Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2013; 19(12): 2000-2004
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.2000
Published online Mar 28, 2013. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.2000
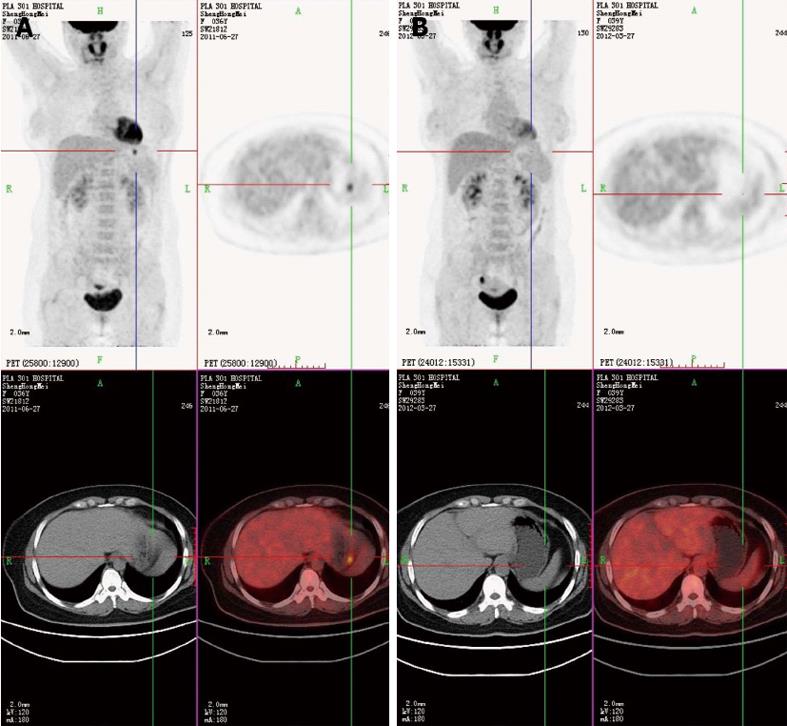
Figure 1 Positron emission tomography-computed tomography.
A: Positron emission tomography-computed tomography showed a nodular strong accumulation point with standardized uptake value 5.6 in the gastric fundus; B: After treatment, the nodular strong accumulation point in the gastric fundus had disappeared.
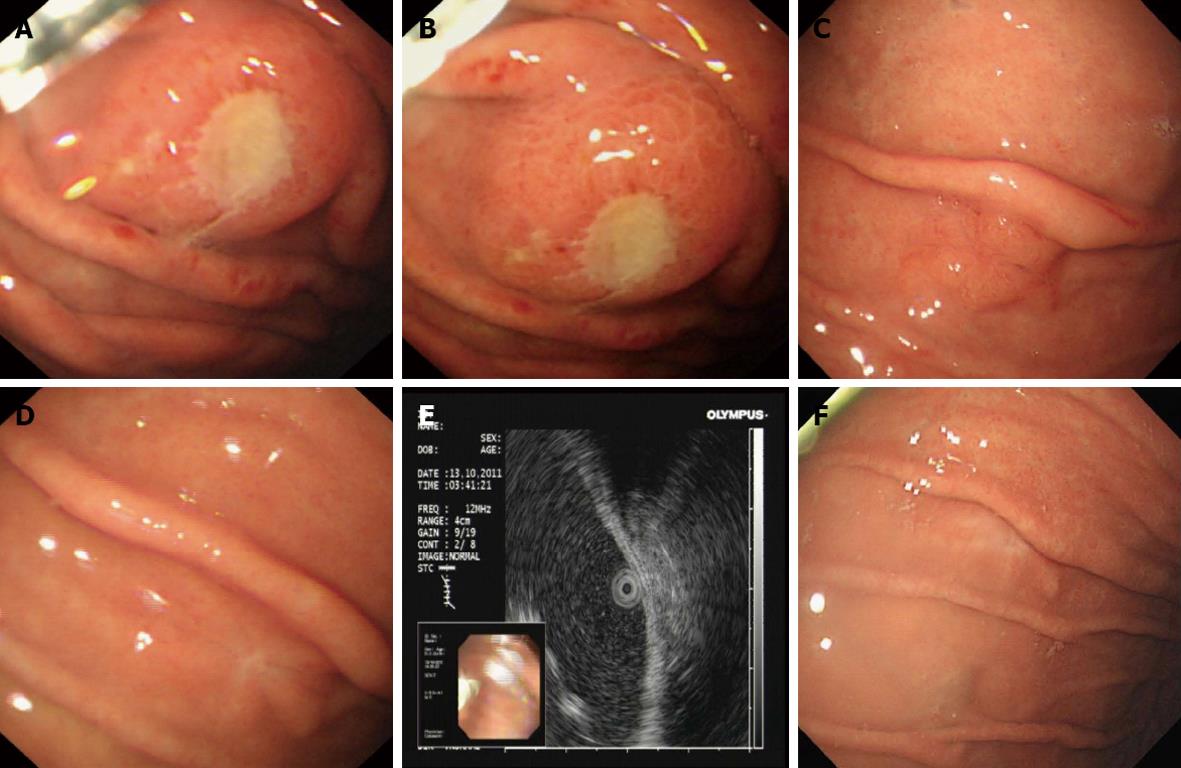
Figure 2 Gastroscopy showed a single arched ulcer and changes after treatment.
