Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2013; 19(18): 2752-2760
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2752
Published online May 14, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2752
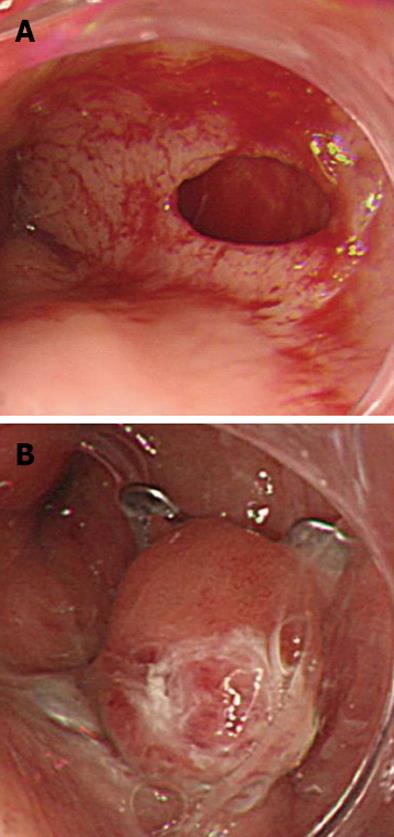
Figure 1 Esophageal perforation caused by a nasogastric tube.
A: During the insertion of a nasogastric tube, the tip of the tube perforated the lower esophagus; B: The wound was successfully closed with a single over-the-scope clip, and there was no leakage.
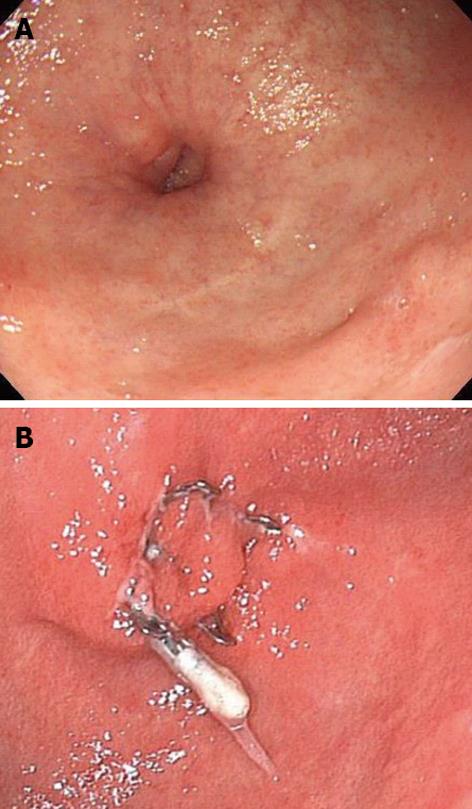
Figure 2 Gastrocutaneous fistula that occurred after percutaneous endoscopic gastronomy removal.
A: After the removal of a gastrostomy tube, the patient was able to eat orally, but a gastrocutaneous fistula was diagnosed; B: The wound was slightly hardened, but was successfully closed with a single over-the-scope clip.
Figure 3 A gastric tube bronchial fistula following a subtotal esophagectomy for esophageal cancer.
A: A gastric tube bronchial fistula occurred after a subtotal esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. Bronchial embolization was performed, but it failed to close the fistula; B: The authors attempted to close the fistula using over-the-scope clip (OTSC) but were unsuccessful. Although 1 OTSC was placed, mucosal hardening (resulting from the prolonged duration of the untreated ulcer) prevented the placement of the additional OTSCs required for closure; C: A chest-abdominal computed tomography scan revealed a gastrobronchial fistula (arrow).
