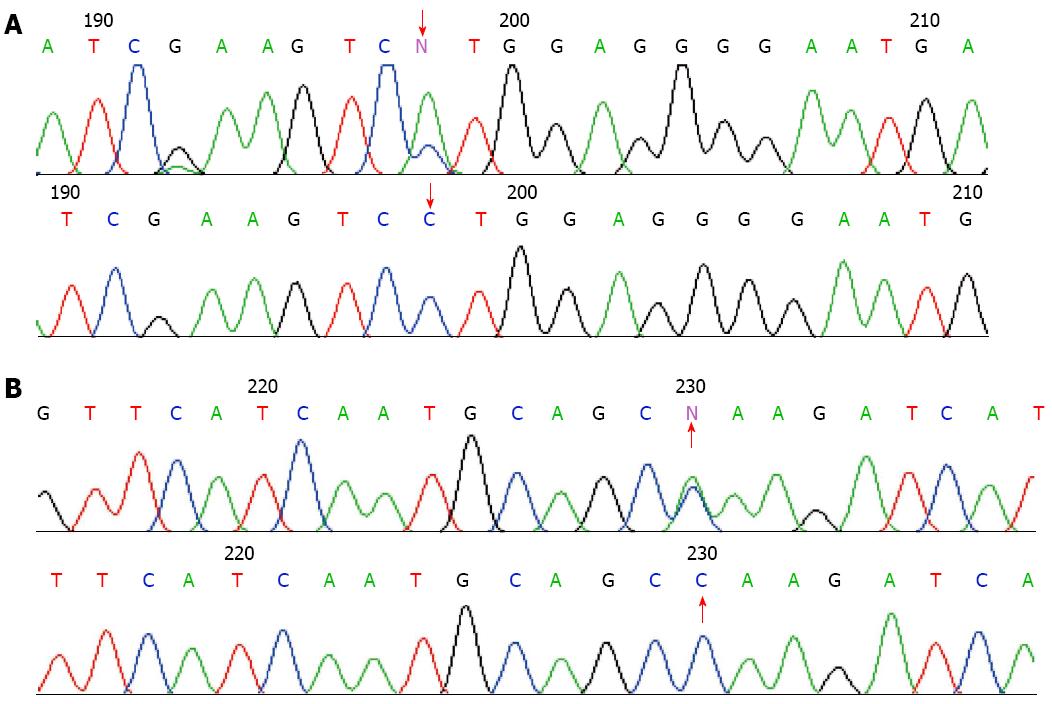
Figure 2 Sequencing of gene mutations from the patients with autoimmune pancreatitis.
A: The sequencing c.247 C > A of PRSS1 gene mutation (p.81Leu→Met); B: Sequencing c.279 C > A of PRSS1 gene silent mutation (p.91Ala→Ala). The red arrow indicates the base mutation.
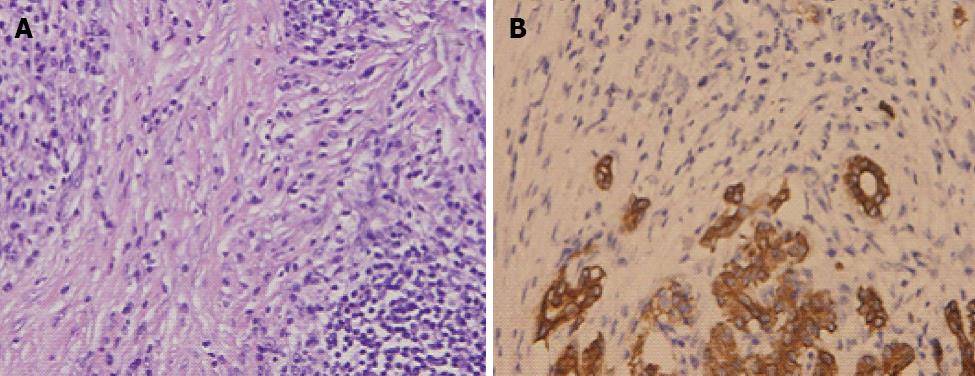
Figure 3 Histopathologic examination of the pancreas.
A: A large number of lymphocytes and plasma cells were found in the bile ducts accompanied by hyperplasia of myofibroblasts (hematoxylin-eosin, × 20); B: The number of pancreatic acinars was markedly decreased (immunohistochemistry staining of cytokeratin, × 20).
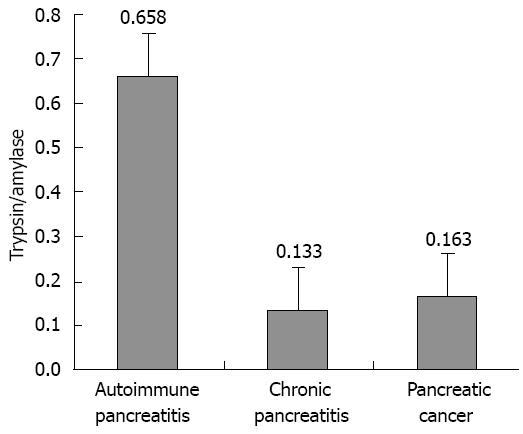
Figure 4 Ratio of trypsin/amylase among the three groups.
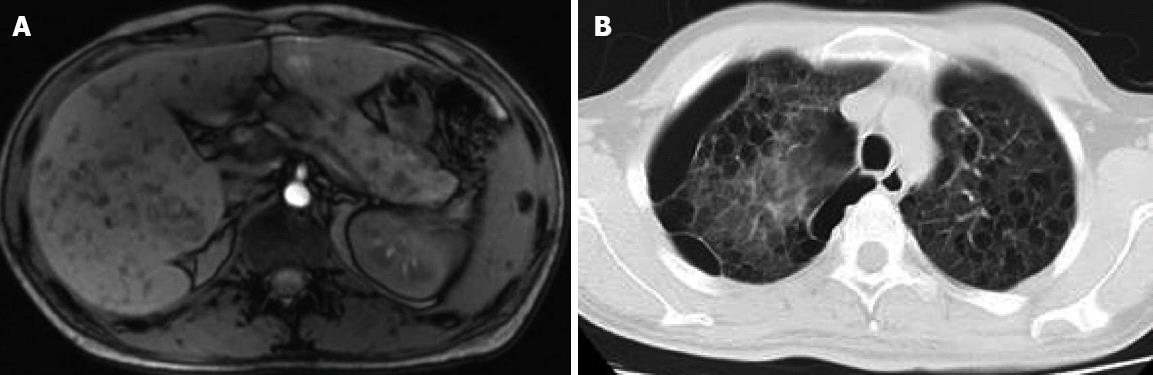
Figure 5 Polycystic lesions in the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and spleen, and retroperitoneal lymphadenopathy and bullae.
A: Abdominal magnetic resonance imaging figure showed diffuse swelling; B: Computed tomography findings image of lung.
-
Citation: Gao F, Li YM, Hong GL, Xu ZF, Liu QC, He QL, Lin LQ, Weng SH.
PRSS1 _p.Leu81Met mutation results in autoimmune pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(21): 3332-3338 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i21/3332.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i21.3332