A, B: A single arched ulcer, measuring 12 mm in size, was found in the gastric fundus (July 1, 2011); C: A single arched ulcer, measuring 10 mm in size, was found in the gastric fundus (August 16, 2011); D: The gastric ulcer was in stage S2 (October 13, 2011 ); E: Endoscopic ultrasonography showed that the local echo was normal and each layer was clearly divided (October 13, 2011); F: The gastric ulcer was in stage S2 (April 25, 2012).
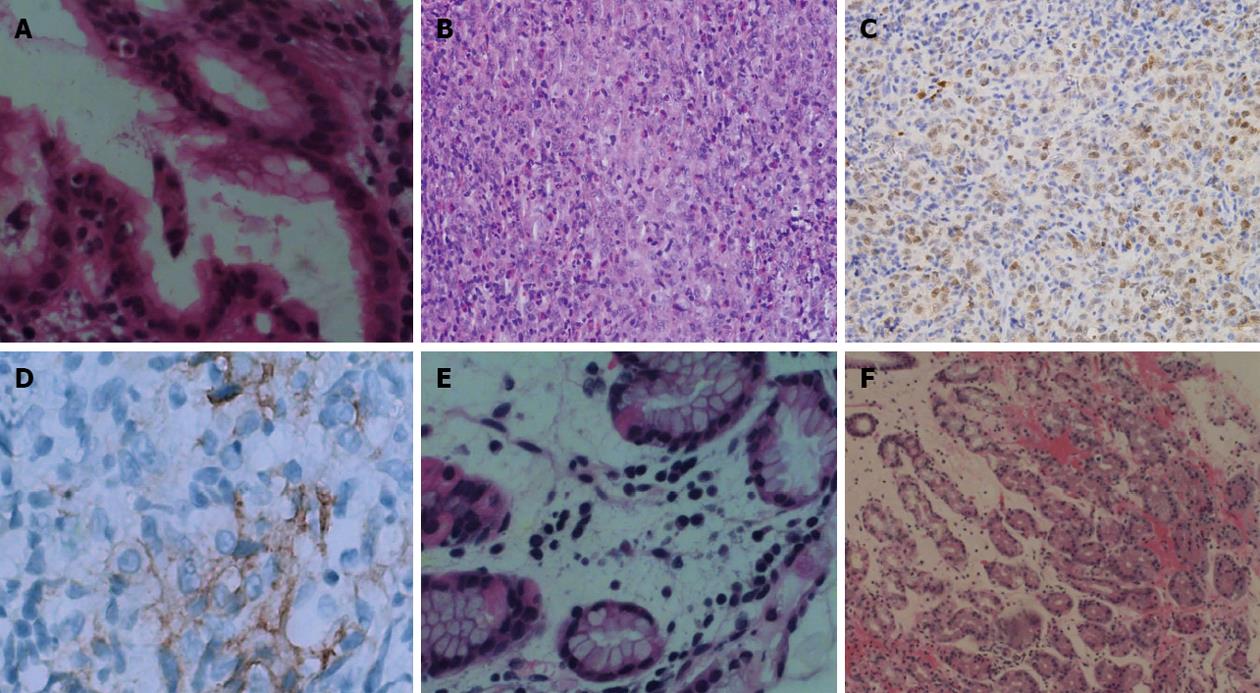
Figure 3 Histopathology changes after treatment.
A: Histopathological examination revealed that the lesion had chronic mucosal inflammation with acute inflammation and a small amount of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection. The mitotic phase was obvious and lymphoma was widespread [hematoxylin and eosin (HE), ×400, July 2, 2011]; B: Histopathological examination revealed chronic mucosal inflammation with acute inflammation and a only a small amount of H. pylori infection. The mitotic phase was 4/10 high power field (HE, ×400, August 17, 2011); C: Immunohistochemical staining showed tissue cell-like cells with S-100 (×400, August 17, 2011); D: Immunohistochemical staining was repeated by the Beijing Cancer Hospital and showed that staining for CD1a was positive for focal lesions (×400, August 25, 2011); E: Histopathological examination showed chronic mucosal inflammation with lymphoid tissue hyperplasia in the lamina propria (HE, ×400, October 14, 2011); F: Histopathological examination revealed that chronic mucosal inflammation with acute inflammation (HE, ×10 , May 8, 2012).
-
Citation: Li TT, Qiu F, Wang ZQ, Sun L, Wan J. Rare case of
Helicobacter pylori -related gastric ulcer: Malignancy or pseudomorphism? World J Gastroenterol 2013; 19(12): 2000-2004 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v19/i12/2000.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i12.2000