Copyright
©2012 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2012; 18(46): 6819-6828
Published online Dec 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6819
Published online Dec 14, 2012. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6819
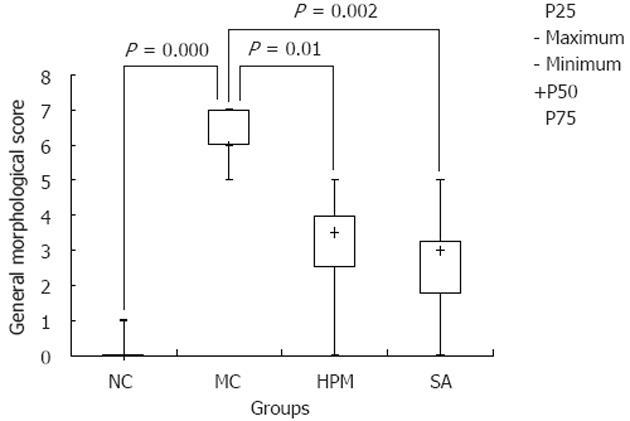
Figure 1 Herb-partition moxibustion inhibits tissue damage in colonic tissues of rats with ulcerative colitis.
The general morphological score of the colonic tissue in the model control (MC) group was significantly higher than the normal control (NC) group (P = 0.000). After treatment, the scores were lower in both the herb-partition moxibustion (HPM) group (P = 0.01) and the control sulfasalazine (SA) group (P = 0.002).
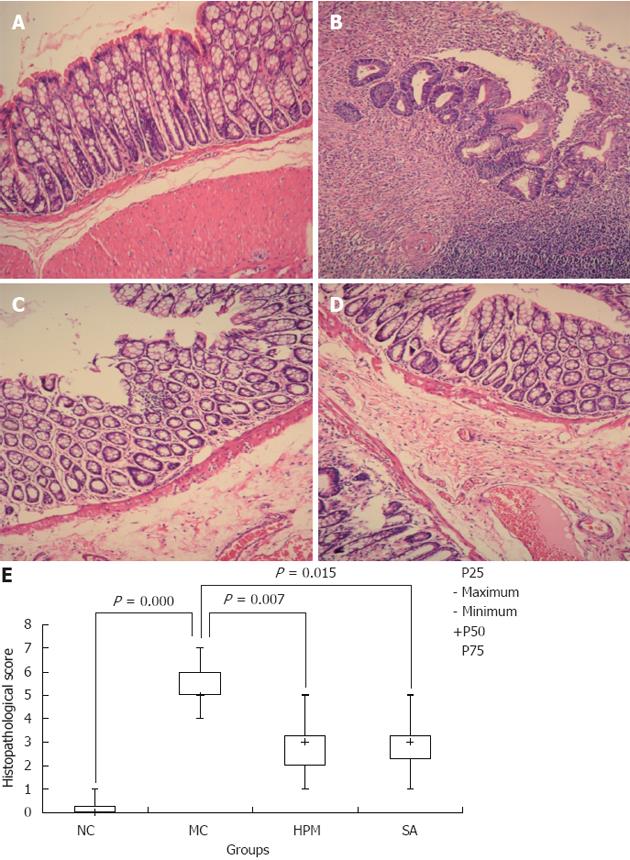
Figure 2 Herb-partition moxibustion inhibits immunopathology and decreases the histopathological scores in colonic tissues of rats with ulcerative colitis.
A: Normal; B: Ulcerative colitis (UC); C: Herb-partition moxibustion (HPM); D: Sulfasalazine (SA); E: The histopathological scores for the colonic tissue in the UC model control (MC) group were significantly higher than the normal control (NC) group (P = 0.000). After treatment, the scores were lower in both the HPM group (P = 0.007) and SA group (P = 0.015). The colonic mucosa was damaged in the UC model group with cell infiltration, congestion, edema, and ulceration. After HPM treatment, there are only slight submucosal edema and inflammatory cell infiltration, and the colonic mucosa epithelium and the colonic gland were more regularly arranged than in the model group, new epithelial cells were observed to be covering the ulcers. Positive control SA treatment showed similar recovery of the UC model as the HPM group.
Figure 3 Herb-partition moxibustion treatment increases the colonic Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus of rats with ulcerative colitis.
The DNA copies of the symbiotic groups Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus were both significantly decreased in the ulcerative colitis (UC) group compared to the normal control (NC) group (P = 0.000). After herb-partition moxibustion (HPM) treatment, the DNA copies of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus were both significantly increased in the HPM group (P = 0.001 and P = 0.000) and sulfasalazine (SA) group (P = 0.000 and P = 0.000) compared with the UC model group.
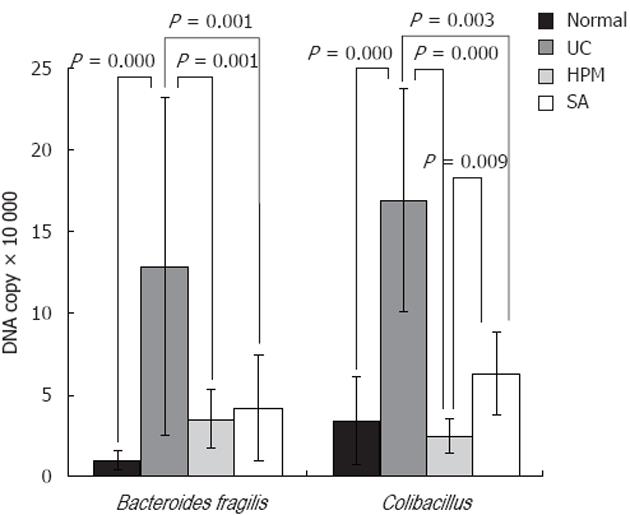
Figure 4 Herb-partition moxibustion treatment decreases the colonic pathogenic bacteria Bacteroides fragilis and Escherichia coli of rats with ulcerative colitis.
The DNA copies of the pathogenic bacteria Bacteroides fragilis (B. fragilis), and Escherichia coli (E. coli) were both significantly increased in the ulcerative colitis (UC) rats compared to the normal control (NC) rats (P = 0.000). After herb-partition moxibustion (HPM) treatment, the DNA copies of B. fragilis and E. coli were both significantly decreased in the HPM group (P = 0.001 and P = 0.000) and sulfasalazine (SA) group (P = 0.001 and P = 0.003) compared with the UC model group.
- Citation: Wang XM, Lu Y, Wu LY, Yu SG, Zhao BX, Hu HY, Wu HG, Bao CH, Liu HR, Wang JH, Yao Y, Hua XG, Guo HY, Shen LR. Moxibustion inhibits interleukin-12 and tumor necrosis factor alpha and modulates intestinal flora in rat with ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012; 18(46): 6819-6828
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v18/i46/6819.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i46.6819