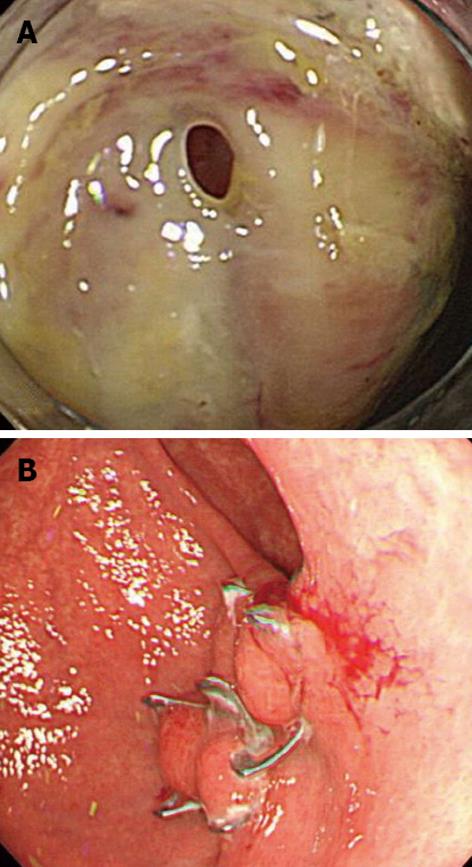
Figure 4 Iatrogenic perforation after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer in the greater curvature of the stomach.
A: A post-endoscopic submucosal dissection ulcer was found in the greater curvature of the stomach. An examination by retroflex view revealed that the muscle layer was separated and perforated; B: The wound was successfully closed using an over-the-scope clip (OTSC). An upper endoscopy performed 2 mo after the closure revealed no displacement of the OTSC or complications, such as ulceration or deformation.
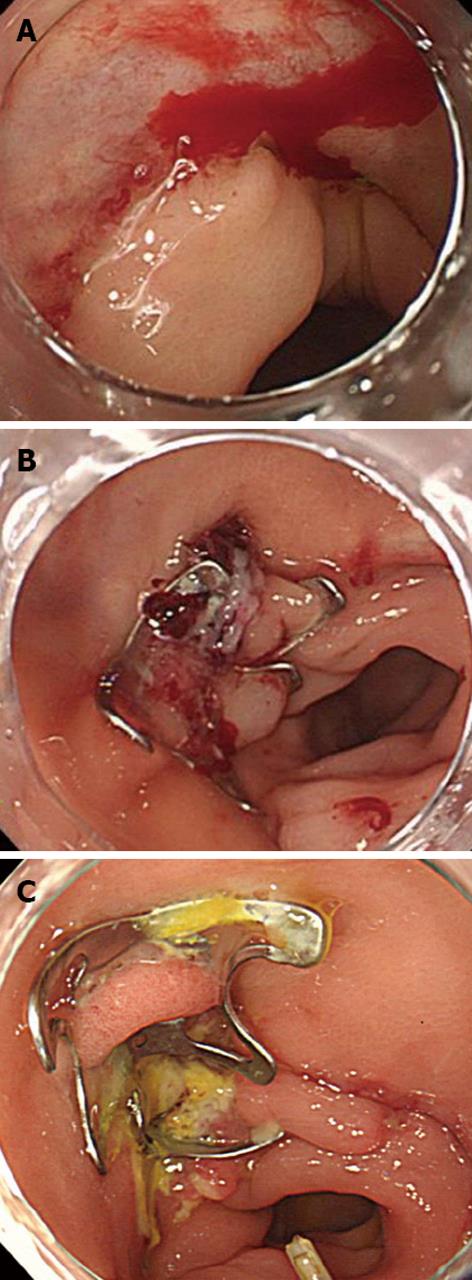
Figure 5 Bleeding from an anastomotic ulcer caused by a sigmoidectomy for sigmoid cancer.
A: Bleeding was observed from the anastomotic site after surgery for sigmoid colon cancer; B: The wound was successfully closed using an over-the-scope clip; C: The postoperative course has been uneventful, with no rebleeding.
- Citation: Nishiyama N, Mori H, Kobara H, Rafiq K, Fujihara S, Kobayashi M, Oryu M, Masaki T. Efficacy and safety of over-the-scope clip: Including complications after endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(18): 2752-2760
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i18/2752.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i18.2752