Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 7, 2012; 18(9): 930-937
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.930
Published online Mar 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.930
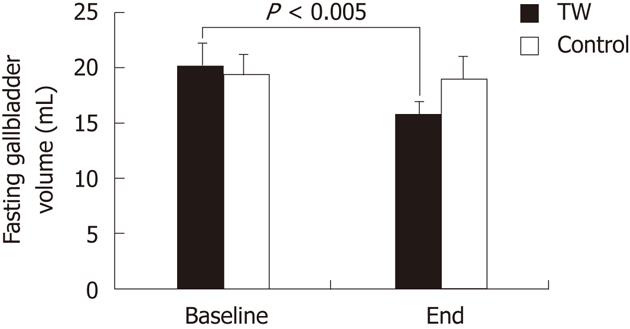
Figure 1 Fasting gallbladder volume at baseline and at the end of the study in the thermal water and in the control group.
TW: Thermal water.
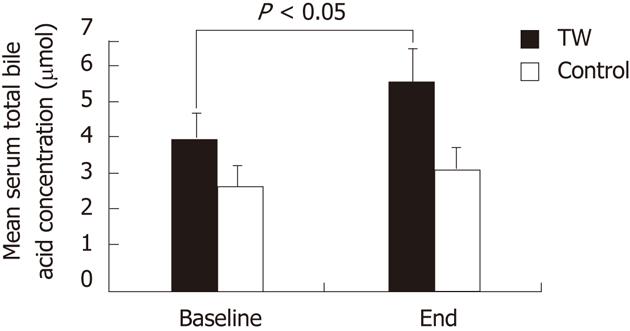
Figure 2 Mean serum total bile acid concentration at baseline and at the end of the study in the thermal water and in the control group.
TW: Thermal water.
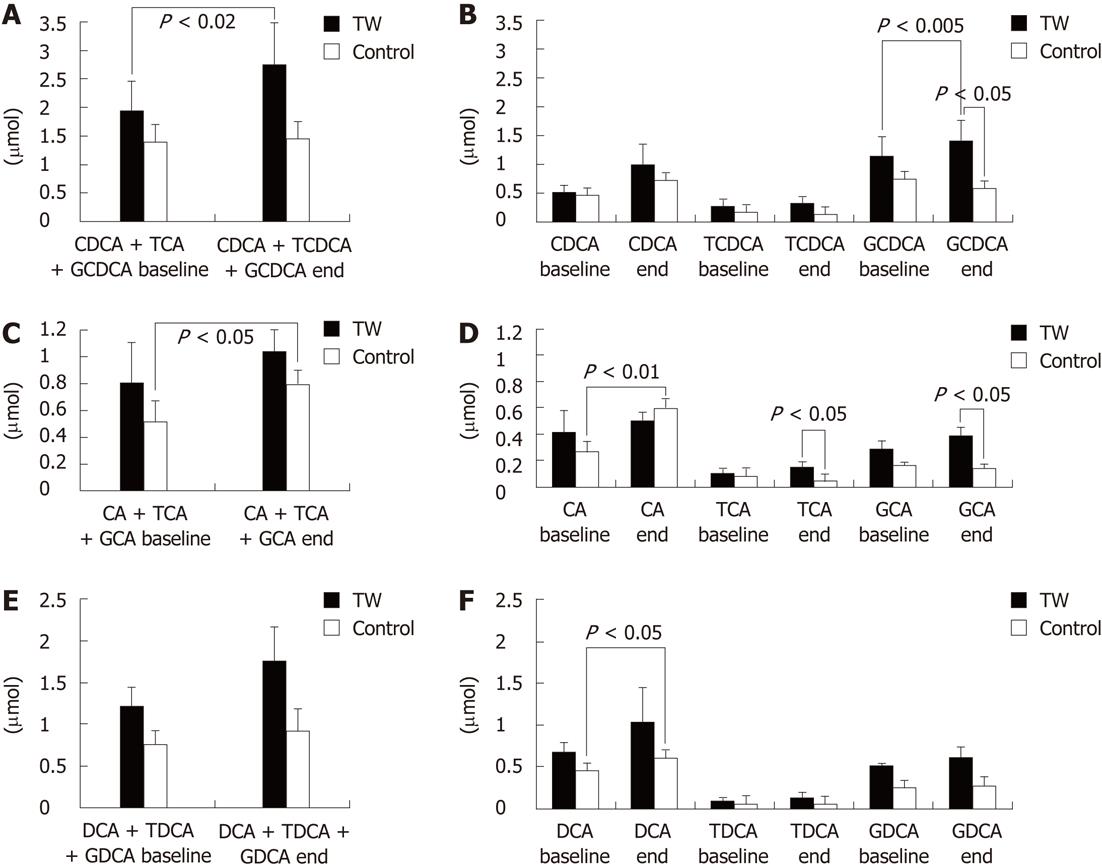
Figure 3 Mean serum bile acid molecular species concentration at baseline and at the end of the study in the thermal water and in the control group.
A: Total chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA); B: Free CDCA, glycochenodeoxycholic acid (GCDCA) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA); C: Total cholic acid (CA); D: Free CA, glycocholic acid (GCA) and taurocholic acid (TCA); E: Total deoxycholic acid (DCA); F: Free DCA, glycodeoxycholic acid (GDCA) and taurodeoxycholic acid (TDCA). TW: Thermal water.
- Citation: Corradini SG, Ferri F, Mordenti M, Iuliano L, Siciliano M, Burza MA, Sordi B, Caciotti B, Pacini M, Poli E, Santis AD, Roda A, Colliva C, Simoni P, Attili AF. Beneficial effect of sulphate-bicarbonate-calcium water on gallstone risk and weight control. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(9): 930-937
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i9/930.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i9.930