Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2012; 18(5): 425-434
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425
Published online Feb 7, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425
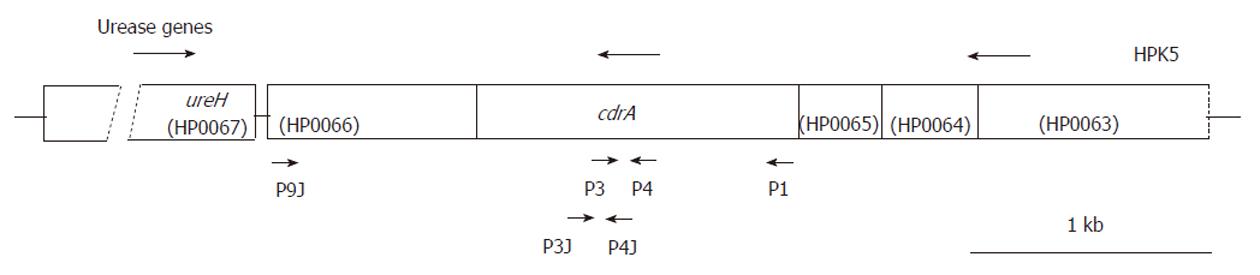
Figure 1 Location of primers used for cell division-related gene A in the region downstream of the urease gene cluster of Helicobacter pylori HPK5.
Arrows above and below the map depict the direction of transcription and primers, respectively. The open reading frames (HP0063 to HP0067) are shown based on strain 26695.
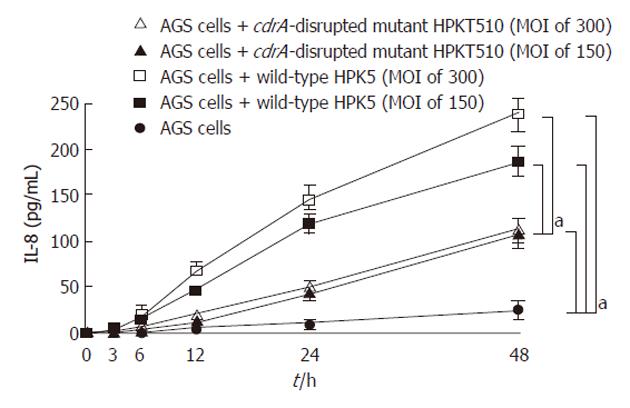
Figure 2 Interleukin-8 production from AGS cells induced by either wild-type or cell division-related gene A-disrupted mutant strains.
aP < 0.01.
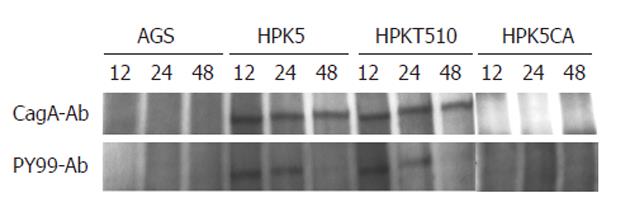
Figure 3 Cytotoxin-associated gene A status in AGS cells co-cultured with or without Helicobacter pylori strains.
The immunoprecipitated proteins with anti-Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) antibody (CagA-Ab) were subjected to Western blotting with CagA-Ab (upper) and PY-99 antibody (PY99-Ab) (bottom), respectively. The assay was carried out with strains at MOI of 150. HPK5: Wild-type; HPKT510: Cell division-related gene A-disrupted mutant; HPK5CA: cagA-disrupted mutant.
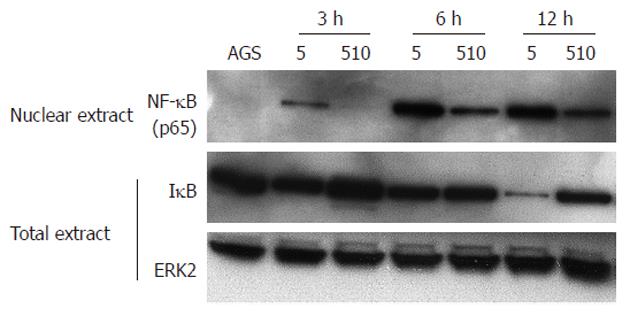
Figure 4 Detection of nuclear factor kappa B (p65) (upper), inhibition kappa B (middle) and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (bottom) in nuclear and total extracts, respectively at 3, 6 and 12 h after being co-cultured with Helicobacter pylori.
Unphosphorylated extracellular signal–regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) was detected as the control in this study[23]. Molecular weights of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB), inhibition kappa B (IκB) and ERK2 are 65, 35-37 and 42 kDa, respectively. The assay was carried out with strains at a MOI of 150. AGS: AGS cells co-cultured without H. pylori; HPK5: AGS cells co-cultured with wild-type HPK5; HPKT510: AGS cells co-cultured with cdrA-disrupted mutant HPKT510.
-
Citation: Takeuchi H, Zhang YN, Israel DA, Peek Jr RM, Kamioka M, Yanai H, Morimoto N, Sugiura T. Effect of
Helicobacter pylori cdrA on interleukin-8 secretions and nuclear factor kappa B activation. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(5): 425-434 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i5/425.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i5.425